Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:on
SP,
le
N₁
in
e
0
W
-d
T
to
S
3)
b
ne
R
A
r
NI
5
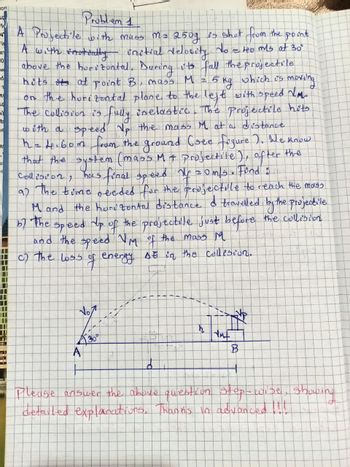
Problem 1
A Projectile with muss ms 250g is shot from the point
A with sooteatly initial velocity. No = 40 mls at 30°
above the horizontal. During its fall the projectile
hits its at point B, mass M 2 2 5 kg
which is
moving
on the horizontal plane to the left with speed NM.
The collision is fully inelastic. The projectile hits
with a speed Up the mass M. at a distance
h = 1.60m from the ground (see figure ). We know
that the system (mass M + projectile), after the
Collision, has final speed My = 0m/s. Find' :
as the time needed for the projectile to reach the mass
M and the horizontal distance & travelled by the projectile
by the speed up of the projectile just before the collision.
and the speed VM of the mass M
c) the loss
SE in the collision.
의
energy
2
30°
A
#
d
54
A
AMF
B
H
Please answer the above question step-wise, showing
detailed explanations. Thanks in advanced !!!
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 15 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a frictionless track as shown in the figure below. A block of mass m, = 4.40 kg is released from O. It makes a head-on elastic collision at ® with a block of mass m, = 13.5 kg that is initially at rest. Calculate the maximum height to which m, rises after the collision. m (A) 5.00 marrow_forwardThe figure shows a two-ended "rocket" that is initially stationary on a frictionless floor, with its center at the origin of an x axis. The rocket consists of a central block C (of mass M-7.90 kg) and blocks Land R (each of mass m - 2.60 kg) on the left and right sides. Small explosions can shoot either of the side blocks away from block C and along the x axis. Here is the sequence: (1) At time t-0, block Lis shot to the left with a speed of 3.40 m/s relative to the velocity that the explosion gives the rest of the rocket. (2) Next, at time t - 0.80 s, block R is shot to the right with a speed of 3.40 m/s relative to the velocity that block C then has (after the second explosion). At t - 2.70 s, what are (a) the velocity of block C (including sign) and (b) the position of its center? (a) Number i -0.172 (b) Number 0.21 Units Units m/s m C 0 Rarrow_forwarda particle of mass .260kg moves head on with a velocity .534x+.374y m/s toward a second particle of mass .486 kg placed on a smooth horizontal table. here x and y are unit vectors along the x and y axis. the collison is completely inelastic. the energy lost in this collision is?arrow_forward
- A bullet of mass m=7.500 [g] is fired horizontally with a speed v=549 [m/s] into the bob of a ballisticpendulum of mass M=1.20 [kg]. Find the maximum height h attained by the bob if the bullet passesthrough the bob and emerges with speed v/2.arrow_forwardThree carts of masses m, = 5.50 kg, m, = 9.00 kg, and m, = 3.00 kg move on a frictionless, horizontal track with speeds of v, = 4.50 m/s to th right, v, = 3.00 m/s to the right, and v, = 5.00 m/s to the left, as shown below. Velcro couplers make the carts stick together after colliding. m2 my (a) Find the final velocity of the train of three carts. m/s magnitude ---Select--- direction (b) Does your answer require that all the carts collide and stick together at the same moment? Yes No What if they collide in a different order?arrow_forwardA 5.0 kg ball is rolling north at 2.50 m/s when it collides with a 6.0 kg ball which isinitially at rest. Given that the collision is perfectly inelastic, calculate the final velocitiesof both balls.arrow_forward
- Consider a frictionless track as shown in the figure below. A block of mass m, = 5.55 kg is released from O. It makes a head-on elastic collision at ® with a block of mass m, = 19.0 kg that is initially at rest. Calculate the maximum height to which m, rises after the collision. A 5.00 marrow_forwardA bumper cap "A" (mass of A = 140kg) with a velocity of 15 km/hr hits a another car "B" (mass of B = 160kg) which was immobile before impact. The collision is perfectly elastic & the frictions are considered negligible. Calculate the time at which the bumper cars are 2m apart from each other after the collisionarrow_forwardA 0.400 kg hammer is moving horizontally at 5.00 m/s when it strikes a nail and comes to rest after driving it 1.00 cm into a board. (a) Calculate the duration of the impact. (b) What was the average force exerted on the nail?arrow_forward
- ? An object with total mass mtotal = 15 kg is sitting at rest when it explodes into three pieces. One piece with mass m1 = 4.8 kg moves up and to the left at an angle of 0, = 24° above the -x axis with a speed of v, = 28.3 m/s. A second piece with mass m, = 5.2 kg moves down and to the right an angle of 02 = 29° to the right of the -y axis at a speed of v2 = 21.5 m/s.arrow_forwardA puck of mass miis moving along a frictionless table at speed viin the +x- direction when it is hit simultaneously by 2lumps of clay, each of mass m2. Both lumps are traveling at a speed of v2when they hit the puck. One is traveling in the -x-direction, while the other one is dropped from above the table in the -y-direction. The puck and lumps of clay stick together. What is the speed of the puck and clay after the collision? Express your answer in terms of mim2v1and v2only. HINT: Write down the initial momentum of the puck m1. In which direction(s) is momentum conserved(i.e. in which direction(s) is there no net external force? Keep in mind that the table can provide an external normal force).Add the momenta of the lump(s) of clay for which momentum is conserved to your initial momentum. At the end of the day, the puck and both lumps of clay stick together so the final momentum is pf=(m1+m2+m2)vf. Set the initial and final momenta equal to each other and solve forvf.arrow_forwardProblem 8 A 1D perfectly inelastic collision occurs between two masses m and M. If the mass m is initially moving right at a speed of vo and the other mass it at rest, what is the ratio of the total kinetic energy after the collision to the original kinetic energy?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios