
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
can u also add a free body diagram if applicable?
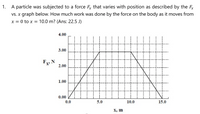
Transcribed Image Text:1. A particle was subjected to a force F, that varies with position as described by the F
vs. x graph below. How much work was done by the force on the body as it moves from
x = 0 to x = 10.0 m? (Ans: 22.5 J)
4.00
3.00
Fy N
2.00
1.00
0.00
0.0
5.0
10.0
15.0
X, m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need help with this question. Can you draw a simple free body diagram if possible too? I will rate thank you!arrow_forwardProblem 4: A ball of mass m is connected to two rubber bands of length L, cach under temsion T, as shown in the Figure. Assume the tension does not change. (a) The ball of mass m is in equilibrium. Draw a free-body diagram on m. (b) Since the ball of mass m is in equilibrium, Enet y = 0. Use Fnet.y=0 to find the equilibrium position for the ball yo. Hint: sin 0=yo/L, Answer: yo = mgL/(2T'). |Yo L. T. L т (c) The ball of mass m is now displaced slightly from equilibrium, as shown in the figure below. Draw a free-body diagram on m. (d) Use Newton's 2nd Law: Fnet,y = ma = -m to show that the motion of m satisfies the SHM differential equation + w²u = 0, where u = y – Yo and w = since the downward gravitational force on the ball is larger than the two upward tension forces on the ball. Hint: sin 0 = y/L. Also, from part (b), yo = mgL/(2T). We can rewrite this expression as mg = 2T(yo/L). Use this expression to substitute for mg in Newton's 2nd Law: Fnet.y = -ma = -my | 2T. For this problem…arrow_forwarda 12.0 kg box is sitting motionless on a plane, which is tilted to an angle of 30 degrees. what must the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction between the box and the surface of the plane be, so that the box does not move? include a system diagram and a FBD in your solution,arrow_forward
- Modified from the AP College Board Engineers are tasked with designing a new solar system themed roller coaster ride. The track starts at Point P, at the top of a sphere with radius R (representing Jupiter). The track goes down to ground level, then to Point Q, the top of a sphere of radius r (representing Neptune) and then back to the ground level. Ignore air resistance, and assume friction between the cart and the track is negligible Jupiter Radius R Neptune radius rarrow_forwardB of mass Car A of mass m is driving with a speed 2v on a road with radius of curvature R. Car 2m is driving with a speed v on the same road. Assume that the only force in the normal direction is the force of friction. By what factor does the required force of friction vary from car A to car B so that the cars do ot slide out?arrow_forwardTwo boxes, as shown below, are sliding along a floor after being given an initial speed u to the right. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the bottom box and the floor is µfloor. The maximum coefficient of static friction between the boxes, box, is 0.28. 2 m 4 m Determine the maximum value of floor that will allow the boxes to stop without the top box slipping with respect to the bottom box.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON