
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
vibrations, show all steps and solutions
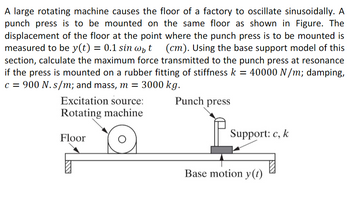
Transcribed Image Text:A large rotating machine causes the floor of a factory to oscillate sinusoidally. A
punch press is to be mounted on the same floor as shown in Figure. The
displacement of the floor at the point where the punch press is to be mounted is
measured to be y(t) = 0.1 sin w₁t (cm). Using the base support model of this
section, calculate the maximum force transmitted to the punch press at resonance
if the press is mounted on a rubber fitting of stiffness k = 40000 N/m; damping,
c = 900 N.s/m; and mass, m = 3000 kg.
Excitation source:
Rotating machine
Punch press
Floor
Support: c, k
Base motion y(t)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The uniform bar shown in the attached figure is pivoted at point O. Its motion is controlled by three springs and a damper as illustrated; find the value of the damping coefficient C, if the damping ratio is to be 0.4. Given the following data Data: k₁-7000 N/m, k₂=8000 N/m, ky 10000 N/m, M = 12 kg, b=0.4 m a=0.2 m J-0.5 Kg.m² Lif ww Bar MJ $0 www.marrow_forwardFind the system's natural frequency shown in the figure with references to x. The block moves downward and the disk has radius r and moment inertia (J.) rotates about the fixed point. Assume the cable is rigid with negligible mass. 24 ww Keg 23kme zmarrow_forwardFigure below shows a rod with mass M = 100 kg, cross section area A = 10 cm². The rod is supported by 4 springs having stiffnesses of k = 1 MN/m. A tip mass with m = 120 kg is attached to the rod. Assume x is the degree of freedom of the equivalent system. The Young's modulus, E, is not known. If the natural frequency of the equivalent mass-spring system is 40 Hz, determine the Young's modulus, E. Assume the length of the rod is L = 5 m. Find the nearest answer. k ww E, A, M k F @www.ww wint L 195 GPa 179 GPa 116 GPa 45 GPa 236 GPa 000 00arrow_forward
- FEAarrow_forwardQuestion in pic.arrow_forwardFind the natural frequency (in Hertz) of the system illustrated in the following figure. Assume the disk is rolling without slipping. K1 = 4 MN/m, K2 = 2K1, M = 165 kg, and R = 0.2 m. Assume the moment of inertia is A K, R. K2 www M No Slip 220.19 Hz 35.04 Hz 25.58 Hz 17.94 Hz 71.49 Hz O 0 O O Oarrow_forward
- Sphere, mass m Find the equivalent stiffness and mass of the system shown in the figure, then find the natural frequency. No slip Bell crank lever, mass moment of inertia Jo 90° 4 k₁ m 00000 x(1)arrow_forwardSphere, mass m 000 Q4: Find the equivalent stiffness and mass of the system shown in the figure, then find the natural frequency. No slip Bell crank lever.- mass moment of inertia Jo 90° k₁ m 00000 TTTTTTT x(t)arrow_forwardSeen in Figure 1, a rotating mass (with mass moment of inertia Id to a fixed wall (on the far left) by a torsional spring (k 1kg* m² and angular position a) is attached 1Nm/rad) and a torsional damper. Consider the spring and damper as concentric and in parallel. Dampers with damping ratios of c = be considered. Att = 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5kg * m²/s will 0, a unit step torque Tin is applied to the rotating mass. A unit step input is a forcing function whose value is 0 from -∞o to some time to and 1 from to to oo. Here, to = 0. Your tasks: k ww + C = la Od A Derive the equation of motion of the rotating mass. Write c as EOM's for the different values of c. Tin 0 Figure 1: Schematic of the mechanical system to model in Problem 1. em, you will solve part B over MA AB Grader Plea LO onment variable. You do not need to write separate ד ו. forarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY