
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
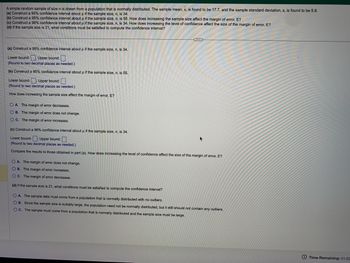
Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 17.7, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 5.8.
(a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about µ if the sample size, n, is 34.
(b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 55. How does increasing the sample size affect the margin of error, E?
(c) Construct a 98% confidence interval about µ if the sample size, n, is 34. How does increasing the level of confidence affect the size of the margin of error, E?
(d) If the sample size is 21, what conditions must be satisfied to compute the confidence interval?
(a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 34.
Lower bound:: Upper bound:
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
(b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 55.
H
Lower bound:: Upper bound:
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
How does increasing the sample size affect the margin of error, E?
OA. The margin of error decreases.
OB. The margin of error does not change.
OC. The margin of error increases.
(c) Construct a 98% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 34.
P
G
Lower bound:: Upper bound:
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Compare the results to those obtained in part (a). How does increasing the level of confidence affect the size of the margin of error, E?
OA. The margin of error does not change.
OB. The margin of error increases.
OC. The margin of error decreases.
(d) If the sample size is 21, what conditions must be satisfied to compute the confidence interval?
OA. The sample data must come from a population that is normally distributed with no outliers.
OB. Since the sample size is suitably large, the population need not be normally distributed, but it still should not contain any outliers.
OC. The sample must come from a population that is normally distributed and the sample size must be large.
Time Remaining: 01:02
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Given information
VIEW Step 2: Calculate level of significance, degree of freedom, t-value
VIEW Step 3: Calculate margin of error and confidence interval
VIEW Step 4: Calculate degree of freedom , t-value
VIEW Step 5: Calculate margin of error and confidence interval
VIEW Step 6: Calculate level of significance, degree of freedom and t-value
VIEW Step 7: Calculate margin of error and confidence interval
VIEW Step 8: Determine condition when sample size is 21
VIEW Step 9: Explanation for the incorrect options
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 10 steps with 26 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A simple random sample of size n = 40 is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be x = 121.2 and the sample standard deviation is found to be s = 12.6. Construct a 99% confidence interval for the population mean. The lower bound is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The upper bound is . (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA random sample of size 49 from normal population yields, mean = 7.2 and standard deviation = 2.8. The lower bound of a 99 percent confidence interval for population mean is O a. 6.40 O b. 6.53 O c. 6.13 O d. 6.68arrow_forwardThe law of large numbers states that as the number of observations drawn at random from a population with finite mean increases, the mean of the observed values: a. tends to get closer and closer to the population mean . b. gets smaller and smaller. c. gets larger and larger. d. fluctuates steadily between 1 standard deviation above and 1 standard deviation below the mean. I collect a random sample of size n from a population and compute a 95% confidence interval for the proportion I observe from the population. What could I do to produce a new confidence interval with a larger width (larger margin of error) based on these same data? a. I could use the same confidence level but compute the interval n times; approximately 5% of these intervals will be larger. b. Nothing can guarantee absolutely that I will get a larger interval; I can only say the chance of obtaining a larger interval is 0.05. c. I could use a smaller confidence…arrow_forward
- A simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 19.6, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 5.6. (a) Construct a 98% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 32. (b) Construct a 98% confidence interval about µ if the sample size, n, is 58. How does increasing the sample size affect the margin of error, E? (c) Construct a 99% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 32. How does increasing the level of confidence affect the size of the margin of error, E? (d) If the sample size is 21, what conditions must be satisfied to compute the confidence interval? (a) Construct a 98% confidence interval about µ if the sample size, n, is 32. Lower bound:; Upper bound: (Round to two decimal places as needed.) C...arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 115, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 10. (a) Construct an 80% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 25. (b) Construct an 80% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 12. (c) Construct a 70% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 25. (d) Could we have computed the confidence intervals in parts (a)-(c) if the population had not been normally distributed?arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean,x, is found to be 112, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 10. A. Construct a 98% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 18. Lower bound- Upper Bound- B. Construct a 98% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 28. Lower bound- Upper Bound- C. Construct a 99% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 18. Lower bound- Upper Bound-arrow_forward
- A simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 110, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 10. (a) Construct a 98% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 15. (b) Construct a 98% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 24. (c) Construct a 99% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 15. (d) Could we have computed the confidence intervals in parts (a)-(c) if the population had not been normally distributed?arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 104, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 8. (a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 22. (b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 16. (c) Construct a 90% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 22. (d) Should the confidence intervals in parts (a)-(c) have been computed if the population had not been normally distributed? (a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 22. Lower bound: 100.5; Upper bound: 107.5 (Round to one decimal place as needed.) (b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 16. Lower bound: Upper bound: (Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 108, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 10. (a) Construct a 96% confidence interval about µ if the sample size, n, is 13. (b) Construct a 96% confidence interval about µ if the sample size, n, is 29. (c) Construct a 99% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 13. (d) Could we have computed the confidence intervals in parts (a)-(c) if the population had not been normally distributed? FClick the icon to view the table of areas under the t-distribution. (a) Construct a 96% confidence interval about μ if the sample size, n, is 13. Lower bound: Upper bound: (Use ascending order. Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forward
- A researcher believes that the mean of a population is 45.2. She collects data from a sample (n = 81) and finds that the sample mean is 40.4, with a standard deviation of 19. Construct a 90% confidence interval to determine whether 45.2 is a reasonable hypothesis about the value of mu.arrow_forwardThis question A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x, is found to be 19.2, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 4.2. Click the icon to view the table of areas under the t-distribution. (a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 35. Lower bound:; Upper bound: (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.) (b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 51. Lower bound: ; Upper bound: (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.) How does increasing the sample size affect the margin of error, E? O A. The margin of error does not change. O B. The margin of error decreases. O C. The margin of error increases. (c) Construct a 99% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 35. Lower bound: : Upper bound: (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.) Compare the results to those obtained in part (a). How does increasing the level of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman