
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A segment of a generator shaft is subjected to a torque T and an axial force P, as shown
in the Figure Q3. The shaft is hollow (outer diameter dɔ= 300 mm and inner diameter
di = 250 mm) and delivers 1800 kW at 4.0 Hz.
Q3
(а)
If the compressive force P = 540 kN, determine the stresses produced and the
state of plane stress on its surface.
Calculate the principal stresses and the maximum in-plane shear stress in the
shaft. Specify the orientation of the element in each case.
(b)
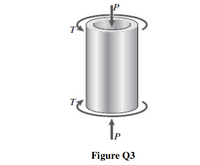
Transcribed Image Text:|P
Figure Q3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solid Mechanics In the figure, solid copper rod with expansion coefficient αB = 165.10-7 1 / 0C It is 20 mm in diameter. Inner diameter is 2mm larger than this bar and expansion into a steel pipe of 30 mm outer diameter with coefficient αÇ = 125.10-7 1 / 0C so that they move together. It is combined with a rigid plate. System with temperature difference Δt = 80 0C Find the stresses that will occur in steel and copper when heated. (Eç= 200 GPa, Eb= 100 GPa)arrow_forward= 1.3-18 A stepped shaft ABC consisting of two solid,circular segments is subjected to uniformly distrib uted torque i,acting over segment 1 and concentrated torqueT₂applied at C,as shown in the figure。Seg ment 1 of the shaft has a diameter ofd₁= 57 mm and length ofL₁= 0.75 m; segment 2 has a diameterd₂= 44 mm and lengthL₂= 0.5 m。Torque intensity1₁3100 N m / m andT₂= 1100 N·m。(a)Find reaction torque T at support A.(b)Find the internal torque T(x)at two locations:arrow_forwardA 3 m long steel angle shown in the figure has a section thickness of 12.7 mm and a cross sectional area of 4350 mm². Since tem = 50 MPa and G = 77.2 GPa, find the maximum applicable torque T.arrow_forward
- Consider the loaded shaft illustrated in Figure Q4 (i). The shaft is simply supported at A and D. The shoulder fillet radius is 0.3 cm at B and C. If the shaft is subjected to a force of F-800 N, determine the following: (a) The reaction forces at the two ends of the shaft A and D. (b) The bending moments at shoulder fillets B andC. (c) The nominal stresses at shoulder fillets B and C. (d) The stress concentration factor at shoulder fillet B. (e) The maximum stress in the shaft taking into account stress concentrations. 800 N T-0.3 can A d, - 3 cm d, = 5 cm d, - 3 cm 5 cm 8 cm 8 cm 12 cm Figure Q4 (i) The reference parameters are shown in Figure Q4 (ii) in the page that follows. For 0.002 srlds 0.3 and 1.01 s Dlds 6.0, the stress concentration factor for bar bending is given as: kn -4.4 = 0.632 + 0.377 -0.14 – 0.363(P/a)" + 0.503(P/a) 1- 2.39(P/a) + 3.368(2la)* -0.5 The nominal stress is: 32M %3D nd3arrow_forwardFor the rod in the figure, an allowable stress of 10 ksi, calculate the maximum torque T which can be applied. d= 0.5 in, D= 0.835 in, r= 0.045 in .arrow_forward5. The shaft shown in the figure is made from a steel tube, which is bonded to a brass core. If a torque of T = 227 Ib-ft is applied at its end, calculate the absolute maximum shear stress developed in each of steel tube, and brass core. The end of the shaft is attached to rigid supports (fixed supports). Take Gst = 11.4 X 10³ ksi, and Gpr = 5.2 X 10³ ksi. В 0.5 in., 4 ft 1 in. A T = 2271b ftarrow_forward
- T.L Tr4 %3D J = " (r* – rf) (Tubular shaft) Tr (Solid shaft) G.J 3. The shaft in the figure below consists of 75 mm diameter bronze segment that is rigidly joint to 50 diameter steel segment. The ends of the shaft are attached to rigid supports (fixed supports). Calculate the absolute maximum shear stress developed in each segment when the torque T= 5.1 kN-m is applied (a = 2 m and b = 1.5 m). Use G = 35 GPa for bronze, and G = 75 GPa for steel. (21 pts) 75 mm 50 mm Bronze Steelarrow_forwardA segment of a generator shaft is subjected to a torque T and an axial force P, as shownin the Figure Q3. The shaft is hollow (outer diameter d2 = 307 mm and inner diameterd1 = 250 mm) and delivers 1800 kW at 4.0 Hz (a) If the compressive force P = 540 kN, determine the stresses produced and thestate of plane stress on its surface. (b) Calculate the principal stresses and the maximum in-plane shear stress in theshaft. Specify the orientation of the element in each case.arrow_forwardCould you please solve A, B and Carrow_forward
- 5 - A thin-walled pressure vessel is subjected to internal pressure p 1 MPa. What is the maximum allowable torque T, applied along the longitudinal axis, if the maximum allowable tensile stress is 80 MPa? ↓t=3mm 240mm polar moment of inertia J=2r³tarrow_forwardA circular hollow shaft is subjected to a torsional moment T = 30 kNm and a compressiveload P = 80 kN, as shown. The shaft has an outer diameter D = 120 mmand inner diameter d = 100 mm. Points A and B are on the surface of the shaft. (a)Calculate the direct and shear stress at point A. (b)Calculate the maximum,minimum and oriention of the max and min principal stresses at point A. (c)Calculate the maximum in-plane shear stress at point A and the orientation.arrow_forwardA hard-drawn steel wire extension spring has a spring index Of 7.5, hook radii of r = 0.106 in and r2 0.089 in, and an initial tension of 1.5 lbf. The number of body turns is 13.5 and the uncorrected initial stress is 16.5 kpsi. From the given information: (a) Determine the physical parameters of the spring. (b) Find all stresses at ends A and B and the body torsion under the static load of 6 Ibf.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY