
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.27 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (φ = 0˚) of magnitude 0.87 T. What is the change ΔΦ in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution?
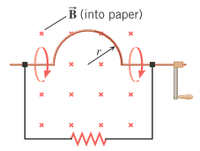
Transcribed Image Text:В into paper)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A conducting loop is in the shape of a square of side ℓ. Current I flows clockwise through the loop. A conducting loop in the shape of a square of edge length ℓ = 480m carries a current I = 10.4 A as in the figure above. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the center of the square. If this conductor is reshaped to form a circular loop and carries the same current, what is the value (magnitude and direction) of the magnetic field at the center?arrow_forwardIn Figure P19.21, the cube is 43.0 cm on each edge. Four straight segments of wire -- ab, bc, cd, and da -- form a closed loop that carries a current of 7 = 5.30 A in the direction shown. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.0200 T is in the positive y-direction. Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on each segment. (Please give the magnitudes to three decimal places.) B Figure P19.21 Segment F(N) Direction ab N Direction bc N -Direction- cd N -Direction- da N Direction- Submit Answerarrow_forwardA single circular loop of wire of radius 0.75 m carries a constant current of 3.0 A. The loop may be rotated about an axis that passes through the centre and lies in the plane of the loop. When the orientation of the normal to the loop with respect to the direction of the magnetic field is 25°, the torque on the coil is 1.8 Nm. What is the magnitude of the uniform magnetic field exerting this torque on the loop?arrow_forward
- A 50 cm × 85 cm rectangular loop of wire is located in a region of uniform magnetic field with a magnitude of B0=2.46 Telsa, and oriented perpendicular to the wire loop. The wire is reshaped into a circular loop of radius r = 43 cm. What is the change in the magnitude of the the magnetic flux through the loop as a result of this change in shape?arrow_forwardA rod of mass 0.720 kg and radius 6.00 cm rests on two parallel rails (see figure below) that are d = 12.0 cm apart and L = 45.0 cm long. The rod carries a current of I = 70.0 A in the direction shown and rolls along the rails without slipping. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.260 T is directed perpendicular to the rod and the rails. If it starts from rest, what is the speed of the rod as it leaves the rails? (Assume that the rod is of uniform density.) m/s L teaarrow_forwardA circular loop of radius 7.7 cm carries a current of 24 A. A flat coil of radius 1.2 cm, having 68 turns and a current of 1.8 A, is concentric with the loop. The plane of the loop is perpendicular to the plane of the coil. Assume the loop's magnetic field is uniform across the coil. What is the magnitude of (a) the magnetic field produced by the loop at its center and (b) the torque on the coil due to the loop? (a) Number Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- An electron moves in a circle of radius r = 6.19 × 10-11 m with a speed 2.47 x 106 m/s. Treat the circular path as a current loop with a constant current equal to the ratio of the electron's charge magnitude to the period of the motion. If the circle lies in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 6.04 mT, what is the maximum possible magnitude of the torque produced on the loop by the field? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA coil consisting of 88 windings of insulated wire is circular in shape with a radius r = 9.5 cm. The magnetic field is uniform throughout the coil and perpendicular to the coil's area, but it is changing with time. The magnitude of the magnetic field is initially 0.45 T and then changes at a constant rate until it has the same magnitude in the opposite direction. This change occurs over a time interval At =0.20 s. What is the magnitude of average emf induced in the coil during this time interval? E = V If instead the magnetic field in the same coil remains constant at B = 0.45 T (in the same direction perpendicular to the coil's area, initially) and the coil itself is then rotated at a constant rate until it has inverted (gone through a rotation of 180°) during a time interval At = 0.10 s, what is the magnitude of the average emf induced in the coil during this time interval?arrow_forwardA coil has 250 turns enclosing an area of 11.8 cm2 . In a physics laboratory experiment, the coil is rotated during the time interval 0.045 s from a position in which the plane of each turn is perpendicular to Earth's magnetic field to one in which the plane of each turn is parallel to the field. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at the lab location is 5.40×10−5 T . What is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through one turn of the coil before it is rotated? What is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through one turn of the coil after it is rotated?arrow_forward
- A circular conductor with r=4cm is in uniform magnetic field B=5.0T that is pointing into the page. There is a clockwise current of 7.0A in the loop. What is the magnitude of torque on the loop along the y-axis which passes through the diameter of the loop?arrow_forwardA loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.12 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (p = 0°) of magnitude 0.73 T. What is the change AO in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution? B (into paper) ΔΦ =arrow_forwardA rod of mass 0.720 kg and radius 6.00 cm rests on two parallel rails (see figure below) that are d = 12.0 cm apart and L = 45.0 cm long. The rod carries a current of I = 36.0 A in the direction shown and rolls along the rails without slipping. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.400 T is directed perpendicular to the rod and the rails. If it starts from rest, what is the speed of the rod as it leaves the rails? (Assume that the rod is of uniform density.) L 2.07 X You appear to have omitted the translational kinetic energy of the rod. m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON