
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A rectangular block below of height L and horizontal cross-sectional area A floats at the interface between two immiscible liquids:
Derive a formula for block density(ρb), in terms of the fluid densities ρ1 and ρ2, heights h0 and h1, and the cross-sectional area A.
(Note, all variables may not appear in the final result).
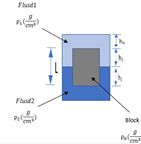
Transcribed Image Text:Flaidi
Fluid?
Block
Pal
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Parallel laminar Flow Between Infinite Planes with a Manometer A Newtonian fluid with viscosity μf and density pf is contained between two infinite horizontal parallel planes (separated by a distance d as shown below). The fluid flows laminarly under the action of a pressure gradient and the velocity U of the upper plane (the bottom plane is fixed). A manometer (with fluid density pm and viscosity μm) is connected between two points L apart along the bottom plane and indicates a differential reading of Ah. Using the coordinate system depicted in the figure below, calculate the velocity distribution in terms of known variables by performing a shell balance. What value must U have so that the frictional drag force on the upper plate is zero? Sketch the velocity profile for this last case (i.e., zero frictional drag force on the upper plate). d Pf ༑ Ah Pm L Xarrow_forwardLook into the figure carefully to get the information.arrow_forwardIn planar flow of an incompressible fluid, the x component of the velocity is given by u = ½ x² + 2x – 4y. Use the equation of continuity to derive the expression for v. %3Darrow_forward
- A pair of concentric glass cylinders, with diameters of 1 and 1.05 cm, respectively are held together in such a way that both annular ends are open to the flow of fluids. The pair of cylinders with its axis vertical are so placed that the open end is slightly below the surface of a reservoir of silicone oil at 25 deg. C. What is the expected height of the oil into the annular space between the cylinders? Take o=0.019 N/m and p=900 kg/m³.arrow_forward2. Consider a flow of liquid in a horizontal circular tube which is mobile. The flow in the tube is assumed to be fully developed and pressures at two ends are Po and PL. The cylindrical tube has radius of R and length of L. The tube itself is moving along the z-direction with a velocity of Vz (R) = -α Trz (R), where a > 0. a) Obtain the radial velocity profile in the circular tube. b) Find the average velocity Hint (Answer): R Z Fluid flows in z- direction L Uz = ΔΡ 4μL ΔΡ 2L - R21 2μ ΔΡ Uavg=8μL R²+ ΔΡ 2L aR - R2V 2μarrow_forwardAn enclosure consists of two black surfaces formed by cutting off a 0.3 m diameter spherical shell by a plane at a distance 0.1 m from the centre and closing it by a black circular disk Determine the view factors of the surfaces. in R dearrow_forward
- Problem 3: A model equation for chemical reactive flow in a one-dimensional reactor is given as ac ac +u. ôt dx :DOC-KC, where C is the dimensionless concentration of the species, u is the velocity, D is a diffusion coefficient, k is a reaction rate, and x,t are the distance from the reactor and time, respectively. (3a) Determine the dimensions of D, k;arrow_forwardThe pressure drop in a 6-in. pipe (I.D. = 6.065 in.) of length L is 1 psi with the flow in the highly turbulent region. If the same liquid flows at the same volumetric flow rate in a 3-in. pipe (I.D. = 3.068 in.) with length L, the pressure drop (psi) is:arrow_forwardSuppose that exactly half of the annular volume between concentric, horizontal cylinders is filled with a liquid and half with a gas, as shown below on the left. When the inner cylinder is rotated at an angular velocity , it is found that one interface rises to a height H above the other. The gap between the cylinders is sufficiently thin (W<< R) that local Cartesian coordinates can be used, as shown on the right. (For clarity, the gap width is exaggerated on the left.) All of the following questions concern flow in the liquid, which is Newtonian with constant properties. g R+W Gas Ω Liquid R H y Enlargement of liquid-filled gap X W ΩR Fixed (a) Assuming steady, fully developed flow, determine Vx(y) in the liquid in terms of dp/dx. (At this point, dp/dx is unknown.) (b) Relate dIP/dx in the liquid to H. You can assume that the absolute pressure in the gas is nearly constant (P = Po) and that surface tension is negligible. (c) Calculate H. That is, relate H to the rotation rate (),…arrow_forward
- 2.8. *The deepest point in the oceans of the world is believed to be in the Marianas Trench, southeast of Japan; there the depth is about 11 000 m. What is the pressure at that point?arrow_forwardplz answer both 2 questionsarrow_forwardHOMEWORK-2 Considering the steady-state laminar flow of a liquid with density p and viscosity p in a vertical tube of length L and radius R; a) Show the momentum flux and velocity profile in the figure. b) Determine the momentum flux distribution, the velocity distribution, the maximum velocity (Vzmax), and the average velocity (Vzaverage) expressions. PL L R ! Po 1111111 Flow inarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The