
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A particle passes through a mass spectrometer as illustrated in the figure below. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector has a magnitude of 8020 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.0918 T. In the deflection chamber the particle strikes a photographic plate 58.0 cm removed from its exit point after traveling in a semicircle.
a) What is the mass-to-charge ratio of the particle?
b) What is the mass of the particle if it is doubly ionized?
c) What is its identity, assuming it's an element? (Enter the name of an element.)
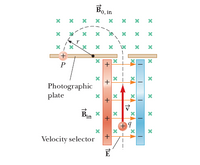
Transcribed Image Text:Bo,in
х х х х
+
P
Photographic
plate
+
Bin
Velocity selector
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) A velocity selector consists of electric and magnetic fields described by the expressions E = Ek and B = Bj, with B = 24.0 mT. Find the value of E (in kV/m) such that a 780 eV electron moving in the negative x-direction is undeflected. 3.97e24 How do you determine the speed of the electron if you know its kinetic energy? kV/m (b) What If? For the value of E found in part (a), what would the kinetic energy of a proton have to be (in MeV) for it to move undeflected in the negative x-direction? MeVarrow_forwardDetermine the velocity of a beam of electrons that goes un-deflected when moving perpendicular to an electric and a magnetic field. E and B are also perpendicular to each other and have magnitudes 7.7 x103 V/m and 7.5x10-3T, respectively.arrow_forward-25 1.58 x 10 A phosphate molecule PO of mass m = difference |AV| = 4.35 V and enters the mass spectrometer with magnetic field of magnitude |B| = 0.090 T. The particle then follows a semi-circular path shown in the picture before kg is accelerated across the potential reaching the detector located to the left of its entry point. В d Δν a) Sketch the described situation (you can start with the figure shown in the problem) CLEARLY indicating the direction of the magnetic field inside the mass spectrometer b) Determine the speed of the particle as it enters the region of magnetic field. c) Determine the distance between the entry point of the particle and the detector.arrow_forward
- A proton travels through a 0.75 T magnetic field in a circle with a radius of 0.30 m. What is the momentum of this proton?arrow_forwardConsider the mass spectrometer shown schematically in the figure below. The magnitude of the electric field between the plates of the velocity selector is 2.60 x 10³ V/m, and the magnetic field in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber has a magnitude of 0.0400 T. Calculate the radius of the path for a singly charged ion having a mass m = 1.82 x 10-26 kg. Bo, in P m Detector array *** xx x x x xxxx x Velocity selector + x x x₂ x² x² x/ xarrow_forward3) Recall that we can analyze the nature of particles with a velocity selector and mass spectrometer. Suppose we know that the charge of the particle we're experimenting with is that of an electron but we don't know their speed and we don't know their mass. a) The velocity selector is constructed to have a magnetic field of 0.157 pointing into the paper plane and an electric field of 70N/C pointing downward. What is the speed of negatively charged particles if they don't experience any deflection? b) Suppose that those particles that are not deflected then enter a magnetic field of 37 pointing into the plane (no electric field). If we measure a diameter of the circular orbit in this magnet field of 1cm what is the mass of the particle?arrow_forward
- wrongarrow_forwardA particle passes through a mass spectrometer as illustrated in the figure below. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector has a magnitude of 8060 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.0920 T. In the deflection chamber the particle strikes a photographic plate 39.6 cm removed from its exit point after traveling in a semicircle. The diagram depicts a velocity selector. The plane of the page is filled with symmetrically arranged crosses labeled vector B0, in above a horizontal plate, and vector Bin below the horizontal plate. Below the horizontal plate, two vertical plates are placed parallel to each other in the right position of the field. The left plate is positively charged and the right plate is negatively charged. The electric field vector E points from the positive plate to the right toward the negative plate. A positively charged particle of charge q and velocity vector v pointing upward…arrow_forwardA particle passes through a mass spectrometer as illustrated in the figure below. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector has a magnitude of 7930 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.0913 T. In the deflection chamber the particle strikes a photographic plate 11.9 cm removed from its exit point after traveling in a semicircle. '0, in Photographic plate Bin x + Velocity selector E (a) What is the mass-to-charge ratio of the particle? kg/C (b) What is the mass of the particle if it is doubly ionized? kg (c) What is its identity, assuming it's an element? (Enter the name of an element.) X- 1x +arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON