
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
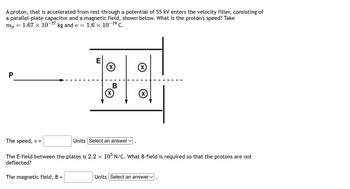
Transcribed Image Text:A proton, that is accelerated from rest through a potential of 55 kV enters the velocity filter, consisting of
a parallel-plate capacitor and a magnetic field, shown below. What is the proton's speed? Take
mp 1.67 × 10-27 kg and e = = 1.6 × 10-¹⁹ C.
P
=
E
The magnetic field, B =
(x)
B
(x)
The speed, v =
The E-field between the plates is 2.2 × 105 N/C. What B-field is required so that the protons are not
deflected?
Units Select an answer ✓
X
Units Select an answer ✓
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 |9192 7.2 |F| This problem checks that you can correctly apply Coulomb's law for point charges, Two point-like particles separated by 7 cm have charges 91=2 nC and 92=4 nC. Note that the force felt by each charge due to the other is a vector and has both a magnitude and a direction. What is the magnitude of the force exerted on the charges due to the electromagnetic interaction, in N (10-6 Newtons)? 4π€0arrow_forward2. A proton travels with a speed of 5 x 105 m/s between the two parallel charged plates shown in the figure below. The plates are separated by 1.0 cm and charged by a 220 V battery. a. Determine the strength and direction of the electric field between the two plates. b. What is the direction and magnitude of the force on the proton due to this electric field? + + + + + + + + + + 1.0 cm c. What magnetic field (strength and direction) will allow the proton to pass between the plates without being deflected?arrow_forwardAn electron is accelerated from rest by a uniform field of magnitude 500000 N/C. a) How long does it take to reach 0.13 c, where c 3 x 10° m/s is the speed of light? ns b) How far does it travel in this time? c) What is its final kinetic energy? х10-16 тarrow_forward
- Consider two protons trapped on the same geomagnetic field line. One proton has kinetic energy 10 eV and the other has kinetic energy of 10 keV. Which statement about the magnetic field strength at their respective mirror points is correct? A. B10 eV < B10 keV B. B10 eV > B10 keV C. B10 eV = B10 keV D. Not enough information is givenarrow_forwardA particle with mass 1,67x10-3 kg and charge of +1.32x10-8 C has, at a given instant, a velocity of 2.90x10 m/s along the +-axis, as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 45.0° C X Part A What is the magnitude of the particle's acceleration produced by a magnetic field of magnitude 1.19 T in the -y plane, directed at an angle of 45.0" counterclockwise from the +-axis? Express your answer with the appropriate units to three significant figures. 0.178 m Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Part B ? * Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining +-direction -a-direction What is the direction of the particle's acceleration?arrow_forwardWhat is the maximum force on a rod with a 0.100 µC charge that you pass between the poles of a 1.79 T strength permanent magnet at a speed of 3.12 m/s? Narrow_forward
- A particle with charge q and and speed venters a region of magnetic field B1 and is deflected from its path into a region with field B2. It enters the second region moving vertically and exits horizontally. a) Draw a sketch of the path of the particle. b)The particle exits the second region at a height d, measured from the interface of the two regions. What is the mass of the particle?arrow_forwardA particle with charge 0.350 C is initially traveling at 90.0 m/s along the +y-direction and encounters a magnetic field of 1.30x10-2 T along the +x-direction. Part A What is the magnitude of the force on the charge? n ΑΣφ ? F = N Submit Request Answer Part B What is the direction of the force? O +x direction -x direction +y direction O -y direction +z direction O -z direction O O O O O Carrow_forwardAt a particular instant, a proton, far from all other objects, is located at the origin. The proton is traveling with velocity (-8 × 106, 0, 0)m/s. Consider the electric and magnetic fields at observation point (8 × 10-¹⁰,5 × 10-¹0,0)m caused by this proton. What is the electric field at the observation point? 1.37E9 1.37×10⁹ 9 1.37E9 X 1.37×10⁹ 9 0 0arrow_forward
- A cyclotron (figure) designed to accelerate protons has an outer radius of 0.333 m. The protons are emitted nearly at rest from a source at the center and are accelerated through 572 V each time they cross the gap between the dees. The dees are between the poles of an electromagnet where the field is 0.720 T. The black, dashed, curved lines Alternating AV represent the path of the particles. -Dg After being accelerated, the particles exit here. -North pole of magnet (a) Find the cyclotron frequency for the protons in this cyclotron. 1.04e33 x rad/s (b) Find the speed at which protons exit the cyclotron. m/s (c) Find their maximum kinetic energy. ev (d) How many revolutions does a proton make in the cyclotron? revolutions (e) For what time interval does the proton accelerate? awranca Barke kay Nationallabarrow_forwardA 68.0-cm-diameter cyclotron uses a 450 V oscillating potential difference between the dees. Part A What is the maximum kinetic energy of a proton if the magnetic field strength is 0.740 T? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Value Submit Part B μA Submit Units Request Answer IV—| ΑΣΦ 3 How many revolutions does the proton make before leaving the cyclotron? ? Request Answer ?arrow_forwardAn electron encounters an E and B fields.B field is given by B = 0.1 j T.Electron experiences a force F = (9.6 x 10^-14 i – 9.6 x 10^-14 k)Find the electric field encountered by the electron. The velocity of the electron isv = 5 x 10^6 i m/s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON