
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
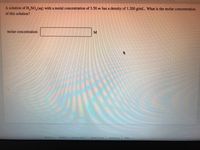
Transcribed Image Text:A solution of H, SO, (aq) with a molal concentration of 3.58 m has a density of 1.200 g/mL. What is the molar concentration
of this solution?
molar concentration:
about us
privacy.policy
terms of use contact us hoelp
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An aqueous solution of isopropanol (MM = 60.10 g/mol) has a molality of 7.91 m and a density of 1.18 g/mL. What is the molarity of isopropanol in the solution?arrow_forwardA solid consists of a mixture of NaNO3 and Mg(NO3)2. When 6.50 g of the solid is dissolved in 50.0 g of water, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 5.11°C. What is the composition by mass of the solid?arrow_forwardThe freezing point of ethanol, CH3CH2OH, is -117.300 °C at 1 atmosphere. Kf(ethanol) = 1.99 °C/mIn a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 13.34 grams of the compound were dissolved in 212.8 grams of ethanol, the solution began to freeze at -117.981 °C. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte.What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound?arrow_forward
- Calculate the molarity of an aqueous solution that is 20.1% by mass calcium chloride. You might need to know that the density is 1.20 g/mLarrow_forwardA student dissolves 14. g of sucrose (C,,H,,0,1) in 450. mL of a solvent with a density of 0.85 g/mL. The student notices that the volume of the solvent 22 does not change when the sucrose dissolves in it. Calculate the molarity and molality of the student's solution. Round both of your answers to 2 significant digits. molarity = | x10 molality %3D Continue Submit O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center MacBook Air 20 888 DD F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 34 00arrow_forwardA solid consists of a mixture of NaNO3 and Mg(NO3)2. When 6.50 g of the solid is dissolved in 50.0 g of water, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 5.04°C. What is the composition by mass of the solid?arrow_forward
- write down in the third column of the table the chemical formula of the major chemical species that will be present in this solution.arrow_forwardA student dissolves 6.7 g of sucrose (C,,H,20) in 375. mL of a solvent with a density of 1.13 g/mL. The student notices 11 that the volume of the solvent does not change when the sucrose dissolves in it. Calculate the molarity and molality of the student's solution. Round both of your answers to 2 significant digits. molarity Ox10 olo Ar molalityarrow_forwardCalculate the molarity of 0.650 mol of Na, S in 1.10 L of solution. molarity: Calculate the molarity of 33.9 g of MgS in 905 mL of solution. M molarity:arrow_forward
- A student dissolves 4.8 g of ammonia (NH,) in 350. mL of a solvent with a density of 1.01 g/mL. The student notices that the volume of the solvent does not change when the ammonia dissolves in it. Calculate the molarity and molality of the student's solution. Round both of your answers to 2 significant digits. molarity |x10 olo molality Ararrow_forward7. A 14.5 g sample of a nonionic solute is dissolved in 50.0 g of water. The solution freezes at -2.50 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the solute.arrow_forwardA solution of H, SO, (aq) with a molal concentration of 3.97 m has a density of 1.216 g/mL. What is the molar concentration of this solution? molar concentration: M + TOOLS x10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY