
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
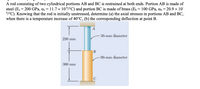
Transcribed Image Text:A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB and BC is restrained at both ends. Portion AB is made of
steel (Es = 200 GPa, as = 11.7 × 106/°C) and portion BC is made of brass (E, = 100 GPa, ab = 20.9 × 10
6°C). Knowing that the rod is initially unstressed, determine (a) the axial stresses in portions AB and BC,
when there is a temperature increase of 40°C, (b) the corresponding deflection at point B.
A
30-mm diameter
250 mm
|B
-50-mm diameter
300 mm
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The brass rod AB is fixed connected at A. When the temperature is T₁-50 °C, there is a 3 mm gap between its end (point B) and the wall C. The cross-sectional area of the rod is 10 cm². Ignore the weight of the bar. The temperature is now increased to T₂-130 °C and the rod AB is pushing against the wall at C. Ebr = 100 GPa, abr = 20 x 10-6/°C Fallow 70 MPa L = 3m A 3 m B/C с 3 mm a. Draw a FBD for when the temperature is increased to T₂ and write down the force balance for this scenario. Call the reactions at FA and FC. Ton =1) und prit brolim volgen Aistis Intelesa si s b. State the compatibility condition and solve for the reactions at A and C.arrow_forwardH.W 3 Two aluminum alloy plates (2) are attached to the sides of a wooden beam (1) as shown in Figure 3. mensions of the composite cross section are b1 = 80 mm, d¡ = 240 mm, b2 = 10 mm, d2 = b2 The di- |di 120 mm, and a = 60 mm. Deter- (2) (2) %3D mine the maximum bending (1) a stresses produced in both the wooden beam and the aluminum b1 plates if a bending moment FIGURE 3 +6,000 N m is applied M2 %3D about the z axis. Assume that Ej = 12.5 GPa and E2 = 70 GPa.arrow_forward2.58 Knowing that a 0.02-in. gap exists when the temperature is 75°F, determine (a) the temperature at which the normal stress in the alu- minum bar will be equal to -11 ksi, (b) the corresponding exact length of the aluminum bar. 0.02 in. - 14 in. - Bronze A = 2.4 in² E = 15 x 106 psi a = 12 x 10-6/°F Fig. P2.58 and P2.59 18 in.. Aluminum A = 2.8 in² E = 10.6 x 106 psi a = 12.9 x 10-6/°F 300 mm 0.5 mm 250arrow_forward
- The copper rod AB and steel rod BC are joined at the collar B and fixed connected at their ends. If there is no load in the members when T1 = 17°C, determine the average normal stress in each member when T2 = 47°C. Also, how far will the collar be displaced? The cross-sectional area of each member is 1130 mm?. %3D Сopper Steel Elastic Modulus (GPa) 120 200 Coefficient of thermal expansion (1/°C) 17x10-6 12x10-6 В 1 m 0.6 m-arrow_forwardH.W 3 Two aluminum alloy plates (2) are attached to the sides of a wooden beam (1) as shown in Figure 3. mensions of the composite cross section are bj = 80 mm, d1 = dz 240 mm, b2 = 10 mm, d2 = The di- di %3D %3D 120 mm, and a = 60 mm. Deter- (2) (2) (1) mine the maximum bending stresses produced in both the wooden beam and the aluminum b1 plates if a bending moment M = +6,000 N m is applied about the z axis. Assume that E = 12.5 GPa and E2 = 70 GPa. FIGURE 3 %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning