
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A masonry dam 4 m on top, 16 m at the bottom and 24 m high has water 21 m deep on its vertical side. Neglecting hydrostatic uplift, what is the soil pressure at the heel? Assume weight of masonry as 2400 kg/m³.
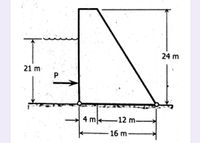
Transcribed Image Text:24 m
21 m
P
4 m
-12 m-
16 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. A dam consists of continuous flat-plat barriers whose masses are negligible. Supporting struts A, B, C and D are placed every 3 metres along the dam structure. A mud sample drawn up to the surface has a density of 1.6 Mg/m³. Determine the force in struts Cand D. All joints can be assumed to be hinged. FRESH WATER 3m B D MUD 3m A 3marrow_forwarda building will have a sitting wall on the north side of the building to allow for seating during outdoor season. the wall will be 1.5 meter tall. what is the minimum width of the wall to ensure that it will not slide or overturning? the soil behind the wall is a sand with Gamma dry= 18.3 kN/m^3 , gamma buoyant =11.5 Kn/m^3 , gamma water= 9.81 kN/m^3 and phi= 36 degrees. the water table is 0.5 m below the ground surface. to enhance the aesthic value of the seating area, the architect has asked that the wall he made of granite ( gamma granite= 25 kN/m^3. Hand written plsarrow_forwardEXAMPLE 10.15 An embankment is shown in Figure 10.29a. Determine the stress increase under the embankment at points A₁ and A₂. 14 m- 5m 11.5 m- 5 m č A₂ At point A₁ -14 m- → 5m → ← 5m 5 m A₂ 11.5 m At point A₂ H=7m ► 5 m 8 A₁ 5m+¦+ H=7m >· 5 m X A₁ 14 m 16.5 m 5 m 14 m EXAMPLE 10.15 An embankment is shown in Figure 10.29a. Determine the stress increase under the embankment at points A, and A₂. 14 m 16.5 m y= 17.5 kN/m³ 5m9 = (2.5 m) x (17.5 - A₂ H A0₂ (1) kN/m³) = 43.75 kN/m2 Aσ₂ (1) y= 17.5 kN/m² B A₁ 1 90 = 122.5 kN/m2 + + T 5m 9=(7 m) x (17.5 kN/m³)= 122.5 kN/m² % = 122.5 kN/m² A₂ 2.5 m →→ ● A0₂ (2) A₁ 14 m- A₂ (2) 9 (4.5 m) x (17.5 kN/m³)= 78.75 kN/m² Aar: (33) A₂ 14 m 9 m ➜ 14 m 1arrow_forward
- Answer in three decimal places pleasearrow_forward50. Whle drlling a well a rock layer Is encountered at 10000 ft. depth with an excess preSsure (overpressure) of 150 psl. An overpressure zone has fluld pressures In excess of the hydrostatic gradlent. If the overburden density Is 2400 kg/m* and the flutd column Is water what Is the effective stress at this depth? a. b. 57.68 MPa 4127.6psl d. 5549.0pslarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning