
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
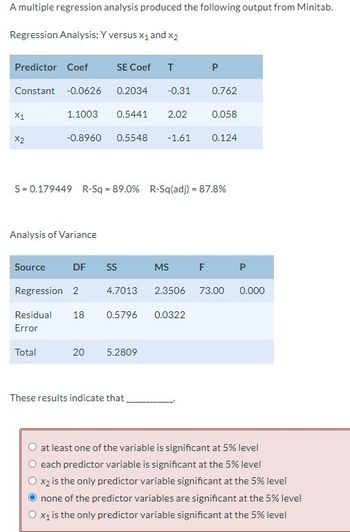
A multiple regression analysis produced the following output from Minitab.
Regression Analysis: Y versus x and x
Predictor Coef SE Coef T P
Constant -0.0626 0.2034 -0.31 0.762
x 1.1003 0.5441 2.02 0.058
x -0.8960 0.5548 -1.61 0.124
S = 0.179449 R-Sq = 89.0% R-Sq(adj) = 87.8%
Analysis of Variance
Source DF SS MS F P
Regression 2 4.7013 2.3506 73.00 0.000
Residual
Error
18 0.5796 0.0322
Total 20 5.2809
These results indicate that____________
Transcribed Image Text:A multiple regression analysis produced the following output from Minitab.
Regression Analysis: Y versus X₁ and X2
Predictor Coef
Constant -0.0626
x1
x2
1.1003
Analysis of Variance
Total
SE Coef T
0.2034
DF
0.5441
Source
Regression 2
Residual 18 0.5796
Error
SS
-0.8960 0.5548 -1.61 0.124
S = 0.179449 R-Sq = 89.0% R-Sq(adj) = 87.8%
4.7013
-0.31
20 5.2809
2.02
These results indicate that
P
MS
0.762
F
0.058
P
2.3506 73.00 0.000
0.0322
at least one of the variable is significant at 5% level
each predictor variable is significant at the 5% level
X₂ is the only predictor variable significant at the 5% level
none of the predictor variables are significant at the 5% level
x₁ is the only predictor variable significant at the 5% level
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are interested in how the number of hours a high school student has to work in an outside job has on their GPA. In your regression you want to control for high school standing and so you run the following regression: GPA = 3.4 0.03 * HrsWrk - 0.7 * Frosh - 0.3 * Soph +0.1 * Junior (1.1) (0.013) (0.23) (0.14) (0.08) where HrsWrk is the number of hours the student works per week, and Frosh, Soph, and Junior are dummy variables for the student's class standing. a) If you include a dummy variable for seniors, that would cause a Hint: type one word in each blank. For the rest of questions, type a number in one decimal place. b) The expected GPA of a Sophomore who works 10 hours per week is c) The expected GPA of a Senior who works 10 hours per week is d) If Dom and Sarah work the same number of hours per week, but Dom is a Junior and Sarah is a Freshman. Dom is expected to have a higher GPA than Sarah. e) Suppose you rewrite the regression as: problem. GPA = ₁HrsWrk + ß2Frosh + B2Soph +…arrow_forwardHelp!arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer along with the calculation. Do not use ChatGPT, otherwise I will give a downvote.arrow_forward
- An analyst working for your firm provided an estimated log-linear demand function based on the natural logarithm of the quantity sold, price, and the average income of consumers. Results are summarized in the following table: SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R R Square Adjusted R Square Standard Error Observations ANOVA Regression Residual Total Intercept LN Price LN Income df 0.968 0.937 0.933 0.003 30 SS MS F 2 0.003637484 0.001818742 202.48598 0.000242516 8.98206E-06 27 29 0.00388 Coefficients Standard Error 0.57 0.00 0.13 0.51 -0.08 0.15 t Stat 0.90 -19.50 1.13 P-value 0.37 0.00 0.27 Significance F 5.55598E-17 Lower 95% -0.65 -0.09 -0.12 How would a 4 percent increase in income impact the demand for your product? Demand would increase by 60 percent. Demand would increase by 0.6 percent. Demand would decrease by 60 percent. Demand would decrease by 0.6 percent. Upper 95% 1.68 -0.07 0.41arrow_forwardq11-arrow_forwardThe data for this question is given in the file 1.Q1.xlsx(see image) and it refers to data for some cities X1 = total overall reported crime rate per 1 million residents X3 = annual police funding in $/resident X7 = % of people 25 years+ with at least 4 years of college (a) Estimate a regression with X1 as the dependent variable and X3 and X7 as the independent variables. (b) Will additional education help to reduce total overall crime (lead to a statistically significant reduction in crime)? Please explain. (c) Will an increase in funding for the police departments help reduce total overall crime (lead to a statistically significant reduction in total overall crime)? Please explain. (d) If you were asked to recommend a policy to reduce crime, then, based only on the above regression results, would you choose to invest in education (local schools) or in additional funding for the police? Please explain.arrow_forward
- The dependent variable in the regression in our cost driver analysis is which of the following? Company sales Total overhead cost for the entire period of time Total overhead cost per montharrow_forwardMita, the manufacturer of copiers, has been spending increasing amounts of money on radio and television advertising in recent years. An analyst employed by Mita wanted to estimate a simple linear regression of the company's annual copier sales versus advertising dollars. Th regression results included SSE = 12593 and SSR = 87663. What is the coefficient of determination for this regression? 0.874 0.935 0.144 0.126arrow_forwardThis exercise refers to the drunk driving panel data regression summarized below. Regression Analysis of the Effect of Drunk Driving Laws on Traffic Deaths Dependent variable: traffic fatility rate (deaths per 10,000). Regressor Beer tax Drinking age 18 Drinking age 19 Drinking age 20 Drinking age Mandatory jail or community service? Average vehicle miles per driver Unemployment rate Real income per capita (logarithm) Years State Effects? Time effects? (1) 0.41* (0.056) 1982-88 no no (2) (3) (4) -0.62** -0.76*** -0.42 (0.39) (0.33) (0.38) 0.023 (0.078) -0.014 (0.084) -0.023 -0.075 (0.053) (0.064) 0.034 -0.109*** (0.058) (0.058) no yes yes no yes Clustered standard errors? yes yes F-Statistics and p-Values Testing Exclusion of Groups of Variables Time effects=0 (5) -0.76** (0.36) 0.041 0.083 (0.111) (0.115) 0.006 0.015 (0.005) (0.011) -0.068* (0.016) 1.66* (0.66) 1982-88 1982-88 1982-88 1982-88 yes yes yes yes yes yes (6) -0.46 (0.39) -0.004 (0.022) 0.043 (0.101) 0.007 (0.005) -0.064*…arrow_forward
- In the regression equation, what is B0? Group of answer choices the population slope the sample y-intercept the sample slope the population y-interceptarrow_forwardAn example of a cubic regression model is Yi= 30 + B1X + 32x2 + 33x³ + ui Yi = 30 + B1X + 32x² + ui. Yi = 30 + ß1ln(X) + ui Yi= 30 + 31X + B2Y2 + ui.arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Consider the following bivariate linear regression model y = a+3x+u. Suppose that E[u]x] #0 and that z is a valid instrument for r. Knowing that Cov(y, z) = 0.5 and Cov(z, x) = 0.5, the IV estimate of 3 is 1. %3D O True O Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education