
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A researcher was observing traffic along one lane of a rural highway. During a 1 minute time interval, ten vehicles were observed travelling 65, 64, 71, 66, 58, 72, 69, 66, 55 and 62 mph. Using these spot speeds, calculate the space mean speed (mph). Provide your answer to the nearest tenth of a mph.
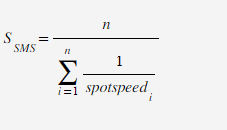
Transcribed Image Text:S
SMS
OM=
n
1
i=1 spotspeed i
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Assume you are observing traffic in a single lane of a highway at a specific location. You measure the average headway and average spacing of passing vehicles as 3 seconds and 150ft, respectively. What is the average speed of the traffic stream? Note: you can use two methods to conduct the calculation. 2. Assume the speed and density at a freeway location follows a linear relationship. You observe traffic flow rate of 2250 vehicles/hour at 45 mph and 3000 vehicles/hour at 30 mph. What are the jam density, free flow speed (max speed), and capacity of this freeway location? How about the density and speed (i.e., the critical density and the critical speed) at the capacity?arrow_forwardVehicle time headways and spacings were measured at a point along a highway, from a single-lane rural roadway, over the course of an hour. The average values were calculated as 2.5 seconds per vehicles for headway and 200 feet per vehicle for spacing. What is the density, in vehicle per mile?arrow_forwardThis is a three-part problem. Two sets of students are collecting traffic data at two roadway stations, station 130 + 00 and station 145 +00. Observations at station 130 + 00 show that five vehicles passed that section at intervals of 0, 3, 4, 3, and 5 sec, respectively. If the speeds of the vehicles were 50, 45, 40, 45, and 50 mph respectively. Note: Stationing is fundamental to highway plans. A station is the horizontal measurement along the Construction Survey Line of a project. Distances are measured and points are identified on plans with reference to station numbers. One hundred feet is equivalent to one station. Highway stationing might be compared with a rope having knots at 100-foot intervals. The beginning end of the rope would be 0, the first knot at 100 feet would be Station Number 1 and would be written as 1+00. The second station number would be 2 (which is 200 feet from the beginning) and would be written as 2+00, and so on. Part A. Determine the time mean speed, in mph.…arrow_forward
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardThe data shown below were obtained by time-lapse photography on a highway. Use regression analysis to fit these data to the Greenshields model and determine The mean free speed The jam density The capacity The speed at maximum flow Speed(mi/h) Density (veh/mi) 14.2 85 24.1 70 30.3 55 40.1 41 50.6 20 55 15arrow_forwardA researcher was observing traffic along one lane of a rural highway. During a 1 minute time interval, ten vehicles were observed travelling 65, 64, 71, 66, 58, 72, 69, 66, 55 and 62 mph. Calculate the flow rate (vph). Provide your answer to the nearest integer.arrow_forward
- 5. An engineering student is driving on a roadway with a -1% grade and sees a traffic barricade 600 ft ahead in the middle of the roadway. Despite his best effort to stop in time, the student strikes the sign at a speed of 40 mi/hr. If the student was traveling at 70 mi/hr when the sign was first spotted, what was the student's associated perception-reaction time (use practical stopping distance). 6. A driver is traveling at 62 mi/hr on a wet road. An object is spotted on the road 600 ft ahead and the driver is able to come to a complete stop just before hitting the object. Assuming perception-reaction time of 2.5 seconds and practical stopping distance, determine the grade of the road.arrow_forwardQUESTION 1 A researcher was observing traffic along one lane of a rural highway. During a 1 minute time interval, ten vehicles were observed travelling 65, 64, 71, 66, 58, 72, 69, 66, 55 and 62 mph. Using these spot speeds, calculate the space mean speed (mph). Provide your answer to the nearest tenth of a mph.arrow_forwardThe time between arrivals of vehicles at a particular intersection follows an exponential probability distribution with a mean of 14 seconds. A. What is the probability that the arrival time between vehicles is 12 seconds or less (to 4 decimals)? B. What is the probability that the arrival time between vehicles is 6 seconds or less (to 4 decimals)? C. What is the probability of 30 or more seconds between vehicle arrivals (to 4 decimals)?arrow_forward
- A 12 ft long loop detector has observed six vehicles that have crossed the device in a 148 second period, for the following durations: 0.44; 0.48; 0.5; 0.41; 0.49; and 0.55. The six vehicles are 18, 21, 20, 23, 17 and 19 ft respectively. Calculate: b. What is the % lane occupancy?arrow_forwardTwo observers have determined that the time headways between successive vehicles are exponentially distributed and that 70% of the headways are 8s or greater. If one of observer decides to count traffic in 40s intervals, and the other in 35s intervals, estimate the probability of each observer counting 5 or more vehicles in their own intervals?arrow_forwardA researcher was observing traffic along one lane of a rural highway. During a 1 minute time interval, ten vehicles were observed travelling 65, 64, 71, 66, 58, 72, 69, 66, 55 and 62 mph. Using these spot speeds, calculate the time mean speed (mph). Provide your answer to the nearest tenth of a mph.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning