
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
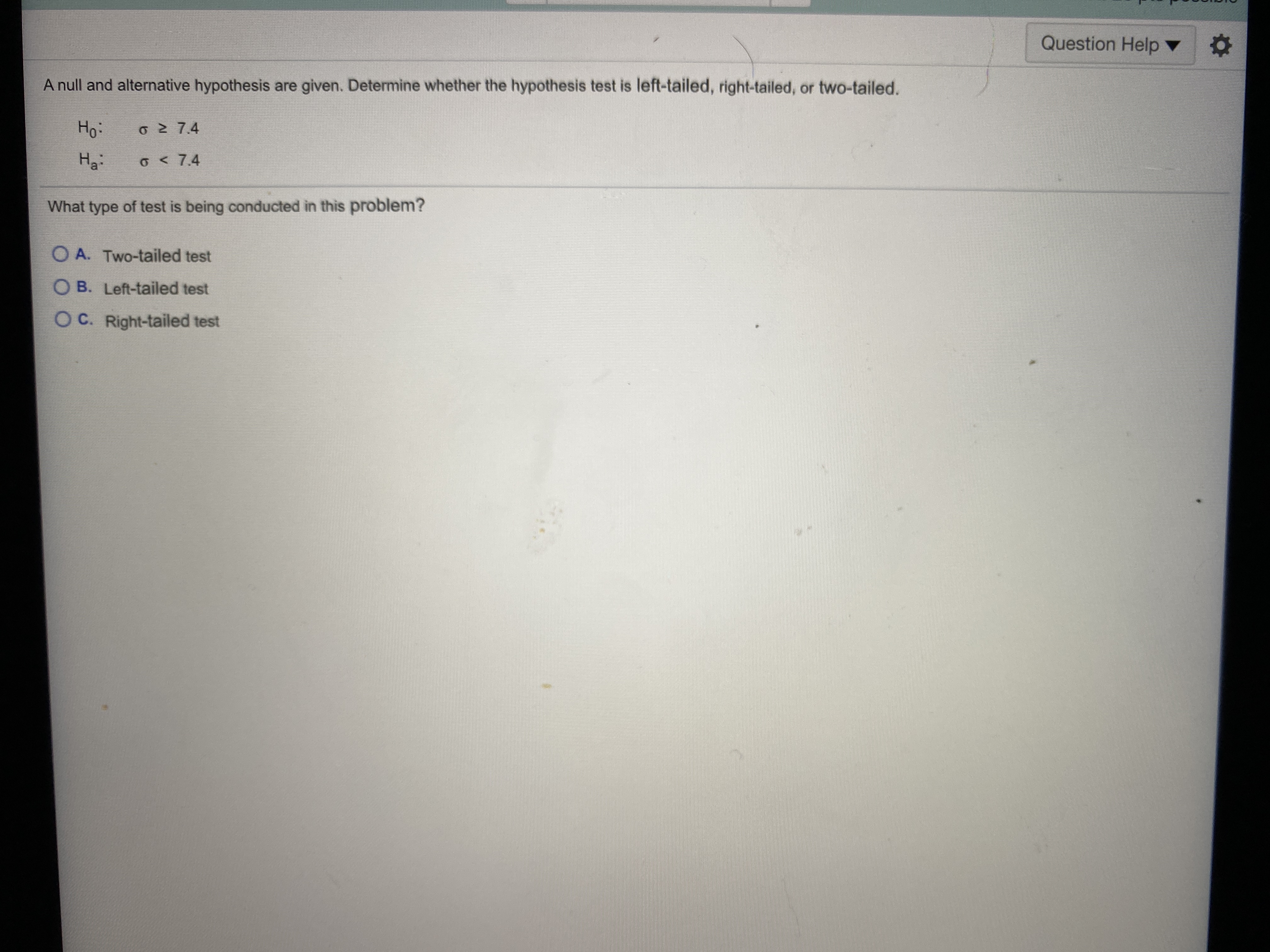
Transcribed Image Text:A null and alternative hypothesis are given. De
Ho:
o 2 7.4
O < 7.4
What type of test is being conducted in this pr
O A. Two-tailed test
O B. Left-tailed test
O C. Right-tailed test
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- he population mean and standard deviation are given bel robability. or a sample of n = 38, find the probability of a sample me or the given sample, the probability of a sample mean be Round to four decimal places as needed.) Would the given sample mean be considered unusual? DA. The sample mean would be considered unusual b- D B. The sample mean would be considered unusual b DC. The sample mean would not be considered unusu D. The sample mean would not be considered unusuarrow_forwardCan I get some help with #19??arrow_forwardE and f plsarrow_forward
- 29arrow_forwardHelp with incorrect and blank ones pleasearrow_forwardA coin-operated drink machine was designed to discharge a mean of 9 ounces of coffee per cup. Suppose that we want to carry out a hypothesis test to see if the true mean discharge differs from 9. State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H, that we would use for this test. Ho: 0 H1: 0 OsO O>o O20 ?arrow_forward
- If your null and alternative hypothesis are:�0:�=0.77�1:�≠0.77Then the test is: left tailed right tailed two tailedarrow_forwardSuppose there is a claim that a certain population has a mean, u, that is equal to 6. You want to test this claim. To do so, you collect a large random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test at the 0.10 level of significance. To start this test, you write the null hypothesis, H, and the alternative hypothesis, H, as follows. 国 Hoi u=6 Hi u#6 An Suppose you also know the following information. The value of the test statistic based on the sample is 1.845 (rounded to 3 decimal places). The p-value is 0.065 (rounded to 3 decimal places). (a) Complete the steps below for this hypothesis test. Normal Distribution Step 1: Select one-tailed or two-tailed. o One-tailed o Two-tailed 0.3 Step 2: Enter the test statistic. (Round to 3 decimal places.) Step 3: Shade the area represented by the p- value. (b) Based on your answer to part (a), which statement below is true? o Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. Since…arrow_forwardYou are conducting a multinomial hypothesis test (a 0.05) for the claim that all 5 categories are equally Likely to be selected. Complete the table. Observed Expected Frequency Frequency Category A 11 8 D 25 E 19 Report all answers accurate to three decimal places. But retain unrounded numbers for future calculations. What is the chi-square test-statistic for this data? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places, and remember to use the unrounded Pearson residuals in your calculations.) What are the degrees of freedom for this test? d.f.= What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... O less than (or equal to) a O greater than a This test statistic leads to a decision to... O reject the null O accept the null O fail to reject the nullarrow_forward
- Answer all A, B, C questionsarrow_forwardA null and alternative hypothesis are given. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Ho: H₂: O O ab What type of test is being conducted in this problem? OA. Two-tailed test OB. Right-tailed test OC. Left-tailed test O O os 6.5 06.5 esc Statcrunch ! 1 Q 2 W #3 E $ ► 4 R % 45 F T MacBook Pro A ^ 6 Y & 7 U * 0arrow_forwardDetermine the probability of making a Type II error for the following hypothesis test, given that µ = 1039. Ho : µ = 1010 H1 : µ > 1010 For this test, take o = 53, 25, and n = a = 0.08. P(Type II Error) =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman