
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
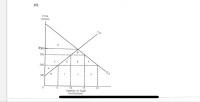

Transcribed Image Text:A) If the U.S. did not trade what price would the good cost? If the world price was $200 what
quantity would the U.S. produce? What quantity would be imported. What is consumer surplus
at the world price? Producer surplus at the world price? Who benefits from the free trade and
who gets hurt?
B) If the U.S. government puts a tariff on the good so now the price is $300 who benefits, who is
hurt? What quantity will U.S. producers now produce? What happens to consumer surplus
from $200 to $300? What does producer surplus do with the price going from $200 to $300?
What does the government gain with the tariff?
C) Who benefits from free trade overall? Who benefits from trade restrictions? Why is a tariff the
most used trade restriction?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure below shows the US domestic supply and demand for CD-ROM drives. The world price is $15 (per million CD-ROM drives). Price ($) 25 15 0 $25 b. $15 $10 3 a. U.S. market C. d. $0 6 9 SU.S. 12 Millions of CD-ROM drives Suppose the US implements a tariff on imports of CD-ROM drives. After the tariff is implemented, the US imports 3 million CD- ROM drives. What is the amount of the tariff? DU.S. Hint: What does it mean/ look like on the graph for the US to import 3 million units? Qarrow_forwardWould the U.S. government gain any advantage from using tariffs or quotas to restrict imports?arrow_forwardYou are watching the nightly news. A political candidate being interviewed says, "I'm for free trade, but it must be fair trade. If our foreign competitors will not raise their environmental regulations, reduce subsidiaries to their export industries, and lower tariffs on their imports of our goods, we should retaliate with tariffs and import quotas on there goes to show them that we won't be played for fools!" A) If a foreign country artificially lowers the cost of production for its producers with lax environmental regulations and direct subsidiaries and then exports the products to us, who gains and who loses in our country, producers or consumers? B) Continuing form part A above, does our country gain or lose? Why? C) If a foreign country subsidizes the production of a good exported to the United States, who bears the burden of their mistaken policy? D) What happens to our overall economic well-being if we restrict trade with a country that subsidizes its export industries?…arrow_forward
- Is it good or bad for American consumers when the United states puts tariffs on imports?arrow_forward3. Two areas, Europe and America, can produce only goods A and B, under constant costs as indicated below. What will be the result of free trade between the two areas? In Europe In America 1 unit of good A 2 hours of labor 3 hours of labor 1 unit of good B 4 hours of labor 5 hours of labor a. Europe will export A and B to America. b. Europe will import A and export B. c. Europe will import B and export A. d. Europe will import A and B from America. e. No trade will take place.arrow_forwardPresident Trump increased tariffs on some goods from China. China retaliated by increasing tariffs on some U.S. goods. If free trade is the ideal, what was President Trump’s goal when increasing tariffs? Do you think this was an effective strategy? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T- shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. The quota on T- shirts causes domestic consumers to A) gain $7 million. B) lose $7 million. C) lose $70 million. D) lose $77 millionarrow_forwardEconomists argue for free trade in import markets because importing goods decreases total surplus. no one is made worse off by importing goods. all consumers and producers benefit from importing goods. O the gains to the U.S. producers outweigh the losses to the U.S. consumers the gains to the U.S. consumers outweigh the losses to the U.S. producersarrow_forwardHome Demand: 90 - 2Pt Foreign Demand: 50 - 4Pt*Home Supply: 30 + 2Pt Foreign Supply: 10 + 2Pt* There are demand and supply functions for good corn for the home country and demand and supply functions for good wheat for the foreign country. Home country as an importer and foreign country as an exporter trade with each other, at zero cost of transportation.A. Find and graph the equilibrium under free trade. What is the world price and thevolume of trade? Also, in the absence of trade, what are the prices that would prevailin home country for corn and in foreign country for wheat?.(Pt = Pt* = Pw -> Pw; world prices)B. Suppose home imposes a specific tariff of 5 on corn imports. Find and graph theeffects of tariff on price of corn in each country, on the quantity of corn supplied anddemanded in each country, on volume of trade? And briefly explain these results inrelation to the effects of the tariff?C. Let the tariff conditions in section (b) be valid. Determine and graph the effect of…arrow_forward
- On the following graph, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus in the Denmark after China's clothing industry expands. Then use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus. Market for Clothing in Denmark Domestic Supply Domestic Demand Consumer Surplus Producer Surplůs New World Price Quantity of Clothing v the Overall, exporting countries the fall in the world price of clothing, and importing countries price change. Price of Clothingarrow_forwardSome economists say the cost of international trade is the loss of American jobs. Do you think this is true? Explain.arrow_forwardTariffs can help or hurt the economy explain the Hawley-Smoot Act with this in mind.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education