
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
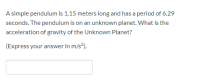
Transcribed Image Text:A simple pendulum is 1.15 meters long and has a period of 6.29
seconds. The pendulum is on an unknown planet. What is the
acceleration of gravity of the Unknown Planet?
(Express your answer in m/s?).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You hang different masses M from the lower end of a vertical spring and measure the period T for each value of M. You use Excel to plot T2 (in s2) on the y-axis versus M (in kg) on the x-axis. The equation for the straight line that gives the best fit to your data is y = 0.0467x + 0.00400. (a) What is the mass of the spring? I found that the force constant of the spring is 845.362 N/m and for the mass of the spring I found it to be 0.085 kg (85.65 g) but it's wrong when I submit it. Am I doing something wrong?arrow_forwardA new dwarf planet was observed recently in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It has an orbital period of 7.93 E 7 s. The ratio from the law of harmonies is approximately 2.98 E−19 s2/m3. What is its average distance from the sun? 1. 2.40 E 11 m 2. 2.66 E 11 m 3. 2.77 E 11 m 4. 3.76 E 11 marrow_forwardA force of 15.0 N is required to stretch a spring a distance of 5.20 cm. What is the force constant of the spring, in units of N/m?arrow_forward
- How do you determine the gravitational acceleration on a planet where the period of a 1.90 m long pendulum is 2.78 s, and express the result in g = in m/s^2?arrow_forwardA 50 cm long spring with spring constant 257 N/m has a mass 1.9 kg attached to it, and it can oscillate on a horizontal table without any friction. When the spring is pulled so that its length is 55 cm, what is the magnitude of the maximum acceleration of the mass? Give your answer in m/s?.arrow_forwardAn object of unknown mass is attached to an ideal spring with force constant 110 N/m and is found to vibrate with a frequency of 5.50 Hz. Part A Find the period. Express your answer in seconds. Part B Find the angular frequency. Express your answer in radians per second. Part C Find the mass of this object. Express your answer in kilograms.arrow_forward
- When a pendulum with a period of 2.00000 s in one location (g = 9.80 m/s2) is moved to a new location from one where the period is now 1.99747 s. What is the change in acceleration (in m/s2) due to gravity at its new location?arrow_forwardA 2.0 kg object compresses a spring with a spring constant of 100 N/m by a distance of 8 cm, and then the object is released. Assuming that the object maintains the same acceleration while the spring returns to equilibrium, how fast is the object moving after 1.2 s?arrow_forwardA pendulum is 0.341m long and has a period of 3.207s. The pendulum is on an unknown planet. What is the gravity of the unknown planet in m/s2?arrow_forward
- An object is oscillating on a spring with a period of 4.60 s. At time t = 0.00 s the object has zero speed and is at x = 8.30 cm. What is the acceleration of the object at t = 2.50 s?arrow_forwardAsimple pendulum which has a frequency of 2.5 Hz.on the surface of the Earth is used by an astronaut visiting a newly discovered planet. On that planet's surface, the pendulum swings with a frequency of 1.6 Hz. How large is the gravitational acceleration of that planet?arrow_forwardDuring an experiment, a student tests a spring's oscillation period with different masses. The testing masses are 50g, 100 g, 200 g, and 500 g. Which of the following statements is correct? The 100 g has the highest frequency. The 500 g has the highest frequency. The 50 g has the highest frequency. O The 200 g has the highest frequency.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON