
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
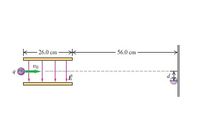
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates an experimental setup involving a charged particle in an electric field. Here is a detailed description of the setup:
1. **Components of the Diagram**:
- A charged particle, labeled with charge \( q \) and mass \( m \), enters an electric field from the left.
- The particle has an initial velocity denoted by \( v_0 \).
- The electric field \( \mathbf{E} \) is represented by vertical arrows pointing downward, indicating the direction of the field.
- The distance covered by the electric field is labeled as 26.0 cm.
2. **Path and Measurement**:
- After passing through the electric field, the particle travels a further horizontal distance of 56.0 cm, presumably unaffected by the field now.
- A screen is positioned at the end of this path.
- There is a vertical displacement labeled \( d \) on the screen, indicating how far the particle has moved from its original path due to the action of the electric field.
3. **Purpose**:
- This setup is typically used to study the deflection of charged particles in an electric field, measuring their displacement \( d \) on the screen to calculate or confirm properties such as charge-to-mass ratio, velocity changes, or the characteristics of the electric field.
This model is often utilized in physics experiments related to electromagnetism, helping illustrate concepts like the force exerted on a charge by an electric field and the effect of this force on the particle's trajectory.
Transcribed Image Text:### Physics Problem: Charge-to-Mass Ratio Calculation
**Problem Description:**
A small object with mass \( m \), charge \( q \), and initial speed \( v_0 = 6.00 \times 10^3 \, \text{m/s} \) is projected into a uniform electric field between two parallel metal plates of length \( 26.0 \, \text{cm} \) (refer to Figure 1). The electric field between the plates is directed downward with a magnitude \( E = 800 \, \text{N/C} \). The field is assumed to be zero outside the region between the plates.
- The separation between the plates is large enough for the object to pass without hitting the lower plate.
- After traversing the field region, the object is deflected downward by a vertical distance \( d = 1.35 \, \text{cm} \) from its initial direction.
- A collecting plate is situated \( 56.0 \, \text{cm} \) from the edge of the parallel plates.
Assumptions: Ignore the effects of gravity and air resistance.
**Part A: Calculation Task**
Calculate the object's charge-to-mass ratio, \( \frac{q}{m} \).
- Express the answer in coulombs per kilogram (C/kg).
**Diagram Explanation:**
No explicit diagrams are provided in the text, but Figure 1 likely illustrates the setup, showing:
- Two parallel metal plates with a uniform downward electric field \( E \).
- The trajectory of the object, marking its deflection \( d \) after passing through the plates.
- The position of the collecting plate relative to the plates.
To solve the problem, apply concepts of electric fields, motion under uniform acceleration (deflection calculation), and kinematics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two large aluminum plates are separated by a distance of 2.0 cm and are held at a potential difference of 195 V. An electron enters the region between them at a speed of 3.2 × 105 m/s by passing through a small hole in the negative plate and continues moving toward the positive plate. Assume the electric field between the plates is uniform. 1. What is the electron’s speed, in meters per second, when it is 0.1 cm from the negative plate? 2. What is the electron’s speed, in meters per second, when it is 0.5 cm from the negative plate? 3. What is the electron’s speed, in meters per second, when it is 1.0 cm from the negative plate? 4. What is the electron’s speed, in meters per second, when it is 1.5 cm from the negative plate? 5. What is the electron’s speed immediately before it strikes the positive plate?arrow_forwardanswer thesearrow_forwardA capacitor is composed of two metal plates. The two plates have the dimensions L = 0.11 m and W = 0.56 m. The plates have a distance between them of d = 0.1 m, and are parallel to each other. Part (a) The plates are connected to a battery and charged such that the first plate has a charge of q. Write an expression for the magnitude of the electric field, |E|, halfway between the plates. Part (b) Input an expression for the magnitude of the electric field, |E2|, just in front of plate two. Part (c) If plate two has a total charge of q = -1 mC, what is its charge density, σ, in C/m2?arrow_forward
- A uniform electric field 3.41E3 N/C is applied in a cubic box with each side being 2.23 m long. What is the energy stored by the electric field in the box (in J)?arrow_forwardTwo parallel, flat, conducting plates with equal but opposite charges are separated by a uniform layer of insulating material with a dielectric constant of 7.1 and a thickness of 1.7mmmm. The electric field in the dielectric material is 2.22MV/mMV/m. What is the magnitude, in microcoulombs per squared meter, of the surface charge density on the conducting plates? What is the magnitude, in microcoulombs per squared meter, of the surface charge density on the conducting plates?arrow_forwardConsider a parallel-plate capacitor with plate separation d, plate area A, whose plates have charge ±Q. A particle of charge q < 0 and mass m is released from rest at the negative plate of the capacitor and allowed to accelerate towards the positive plate. With what speed does the charge strike the positive plate? Answer in terms of d, A, Q, q, m, and/or e0.arrow_forward
- Answer A and B on the image below.arrow_forwardThe drawing shows an electron entering the lower left side of a parallel plate capacitor and exiting at the upper right side. The initial speed of the electron is 3.13 × 106 m/s. The capacitor is 2.00 cm long, and its plates are separated by 0.150 cm. Assume that the electric field between the plates is uniform everywhere and find its magnitude. 15.30 + A + 2.00 cm Number i + + + 0.150 cm Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON