
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A rigid bar, AB, is pinned at point B. Two other bars, AC and AD, are connected to point A to provide support for AB. We are investigating the behavior of this system under a specific load.
Key Details:
- Bar properties:
- Material: Steel with Young's modulus (Esteel) of 200 GPa and coefficient of thermal expansion (a) of 11.7 x 10^-6 /°C.
- Cross-sectional area:
- AC: 1960 mm²
- AD: 1250 mm²
- Length:
- AC: √2 meters (square root of 2 meters)
- AD: 1 meter
- Inclination angles:
- AC: θ₁ (theta 1) = 30° from horizontal
- AD: θ₂ (theta 2) = 20° from horizontal
- Load on bar AB: Idealized linearly increasing load with a maximum value of 30 kN/m at point B.
Problem Objectives:
- Determine the internal forces (axial forces) acting within bars AC and AD due to the applied load on AB.
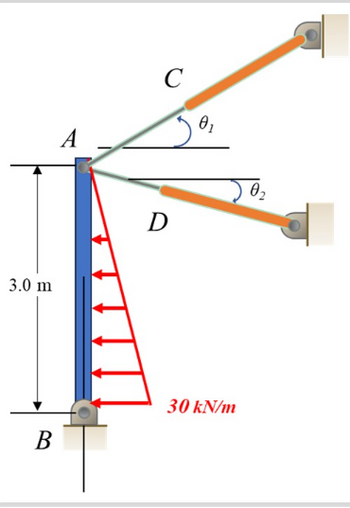
Transcribed Image Text:Ꭺ
C
Ꮎ
3.0 m
Ꭰ
B
30 kN/m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q2: The pin-connected structure shown in Figure consists of a rigid bar ABCD and two axial members. Bar (1) is steel /E = 200 GPal with a cross-sectional area of (4,= 400 mm). Bar (2) is an aluminum alloy (E = 70 GPaj with a cross-sectional area of (A, = 400 mmj. The bars are unstressed when the structure is assembled. After a concentrated load of [P- 36 kNJ is applied, determine: (a) the normal stresses in bars (1) and (2). (b) the deflection of point D on the rigid bar. 900 mm Area=40omnt (1) 350 mm alumiaum (2) 36 AN 600 mm Ag= Yoom 720 mmarrow_forwardCan you please help me with all parts of the question? Thank youarrow_forwardA load P is supported by a structure consisting of rigid bar ABC, two identical solid bronze [E = 17200 ksi] rods, and a solid steel [E = 31400 ksi] rod, as shown. The bronze rods (1) each have a diameter of 0.69 in. and they are symmetrically positioned relative to the center rod (2) and the applied load P. Steel rod (2) has a diameter of 0.53 in. Assume L₁=45 in and L₂=67 in. If all bars are unstressed before the load P is applied, determine the normal stresses in bronze rods (1) and steel rod (2) after a load of P = 16 kips is applied. (1) Answers: 01 02 = i i L2 (2) Save for Later B P eTextbook and Media (1) ksi. ksi. L₁ Attempts: 0 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forward
- A load P is supported by a structure consisting of rigid bar ABC, two identical solid bronze [E = 14100 ksi] rods, and a solid steel [E = 28000 ksi] rod, as shown. The bronze rods (1) each have a diameter of 0.61 in. and they are symmetrically positioned relative to the center rod (2) and the applied load P. Steel rod (2) has a diameter of 0.47 in. Assume L₁-39 in and L2-72 in. If all bars are unstressed before the load P is applied, determine the normal stresses in bronze rods (1) and steel rod (2) after a load of P = 29 kips is applied. O (1) A Answers: 0₁ = i 0₂ = i L2 (2) B P ksi. ksi. Larrow_forward2. Two initially rigid bars AC and DG are pinned at A and G and are also connected by vertical bars BD and CF, each having rigidity = AE. The temperature of bar BD is then raised by an amount AT. 1.5L B D F -2L- Address the following: a. Draw accurate and complete FBD of AC, DG, BD, CF b. Which of a. are two-force members? c. Compute the force in BD in terms of a, AT, AE d. Compute the force in CE in terms of a,AT, AEarrow_forwardplease help me with thisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY