
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
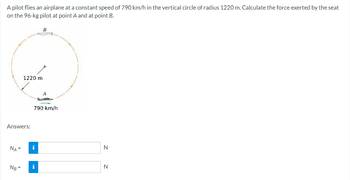
Transcribed Image Text:A pilot flies an airplane at a constant speed of 790 km/h in the vertical circle of radius 1220 m. Calculate the force exerted by the seat
on the 96-kg pilot at point A and at point B.
Answers:
NA =
NB =
1220 m
B
790 km/h
i
i
N
N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Know the concept:
VIEW Step 2: Draw a free-body diagram for the person at point A and find the expression for the normal force N_A:
VIEW Step 3: Calculate the normal force N_A:
VIEW Step 4: Draw a free-body diagram for the person at point B and find the expression for the normal force N_B:
VIEW Step 5: Calculate the normal force N_B:
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 28 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A child of mass 40.0 kg is in a roller coaster car that travels in a loop of radius 9.00 m. At point A the speed of the car is 11.6 m/s, and at point B, the speed is 12.6 m/s. Assume the child is not holding on and does not wear a seat belt. B A 30° (a) What is the force (in N) of the car seat on the child at point A? (Enter the magnitude.) 205.6 ✓N (b) What is the force (in N) of the car seat on the child at point B? (Enter the magnitude.) XN 109.8 (c) What minimum speed (in m/s) is required to keep the child in his seat at point A? 9.40 m/sarrow_forwardA 70.0 kg pilot is pulling out of a dive which follows a part of a vertical circular path of radius, R. If the airplane is traveling 150 m/s at the bottom of this path and experiences an apparent weight of 3310. N, find the radius of the circular path.arrow_forwardAt what maximum speed can a car negotiate a turn on a wet road with coefficient of static friction 0.200 without sliding out of control? The radius of the turn is 27.5 m.arrow_forward
- A banked circular highway curve is designed for traffic moving at 60 km/h. The radius of the curve is 200 m. Traffic is moving along the highway at 40 km/h on a rainy day. What is the minimum coefficient of friction between tires and road that will allow cars to take the turn without sliding off the road? (Assume the cars do not have negative lift.)arrow_forwardAs shown above, a bead is at the end of a string and moves in a horizontal circle with a constant speed of 1.43 m/s. The length of the string, L, is 185 cm and the mass of the bead is 27.0 g. The angle, 0, is known to be 19.0°. As outlined below, use two different approaches to find the tension, T, of the string. Assume that the air resistance is negligible. Although this is a multiple-choice question that you will answer on Bb and I will not be collecting the details of your work, I urge you to follow the steps outlined below to solve it. We will do the FBD of the bead together in class before this problem is due. Hint: be careful with your units. (a) Use the GFS method to show and explain each step of your work. (b) Draw a sketch of the bead. Next, clearly draw and label the FBD of the bead, showing all the external forces that are acting on it. Each external force must be represented by an arrow that is properly labeled. Be sure to show explicitly the x and y coordinate system you…arrow_forwardA child of mass 40.0 kg is in a roller coaster car that travels in a loop of radius 7.00 m. At point A the speed of the car is 10.0 m/s, and at point B, the speed is 10.5 m/s. Assume the child is not holding on and does not wear a seat belt. (a) What is the force of the car seat on the child at point A? (b) What is the force of the car seat on the child at point B? (c) What minimum speed is required to keep the child in his seat at point A?arrow_forward
- A circular curve of highway is designed for traffic moving at 75 km/h. Assume the traffic consists of cars without negative lift. (a) If the radius of the curve is 260 m, what is the correct angle of banking of the road? (b) If the curve were not banked, what would be the minimum coefficient of friction between tires and road that would keep traffic from skidding out of the turn when traveling at 75 km/h? (a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forwardIn an old-fashioned amusement park ride, passengers stand inside a 3.90 m diameter hollow steel cylinder with the backs against the wall. The cylinder begins to rotate about a vertical axis. Then the floor on which the passengers are standing drops away! If all goes well, the passengers will "stick" to the wall and not slide. Clothing has a coefficient of static coefficient of friction against steel in the range of 0.690 to 1.0 and a kinetic coefficient in the range 0.480 to 0.70. A sign next to the entrance says "No children under 30 kg allowed." What is the minimum angular speed in rpm (do not enter units) for which the ride is safe? Assume that the local acceleration due to gravity is -9.80 m/s². Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forwardA curved portion of highway has a radius of curvature of 65 m. As a highway engineer, you want to bank this curve at the proper angle for a steady speed of 22 m/s.(a) What banking angle should you specify for this curve?(b) At the proper banking angle, what normal force and what friction force does the highway exert on a 750 kg car going around the curve at the proper speed?arrow_forward
- A stuntman whose mass is 69 kg swings from the end of a 3.1-m-long rope along the arc of a vertical circle. Assuming that he starts from rest when the rope is horizontal, find the magnitudes of the tensions in the rope that are required to make him follow his circular path at each of the following points. army medio docume (a) at the beginning of his motion kN (b) at a height of 1.5 m above the bottom of the circular arc Fobiology kN (c) at the bottom of the arc kN hapter 3 Need Help? Watch It Read Itarrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forwardb) The maximum speed that a car can turn a curve of 9.00 m radius without skidding is 70.0 mph (miles per hour). If the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road is 0.600, what is the rated speed of the banked curve? On a wet day, the same car begins to skid on the curve when its speed reaches 60.0 mph. What is the coefficient of friction in this case? Please answer with complete solution and fre body diagramarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON