Question
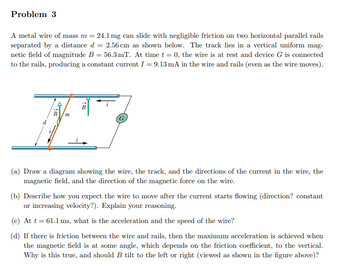
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3
A metal wire of mass m = 24.1 mg can slide with negligible friction on two horizontal parallel rails
separated by a distance d = 2.56 cm as shown below. The track lies in a vertical uniform mag-
netic field of magnitude B = 56.3 mT. At time t = 0, the wire is at rest and device G is connected
to the rails, producing a constant current I = 9.13 mA in the wire and rails (even as the wire moves).
410
150
(a) Draw a diagram showing the wire, the track, and the directions of the current in the wire, the
magnetic field, and the direction of the magnetic force on the wire.
(b) Describe how you expect the wire to move after the current starts flowing (direction? constant
or increasing velocity?). Explain your reasoning.
(c) At t = 61.1 ms, what is the acceleration and the speed of the wire?
(d) If there is friction between the wire and rails, then the maximum acceleration is achieved when
the magnetic field is at some angle, which depends on the friction coefficient, to the vertical.
Why is this true, and should B tilt to the left or right (viewed as shown in the figure above)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A wire with current i = 2.47 A is shown in the figure. Two semi-infinite straight sections, both tangent to the same circle with radius 4.51 cm, are connected by a circular arc that has a central angle 0 and runs along the circumference of the circle. The connecting arc and the two straight sections all lie in the same plane. If B = 0 at the center of the circle, what is 0? 2Connecting arc Number i Unitsarrow_forwardThree long parallel wires, lie perpendicular to this page, as shown in the figure, and carry the same current intensity I = 2 A. The current along the wire A is going into the page. The current along the wire B is also going into the page. The current along the wire C is coming out of the page. Knowing that d = 1 cm, find the direction and magnitude of the net force per unit length acting on the wire B. (Force per unit length just means divide the force by the length.) 2d d A Вarrow_forwardIn the figure below, the two ends of a U-shaped wire of mass m = 7.00 g and length L = 17.0 cm are immersed in mercury (which is a conductor). The wire is in a uniform field of magnitude B = 0.0860 T. A switch (unshown) is rapidly closed and then reopened, sending a pulse of current through the wire, which causes the wire to jump upward. If jump height h = 4.00 m, how much charge was in the pulse? Assume that the duration of the pulse is much less than the time of flight. Hg. Number i X L X Units X Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios