
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:rmResponse
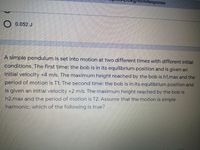
O 0.052 J
A simple pendulum is set into motion at two different times with different initial
conditions. The first time: the bob is in its equilibrium position and is given an
initial velocity +4 m/s. The maximum height reached by the bob is h1,max and the
period of motion is T1. The second timne: the bob is in its equilibrium position and
is given an initial velocity +2 m/s. The maximum height reached by the bob is
h2,max and the period of motion is T2. Assume that the motion is simple
harmonic, which of the following is true?
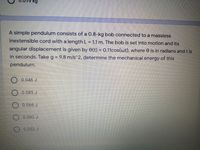
Transcribed Image Text:kg
A simple pendulum consists of a 0.8-kg bob connected to a massless
inextensible cord with a length L = 1.1 m. The bob is set into motion and its
angular displacement is given by 0(t) = 0.11cos(wt), where e is in radians and t is
in seconds. Take g = 9.8 m/s^2, determine the mechanical energy of this
pendulum.
0.046 J
0.085 J
0.066 J
O 0.090 J
0.052 J
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the shown system: θ = 54 ∘, k = 640 N/m , m = 3 kg , and the unstretched spring length is 290 mm . It is released from rest from the shown position; answer the following 1) Part A: Calculate the work of the spring force at θ=0∘. 2) Part B: Determine the angular velocity of the rod at θ=0∘. 3) Part C: Determine the angular acceleration of the rod at θ=0∘.arrow_forwardQuestion 25 part b.arrow_forwardA spring with spring constant 29 N/m is compressed a distance of 9.0 cm by a ball with a mass of 206.5 g (see figure below). The ball is then released and rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface, leaving the spring at point A. The process is repeated, using a block instead, with a mass identical to that of the ball. The block compresses the spring by 9.0 cm and is also released, leaving the spring at point A. Each object travels up the incline shown in the figure before coming to rest momentarily. Assume the ball rolls, but ignore other effects of friction. (Assume the ball rolls without slipping up the incline until it comes to rest.) (a) How high above the starting position is the ball when it comes to rest momentarily? m(b) How high above the starting position is the block when it comes to rest momentarily?arrow_forward
- A simple pendulum has a mass of 0.650 kg and a length of 5.00 m. It is displaced through an angle of 5.0° and then released. Using the analysis model of a particle in simple harmonic motion, calculate the following. (Give your answer to the thousandths place.) (a) What is the maximum speed of the bob? m/s (b) What is the maximum angular acceleration of the bob? rad/s² (c) What is the maximum restoring force of the bob? N (d) Solve parts (a)through (c) by using other analysis models. (Hint: you may need to use separate analysis models for each part.) maximum speed maximum angular acceleration m/s rad/s² N maximum restoring force (e) Compare the answers.arrow_forwardThis, the length of the pendulum is 2.16 m. Now you start with the pendulum at 30.5 degrees with respect to the vertical, but rather than releasing it from rest, you give it a push downward. It swings to the other side, and reaches a maximum angle of 50.8 degrees with respect to the vertical. What must have been the initial speed of the pendulum just after you pushed it? 3.12 m/s 3.95 m/s 2.42 m/s 6.32 m/sarrow_forwardA 185.4 g mass-spring system is rapidly oscillating. The spring used in the system has a spring constant of 12.4 N/m. The system was initially displaced 1.50 m, and has a measured total energy (TE) of 14.95 J. What is the maximum velocity that the mass will reach during its oscillation?arrow_forward
- ege.com/course.html?courseld%=16202200&OpenVellumHMAC=a34faccb64fc064a9ce89812d0e27d84#10001 PH114 Fall 2020 Godang Course Home <9 Problem 11.54 A 0.019 kg record with a radius of 11 cm rotates with an angular speed of 33 3 rpm. Part A Find the angular momentum of the record. Express your answer using two significant figures. Hνα ΑΣφ L = kg · m² /s Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; One attempt remaining Provide Feedback MacBook Air 80 DII DD F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 23 %24 & * 4. 7 8 < CO 5arrow_forwardVelocity and Acceleration of Simple Pendulum. L= 1m,T0 = 0, θ = 0, θ’ = 10deg/s, θ’’ = 2deg/s*s. Tf = 1sec, θ = 45 deg, θ’ = 5deg/s, θ’’ = 1 deg/s*s a.Find the position at T0 and Tfarrow_forwardA spring AB of constant k=150kn/m is attached to a support at A and to a collar of mass m=150 gm. The unstretched length of the spring is l=0.8m. Knowing that the collar is released from rest at x0 = 90 cm and neglecting friction between the collar and the horizontal rod, determine : the magnitude of the velocity of the collar as it passes through point C. A - Xo-arrow_forward
- A horizontal spring is lying on a frictionless surface. One end of the spring is attaches to a wall while the other end is connected to a movable object. The spring and object are compressed by 0.058 m, released from rest, and subsequently oscillate back and forth with an angular frequency of 11.0 rad/s. What is the speed of the object at the instant when the spring is stretched by 0.031 m relative to its unstrained length?arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a simple pendulum. The length of the string is l and the bob has mass mj. m. If the mass is released from rest when 0 = 75.4°, at which values of 0 does the mass have half of its maximum kinetic energy?arrow_forwardA grandfather clock can be approximated as a simple pendulum of length 1.00 m and keepsaccurate time at a location where g = 9.83 m/s2. In a location where g = 9.68 m/s2, what mustbe the new length of the pendulum, such that the clock continues to keep accurate time (thatis, its period remains the same)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON