
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079113
Author: David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
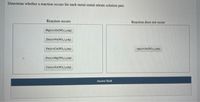
Transcribed Image Text:Determine whether a reaction occurs for each metal-metal nitrate solution pair.
Reaction occurs
Reaction does not occur
Mg(s)+Zn(NO,), (aq)
Zn(s)+Fe(NO,), (aq)
Fe(s)+Cu(NO,), (aq)
Agco+Za(NO,),(ag)
Fe(s)+Mg(NO,), (aq)
Cu(s)+Fe(NO,),(aq)
Answer Bank
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider only the species (at standard conditions) Na+, Cl, Ag+, Ag, Zn2+, Zn, Pb in answering the following questions. Give reasons for your answers. (Use data from Table 17-1.) a. Which is the strongest oxidizing agent? b. Which is the strongest reducing agent? c. Which species can be oxidized by SO42 (aq) in acid? d. Which species can be reduced by Al(s)?arrow_forwardAn aqueous solution of an unknown salt of gold is electrolyzed by a current of 2.75 amps for 3.39 hours. The electroplating is carried out with an efficiency of 93.0%, resulting in a deposit of 21.221 g of gold. a How many faradays are required to deposit the gold? b What is the charge on the gold ions (based on your calculations)?arrow_forwardDetermine whether a reaction occurs for each metal-metal nitrate solution pair.arrow_forward
- O ||| Microsoft O W Balance the following redox reaction in basic solution. G Microsoft O ELECTROCHEMISTRY Balancing a complex redox equation in acidic or basic solution Microsoft 6.52.210... 2- Cr(OH)₂(s) + Cl₂(g) → Cro (aq) + Cl(aq) 4 2- Cr(OH), (s) + Cl₂(g) → Cro (aq) + Cl (aq) 4 Explanation BO 5 Check 9,214 240 103 NOV 1 tv e + Ś 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of SIJZA Warrow_forwardDecide whether or not each metal dissolves in 1 molL-1HIO3(aq) Au3+ (aq) + 3e- - > Au(s) 1.50 103–(aq) + 6H +(aq) +5e--> 1212 (s) + 3H2O(l) Ni2 + (aq) + 2e--> Ni(s) Write a balanced redox equation for the reaction that occurs between Au and Ni. When entering the equation, use whole numbers as coefficents.arrow_forwardPt(s)|Fe2+(aq),Fe3+(aq)||F-(aq)|F2(g)|C(s) Which is the reducing agent? F2 Fe3+ Fe2+ F-arrow_forward
- What is the concentration of Cu2+(aq) in the solution?arrow_forwardBalance the following redox reaction in basic solution. 3+ Fe (aq)+Cro (aq) - Fe (aq)+Cr(OH),(s) 2+ 3+ Fe (aq) + Cro (aq) Fe (aq) + Cr(OH), (s)arrow_forwardAn unknown metal, x, was placed in a solution of CuCl2(aq) and black solid appeared on the metal. However, when metal x was placed in the solution of ZnCl2(aq), no observable change occurred. What is the possible identity of metal X? Explain your reasoningarrow_forward
- Balance the following redox equations. All occur in basic solutions. (A) Fe(OH)3(s) + Cr(s) --> Cr(OH)3(s) + Fe(OH)2(s) (B) NiO2(s) + Zn(s) --> Ni(OH)2(s) + Zn(OH)2(s) (C) Fe(OH)2(s) + CrO42-(aq) --> Fe(OH)3(s) + [Cr(OH)4]-(aq) (D) N2H4(aq) + Ag2O(s) --> N2(g) + Ag(s)arrow_forwardA sample of impure tin of mass 0.530 gg is dissolved in strong acid to give a solution of Sn2+Sn2+. The solution is then titrated with a 0.0448 molL−1molL−1 solution of NO3−(aq)NO3−(��), which is reduced to NO(g)NO(�). The equivalence point is reached upon the addition of 3.91×10−2 LL of the NO3−(aq)NO3−(��) solution. Part A Find the percent by mass of tin in the original sample, assuming that it contains no other reducing agents.arrow_forwardBalance the following reaction in acidic solution. Fe?+ (ag) + MnO, (aq) → Fe+ (ag) + Mn²+(aq) Fill in the coefficients and substances for the balanced overall equation. Note: Do NOT leave any coeffient fields empty. If the coefficient is 1, choose "1" as opposed to leaving it blank. Fe2+ + MnO,¯ + 4 Fe3+ + Mn2+ +arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning