
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A pole is attached at one end to a hinge on a wall and on the other end with
a cable that goes from the end of the pole to the wall. The pole is uniform
density and its mass is 12.3 kg. The pole makes an angle of 53° with the wall
and the cable makes an angle of 32° with the wall.
(a) Draw a force diagram for the forces on the pole. Clearly label the forces.
(b) Using the forces on the pole, write out the equations for static equilibrium. (This should be in variables, do not solve.)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
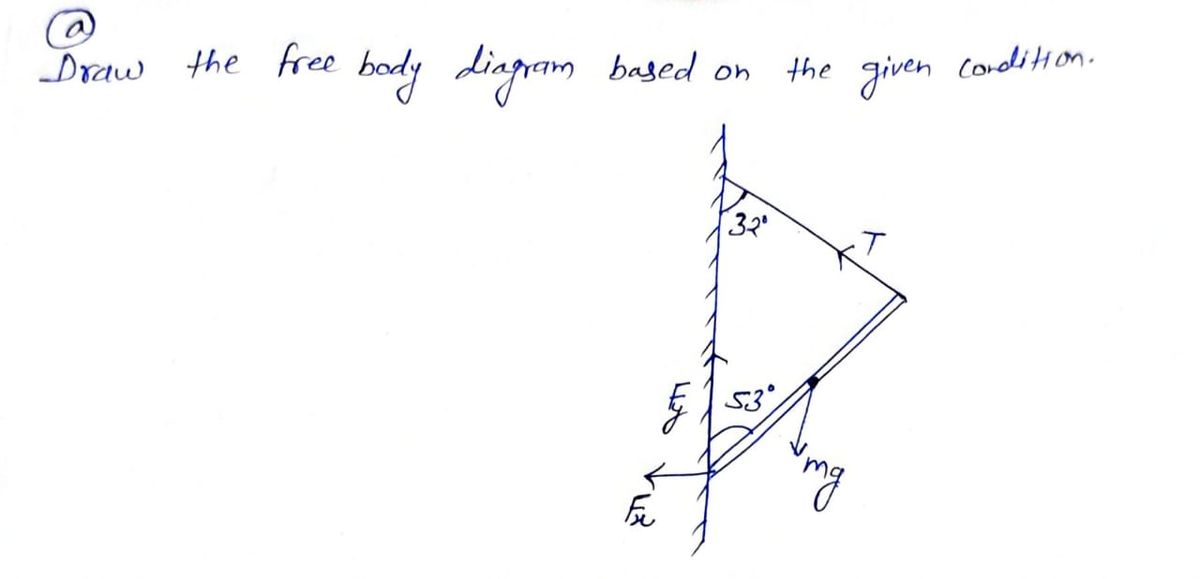
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 8 000-N shark is supported by a rope attached to a 5.00-m rod that can pivot at the base. 20.0° 60.0° (a) Calculate the tension in the cable between the rod and the wall, assuming the cable is holding the system in the position shown in the figure. (Give you answer to three significant digits.) N (b) Find the horizontal force exerted on the base of the rod. magnitude direction to the right N (c) Find the vertical force exerted on the base of the rod. Ignore the weight of the rod. magnitude direction upwards Narrow_forwardA uniform ladder of mass (m = 13.5 kg) and length (L) leans against a frictionless wall, see figure. If the angle θ = 56.0°, find the static friction force between the ladder and the floor when a 95.0-kg person stands half way up the ladder?arrow_forwardTwo individual apply force to opposite sides of a frictionless swinging door. If A applies a 30 N force at a 40° angle from the door’s high and B applies force a 90° angle 0.38 m from the door’s hinge. What amount of force is applied by B if the door remains in a static position?arrow_forward
- The 20kg flowerpot is supported at A by the three cords.(a) Determine the magnitude of the force acting in cord AB for equilibrium. (Express your answer using three significant figures and in N)(b) Determine the magnitude of force acting in cord AC for equilibrium. (Express your answer using three significant figures and in N)(c) Determine the magnitude of force acting in cord AD for equilibrium. (Express your answer using three significant figures and in N)arrow_forwardA 14.0 m uniform ladder weighing 480N rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes a 61.0°-angle with the horizontal. (a) Find the horizontal and vertical forces (in N) the ground exerts on the base of the ladder when an 830-N firefighter has climbed 4.10 m along the ladder from the bottom. horizontal force magnitude 483 It may be helpful to think first about the force the wall exerts on the ladder. How is this related to the force that the ground exerts on the ladder?N direction towards the wall vertical force magnitude 1310 direction up (b) If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when the firefighter is 9.30 m from the bottom, what is the coefficient of static friction between ladder and ground? 0.604 It may be helpful to think first about the force the wall exerts on the ladder. How is this related to the force that the ground exerts on the ladder? (c) What If? If oil is spilled on the ground, causing the coefficient of static friction to drop to half the value found…arrow_forwardSuppose a horse leans against a wall as in the figure below. (a) F₁ wall 1.2 m CG W 0.35 m (b) 1.4 m Calculate the force exerted on the wall assuming that force is horizontal and using the data in the schematic representation of the situation. Note that the force exerted on the wall is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force exerted on the horse, keeping it in equilibrium. The total mass of the horse and rider is 800 kg. Take the data to be accurate to three digits.arrow_forward
- You stand near the end of a uniform diving board a distance d from support 2 (as shown in the picture below. Your mass is m and the distance between the for of supports is a. Create an extended-body force diagram and use it to find the forces (magnitude and direction) that supports 1 and 2 exert on the board (you can neglect the force Earth exerts on the board itself).arrow_forwardThe uniform plank ABC weighs 400 N. It is supported by a pin at A and a cable that runs aroundthe pulley D. Determine the tension in the cable and the components of the pin reaction at A. Note thatthe tension in the cable is constantarrow_forwardb) Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force acting on the hing 3. A uniform 4.0 m long beam with a mass of 15 kg rests on a pivot at one end and is kept horizontal by a cable at the other end. The beam is supporting a 25 kg mass as shown. What is the tension in the cable? pluct 15 kg beam 2.5m - Fird ferce or support) сп вест of 25 kg -1.5 m 55⁰ 55° weight of beam = middle weight of dhject = pa te middle onarrow_forward
- One end of a uniform beam of length L=3mandweight 185 Nis connected to a vertical wall with a cable. The other end is connected to a hinge. The cable makes an angle of 30 degrees with the beam. The cable can withstand a mnaximum tension of 427.0 N. A block of weight 204.0 N is placed on the beam at a distance xWhat is the maximum possible distance xbefore the cable breaks? Actiarrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forwardA uniform drawbridge must be held at a 37° angle abovethe horizontal to allow ships to pass underneath. The drawbridge weighs45,000 N and is 14.0 m long. A cable is connected 3.5 m from thehinge where the bridge pivots (measured along the bridge) and pullshorizontally on the bridge to hold it in place. What is the tension in the cable?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON