
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
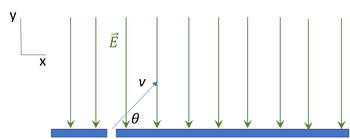
A proton (q=e= 1.602x10-19 C, m=1.67x10-27 kg) goes through a small hole in a negatively charged metal plate with an initial velocity of v 4.59x105 m/s at =11 degrees above the horizontal. The field above the plate has a magnitude of E= 3.42x103 N/C.
a) What is the acceleration of the proton?
b) How much time does it take from going through the small whole til it hits the plate?
c) How far in meters will the proton travel horizontally before it hits the plate?
Transcribed Image Text:T
X
Ꮎ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An electron has an initial velocity of 10.0 × 106 m/s in a uniform 3.00 x 105 N/C strength electric field. The field accelerates the electron in the direction opposite to its initial velocity. (a) What is the direction of the electric field? same direction as the electron's initial velocity V (b) How far does the electron travel before coming to rest? m (c) How long does it take the electron to come to rest? S (d) What is the electron's speed when it returns to its starting point? m/sarrow_forwardAn electron with a speed of 6.19 × 108 cm/s in the positive direction of an x axis enters an electric field of magnitude 1.23 × 10³ N/C, traveling along a field line in the direction that retards its motion. (a) How far will the electron travel in the field before stopping momentarily, and (b) how much time will have elapsed? (c) If the region containing the electric field is 5.29 mm long (too short for the electron to stop within it), what fraction of the electron's initial kinetic energy will be lost in that region? (a) Number (b) Number (c) Number 0.08868 2.9E-8 M Units Units m S Units This answer has no unitsarrow_forwardAn electron is placed in a uniform electric field of 32nN/C directed north created by two horizontal parallel plates that are 131fm apart. The electron accelerates from rest, starting at the negative plate. What is the net force and acceleration acting on the electron? How long did it take the electron to get from one side of the plate to the other?arrow_forward
- s In the microscopic view of electrical conduction in a copper wire, electrons are accelerated by an electricfield and then collide with metal atoms after traveling about3.9 * 10-8m. If an electron begins from rest and is accelerated bya field of 0.065 N>C, what is its speed when it collides with a metalatom?arrow_forwardInside a vacuum tube, an electron is in the presence of a uniform electric field with a magnitude of 320 N/C. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the electron (in m/s2)? (b) The electron is initially at rest. What is its speed (in m/s) after 1.10 ✕ 10−8 s?arrow_forwardThe positive and negative plates of a parallel-plate capacitor have an area of 1.60 cm by 1.60 cm. Their surface charge densities are +1.00×10-6 C/m2and -1.00×10-6 C/m2, respectively. A proton moving parallel to the plates enters the middle of the space between them at a speed of 2.65×106 m/s. Assuming the field outside the capacitor is 0 and the field inside is uniform, how far to the side will the proton's path have deviated when it gets to the far end of the capacitor?arrow_forward
- Inside a vacuum tube, an electron is in the presence of a uniform electric field with a magnitude of 293 N/C. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the electron (in m/s²)? m/s² 4.0 (b) The electron is initially at rest. What is its speed (in m/s) after 1.05 x 10-8 s? 4.0 m/sarrow_forwardA particle (m = 70 mg, q = -5.0 µC) %3D moves in a uniform electric field of 60 kN/C in the positive x-direction. At t = 0, the particle is moving 30 m/s in the positive x-direction and is passing through the origin. Determine the maximum distance beyond x = 0 the particle travels in the positive x- direction. Select one: A. 315.0 m B. 210.0 m C. 52.5 m D. 105.0 marrow_forwardAir breaks down (loses its insulating quality) and sparking results if the field strength is increased to about 3.0 x 106 N/C. a) What acceleration does an electron experience in such a field (me=9.11x10’31kg)? (b) if the electron starts from rest, in what distance does it acquire a speed equal to 10% of the speed of light (3x107 m/s)?arrow_forward
- An electron is traveling through a uniform electric field. The field is constant and given by E=(2.00×10−11N/C) i^− (1.20×10−11N/C) j^. At t=0 , the electron is at the origin and traveling in the x direction with a speed of 2.20 m/s. Part A) What is its position 2.50 s later? x= ? (in m) Part B) y=?arrow_forward02arrow_forwardAn electron with a speed of 5.00E8 cm/s enters an electric eld of magnitude 1.00E3 N/C, traveling along a field line in the direction that retards its motion. (a) How far will the electron travel in the eld before stopping momentarily? (b) How much time will have elapsed? (c) If the region containing the electric eld is 8.00 mm long (too short for the electron to stop within it), what fraction of the electron's initial kinetic energy will be lost in that region?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON