
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A small car with mass 0.650 kg travels at constant speed on the inside of a track that is a vertical circle with radius 5.00 m.
a. If the normal force exerted by the track on the car when it is at the top of the track (point B) is 6.00 N, what is the normal force on the car when it is at the bottom of the track (point A)?
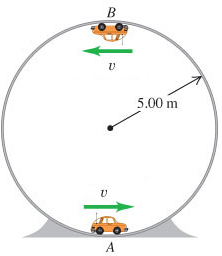
Transcribed Image Text:B
V
V
A
5.00 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A car travels at a steady 37.4 m/s around a horizontal curve of radius 161 m. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the road and the car's tires that will allow the car to travel at this speed without sliding?arrow_forwardA hang glider and its pilot have a total mass equal to 120 kg. While executing a 360 degree turn, the glider moved in a circle with an 8 m radius at a speed of 10 m/s a) What is the net force on the hang glider? b) What is the acceleration?arrow_forwardA pilot flies an airplane at a constant speed of 790 km/h in the vertical circle of radius 1220 m. Calculate the force exerted by the seat on the 96-kg pilot at point A and at point B. Answers: NA = NB = 1220 m B 790 km/h i i N Narrow_forward
- A) A 480.0 g ball moves in a vertical circle on a 88.0 cm-long string.If the speed at the top is 6.20 m/s, then what is the speed at the bottom? (Hint: Use conservation of energy) Assuming that y is positive in the upward direction, what is the gravitational force (in N) acting on the ball? B) Assuming that y is positive in the upward direction, what is the tension force (in N) acting on the ball when it is at the top? Assuming that y is positive in the upward direction, what is the tension force (in N) acting on the ball when it is at the bottom?arrow_forwardA car is traveling on a curved road with a radius of R=150m. The car is traveling at speed v=22 m/s and has mass m=1450kg. a) What is the net force exerted on the car in Newtons? b) The force on the car is provided by friction. What should the coefficient of friction be between the tires and the road to give the net force found in part a?arrow_forwardYour brother’s toy car has a mass 0f 250. g. The car is going in a vertical circle in 3.50 s. The radius of the track is 40.0 cm. a. Draw Free Body Diagram of the car when it is at the bottom of the circle. b What is the magnitude of the force of the track on the car at the lowest point of the circle? a. Draw Free Body Diagram of the car when it is at the bottom of the circle.arrow_forward
- A child of mass 40.0 kg is in a roller coaster car that travels in a loop of radius 9.00 m. At point A the speed of the car is 11.6 m/s, and at point B, the speed is 12.6 m/s. Assume the child is not holding on and does not wear a seat belt. B A 30° (a) What is the force (in N) of the car seat on the child at point A? (Enter the magnitude.) 205.6 ✓N (b) What is the force (in N) of the car seat on the child at point B? (Enter the magnitude.) XN 109.8 (c) What minimum speed (in m/s) is required to keep the child in his seat at point A? 9.40 m/sarrow_forwardA stone that is connected to a string is being rotated horizontally. The stone completes one full circle every second; and the magnitude of the tension in the string is F-. What happens to the tension in the string if the stone speeds up such that it goes around the circle twice every second while the radius stays the same. O The magnitude of the tension increases to twice its original value. O The magnitude of the tension increases to four times its original value. O The magnitude of the tension reduces to one-fourth of its original value. O The magnitude of the tension is unchanged. O The magnitude of the tension reduces to half of its original value.arrow_forwardA 55.8kg ice skater is moving at 4.03 m/s when she grabs the loose end of rope, the opposite end of which is tied to a pole. She then moves in a circle of radius 0.797 m around the pole . A.)Determine the force exerted by the horizontal rope on her arms. B.) what is the ratio of this force to her weightarrow_forward
- A car (m = 1069 kg) is moving at 16 m/s when it encounters a circular dip in the road of radius 97 m. Assuming the car maintains constant speed the entire time, what would be the magnitude of the force of gravity at the bottom of the dip? b.What is the magnitude of the car's acceleration at the bottom of the dip? c.What is the magnitude of the Normal Force on the car at the bottom of the dip?arrow_forwardA jet flying at 136 m/s banks to make a horizontal circular turn. The radius of the turn is 3810 m, and the mass of the jet is 2.08 x 105 kg. Calculate the magnitude of the necessary lifting force. L= iarrow_forwardA 2.0kg ball swings in a vertical circle on the end of an 80cm long string. The tension in the string is 20N when its angle from the highest point on the circle, 0, is 30deg. a) What is the ball's speed when 0-30deg? b) What are the magnitude and direction of the ball's acceleration when 0=30deg?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON