
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
4.102 - A mobile support is maintained in rest by a stuck cable in C and by rolls without friction in A e B. For the structure shonw in the picture, determine (a) the traction in the cable and (b) the reactions in A and B.
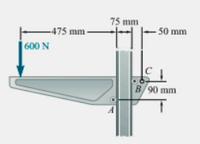
Transcribed Image Text:75 mm
-475 mm
600 N
50 mm
C.
B/90 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Statics-Two Force Members 1. Determine the force required to maintain equilibrium of the pulley system, and the reactions at the ceiling. The 160 kg Box-M is supported by the pulley-rope system shown. a. Determine the force in Newtons in the rope connected to Box M.b. Determine the force F in the ropec. Determine the reaction force at the ceilingarrow_forwardProblem 3.50 Body D is in equilibrium when cable AC suddenly breaks. If B is fixed, does the tension in the inextensible cable BC increase or decrease at the instant of release?arrow_forward4.9 A steel strip of cross-section 5 cm by 1.25 cm is bolted to two copper strips, each of cross-section 5 cm by 0.9375 cm, there being two bolts on the line of pull. Show that, neglecting friction and the deformation of the bolts, a pull applied to the joint will be shared by the bolts in the ratio 3 to 4. Assume that E for steel is twice E for copper.arrow_forward
- Fundamentals of BlUmUT If the diving board has a total weight of 1500 N, determine the reactions on the beam at points A and D. Answers: RA 2318 N (1) Rp = 4602N (1) Problem 4.3 The uniform, horizontal beam shown in Fig. 4.50 is hinged to the ground at point A and supported by a friction- less roller at point D. The distance between points A and B is 1 = 4 m and the distance between points A and D is d = 3 m. A force that makes an angle B= 60° with the horizontal is applied at point B. The magnitude of the applied force is P = 1000 N. The total weight of the beam is W = 400 N. %3D d A By noting that three-quarters of the beam is on the left of the roller support and one-quarter is on the right, calculate the x and y components of reaction forces on the beam at points A and D. Fig. 4.50 Problem 4.3 Answers: Rp = 1421 N (↑) RAX 500N (-) RAy %3D 155N (1) %3D Problem 4.4 The uniform, horizontal beam shown in Fig. 4.51 is hinged to the wall at point A and supported by a cable attached to…arrow_forwardPlease answer all aligned with our honor code.arrow_forwardProblem 5 FN 4.5N K 20 B. 60 7.5N A small ring Pis threaded on a fixed smooth horizontal rod AB. Three horizontal forces of magnitudes 4.5N, 7.5N and FN act on P (see diagram). () Given that these three forces are in equilibrium, find the values of F and 0. (i) It is given instead that the values of F and 0 are 9.5 and 30 respectively, and the acceleration of the ring is 1.5 ms. Find the mass of the ring.arrow_forward
- 4. A garage door (8 ft by 10 ft) weighs 200-lbs is pulled with a constant 25-lb horizontal force to open it as shown. Assume the door rollers (A & B) are frictionless and the door does not rotate or lift off rollers A & B. G is the center of mass of the door. Determine: a. Reactions forces at each roller support (A & B) b. The constant acceleration of the door. c. The time for the door to move 10 feet. Assume it starts from rest. Draw FBD and write governing equations. Show all work. 8 ft 1 ft 5 ft 4 ft -8 ft 10 ft B 3 ft 25 lbsarrow_forward(1) A 50 lb roller, with diameter 10 in, is used to level a tile floor, and is resting directly on the subflooring as shown. If the thickness of the tile is 30° 0.25 in, what is the minimum force P required to pull the roller onto the tiles when it is pulled slowly to the right? Fig. P4.75 and P4.76arrow_forward4.7 A hand truck is used to move a compressed-air cylinder. Knowing that the combined weight of the truck and cylinder is 180 lb. determine (a) the vertical force P that should be applied to the handle to maintain the cylinder in the position shown, (b) the corresponding reaction at each of the two wheels.arrow_forward
- Question 2: 600 N A EO 1 2.5 m B- I 2.5 m D+ 2.5 m 2.5 m A 600-lb horizontal force is applied to pin A of the frame shown. Determine the support reactions and the forces acting in the joints on the two vertical members of the frame.arrow_forward4.142 Do not typearrow_forwardA uniform pole of 2.5m length and 4.0kg mass is suspended horizontally fromthe side of a building where it is affixed with a hinge. It is held in place by awire that extends from the unattached end of the pole at an angle of 53 degrees andattached firmly to the wall. A 10.0kg mass is hanging from the end of the poleas well under the influence of gravity.a. Draw a picture of the situation.b. Draw a comprehensive free body diagram showing the force on the wire,the mass, the pole, and both the horizontal and vertical forces on thehinge.c. Use the hinge as the axis of rotation and balance the vertical torques anddetermine the tension in the wire.d. Use inertial dynamics to find the horizontal and vertical forces on thehinge.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY