
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A spring with constant k = 5 N/m hanging from the ceiling is placed at its lower end with an object of 1 N, which causes it to remain in equilibrium. The weight is then pulled 0.5 m above the equilibrium position.
and is released with no initial velocity. There is no damping force acting on the system. SI x(t) represents the displacement of the weight, in meters, from the equilibrium point and taking upwards as the
positive direction, an equation that describes the position of the weight as a function of time t (in seconds) is:
If necessary, use the gravity constant g as g = 9.8 m/s2
Possible answer in the images.
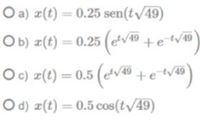
Transcribed Image Text:O a) ¤(t) = 0.25 sen(t/49)
O b) z(t) = 0.25 (evo tetv
O c) z(t) = 0.5 (evão tetveD
49
O d) z(t) = 0.5 cos(t/49)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A damped mass-spring oscillator loses 13% of its energy during each cycle. (a) The period is 7.2 s, and the mass is 0.85 kg. What is the value of the damping constant? b = kg/s (b) If the motion is started with an initial amplitude of 0.46 m, how many cycles elapse before the amplitude reduces to 0.13 m? (c) What is the spring constant k? k = N/marrow_forwardA spring with a mass of 2 kg has a damping constant 14 kg/s. A force of 3.6 N is required to keep the spring stretched 0.3 m beyond its natural length. The spring is stretched 0.6 m beyond its natural length and then released. Find the position of the mass at any time t. (Assume that movement to the right is the positive x-direction and the spring is attached to a wall at the left end.) x(t) =arrow_forwardA 0.500-kg mass is suspended from a string, forming a pendulum. The period of this pendulum is 1.58 s when the amplitude is 1.00 cm. The mass of the pendulum is now reduced to 0.250 kg. What is the period of oscillation now, when the amplitude is 2.00 cm?arrow_forward
- An object weighing 32 lb stretches a spring 2ft in equilibrium. There is also a damping force with c = 8. The spring is raised 2 ft and thrown upwards with a velocity of 4ft/sec. Determine the mass m and the spring constant k, and give the differential equation describing the harmonic motion of this system. Solve the differential equation to find the displacement y.arrow_forwardA 10.0 kg object oscillates at the end of a vertical spring that has a spring constant of 1.90 x 104 N/m. The effect of air resistance is represented by the damping coefficient b = 3.00 N-s/m. (a) Calculate the frequency of the dampened oscillation. Hz (b) By what percentage does the amplitude of the oscillation decrease in each cycle? % (c) Find the time interval that elapses while the energy of the system drops to 3.50% of its initial value.arrow_forwardA metal sphere with a mass of 4.00 kg oscillates at the end of a vertical spring with a spring constant of 2.20 x 104 N/m. The motion is damped by air resistance, and the damping coefficient is b = 3.00 N · s/m. (a) What is the frequency (in Hz) of the damped oscillation? 11.802 Hz (b) By what percentage does the amplitude of the oscillation decrease in each cycle? 3.1 % (c) Over what time interval (in s) does the energy of the system drop to 3.00% of its initial value? 4.68 S (d) What If? The atmosphere of Venus is 50 times thicker than that on Earth. If the effect of air resistance on Venus is 150 N · s/m, recalculate the answers for parts (a) to (c) for this system if it is set in motion in the represented by b atmosphere of Venus. What is the frequency (in Hz) of the damped oscillations? 11.419 Hz What is the percentage decrease in amplitude in each cycle? 74.45 Follow the same steps as in part (b), only use the new value of b. Remember the angular frequency has now changed as…arrow_forward
- The suspension system of a 2100 kg automobile "sags" 7.0 cm when the chassis is placed on it. Also, the oscillation amplitude decreases by 45% each cycle. Estimate the values of (a) the spring constant k and (b) the damping constant b for the spring and shock absorber system of one wheel, assuming each wheel supports 525 kg. (a) Number (b) Number 73500 Units N/m Units kg/s 4arrow_forwardA spring with spring constant k=12.5N/m is hung vertically. A mass of 0.500 kg is then suspended from the spring. Determine the displacement of the spring’s end due to the weight of the 0.500 kg object.arrow_forwardAn oscillating block-spring system takes 0.635 s to begin repeating its motion. Find (a) the period, (b) the frequency in hertz, and (c) the angular frequency in radians per second.arrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 600 g is attached to a horizontal spring with a spring constant of k = 3.6 N m¹. When it is in motion, the system is damped by a force Fdamp = -4.2x (SI units). At time t = 0, the block is pulled out to a position x(0) = -20 cm relative to its equilibrium, and set in motion with a velocity (0) = -1.3 m s¯¹. Find the displacement and the velocity of the block as functions of time thereafter.arrow_forwardA body with mass of 250 g is attached to the end of a spring that is stretched 25 cm by a force of 9 N. At time t=0 the body is pulled 1 m to the left. stretching the spring, and set in motion with an initial velocity of 5 m/s to the right. (a) Find x(t) in the form C cos (-a). (b) Find the amplitude and the period of motion of the body.arrow_forwardA 2-kg mass is attached to a spring hanging from the ceiling, thereby causing the spring to stretch 1.4 m upon coming to rest at equilibrium. At time t= 0, an external force of F(t) = cos 2t N is applied to the system. The damping constant for the system is 4 N-sec/m. Determine the steady-state solution for the system. The steady-state solution is y(t)=- plz helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON