
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A standard of solution was put through appropriate dilutions to give the concentrations of glucose (mM) shown in the accompanying table. The absorbances in the table (1.00-cm cells) were recorded at 490 m table. Use the method of least squares to find an equation relating absorbance and the concentration of glucose.
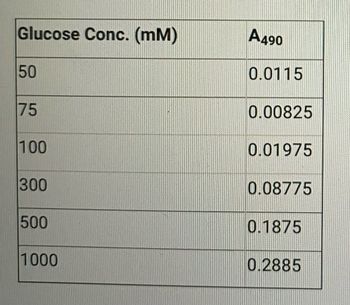
Transcribed Image Text:Glucose Conc. (mm)
50
75
100
300
500
1000
A490
0.0115
0.00825
0.01975
0.08775
0.1875
0.2885
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 14 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How do I find the theoretical molarity?arrow_forwardSuppose that a solution has an absorbance of 0.250 at a wavelength of 450 nm. If the concentration of the solution is 22 μM, what is the value of the molar absorptivity? The data were taken with a standard 1-cm cuvette. molar absorptivity in (L cm^−1 mol^-1):arrow_forwardpermanganate solution using the color wheel. ART II: INVESTIGATING ABSORBANCE AND PATHLENGTH 12. Based on Beer's law (A = ɛlC, A = absorbance, ɛ = molar absorptivity, I pathlength and C = concentration), what do you predict is the relationship between pathlength and absorbance? What about pathlength and transmittance?arrow_forward
- 15) You measure a solution that contains two organic molecules in a 1.00 cm cuvette. The measurement is 0.2265 at 700 nm and 0.9205 and 320 nm. What are the concentrations of compound A and compound B. = 3520 M'cm';e, Compound A: Compound B: e = 620 M'cm' 700m 320nm e = 13130 M'cm" ; e = 3600 M 320nm 700m 'cm'arrow_forwardA liquid sample was analyzed for Fe³+. A plot of absorbance (y-axis) vs. concentration (ppm; x-axis) of the external standards produced a calibration line with an equation y = 0.2256x -0.0903 (R² = 0.9973). The absorbance of the sample was 1.25. Determine the amount of Fe³+ in the sample (in ppm).arrow_forwardCalculate the path length in centimetres which would give an absorbance of 0.134 of a colored dye with a molar absorptivity of 0.759 L mol-1 cm-1 at a wavelength of 645 nm if the concentration of the dye is 6.82x10-2 M. Report your answer to 3 significant figures.arrow_forward
- The equation to calculate for molar absorptivity (ε) is ε = A/(bc) where A is absorbance (unitless), b is path length in cm, and c is concentration in M. Suppose you have a solution with concentration of 2.9 ± 0.25 M, a path length of 1 ± 0.1 cm, and an absorbance of 0.4629 ± 0.0006. What is the uncertainty or error for the molar absorptivity?arrow_forwardA colored ion solution has a concentration of 0.200 M with a measured absorbance A = 0.880. Another ion solution made of the same chemicals has an absorbance A = 0.172. What is the concentration of this unknown sample solution?arrow_forwardA compound with a molecular weight of 229.61 g/mol was dissolved in 50.0 mL of water. 1.00 mL of this solution was placed in a 10.0 mL flask and diluted to the mark. The absorbance of this diluted solution at 510 nm was 0.472 in a 1.000 cm cuvet. The molar absorptivity of the compound, at 510 nm, is 6,310 M-1 cm-1. Calculate the concentration of the compound in the initial 50.0 mL solution. A. 1.50 x 10-5 M B. 7.48 x 10-5 M C. 7.48 x 10-4 M D. 7.48 x 10-6 Marrow_forward
- If the absorbance for the solution was 0.342, calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, with zero places after the decimal.arrow_forwardMaria was tasked to determine the concentration of a Fe2(SO4)3 solution. She prepared 5 different standards of Fe2(SO4)3 using the table below as her guide. She ran the standards and the unknown solution through UV-VIS spectroscopy and recorded the absorbances of each solution. HINT: use the dilution equation to determine the concentration of Fe2(SO4)3 in each test tube before preparing the standard curve. NOTE: No need to force the line to pass through zero. Just graph the data as is. What is the slope of the line of the standard curve from the given data? What is the concentration of the unknown solution?arrow_forwardWhile performing absorbance measurements of standard solutions, Taranpreet used - 8 mL of solution in the cuvette for each determination. She then repeated the same measurements using - 6 mL of solution In the cuvette for each determination, For each set of measurements, she used the same spectrometer with the same cuvette, and assume that for each set of measurements the cuvette was filled high enough such that the light from the spectrometer passed through the solution. Which statement is true? O a) Using a lower volume in the cuvette will have no effect on the measured values O b) Using a lower volume in the cuvette will result in a smaller slope for the calibration curve c) Using a lower volume in the cuvette will result in a lower concentration of analyte determined in the unknown sample O d) Using a higher volume in the cuvette may result in absorbance values that are above the detection range of the spectrometer O e) Using a higher volume in the cuvette may result in a…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY