
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
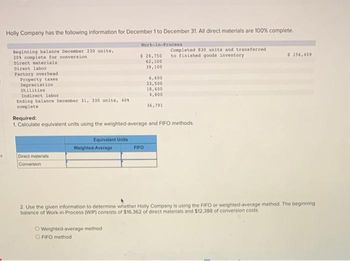
Transcribed Image Text:4
Holly Company has the following information for December 1 to December 31. All direct materials are 100% complete.
Work-in-Process
Beginning balance December 230 units,
20% complete for conversion
Direct materials.
Direct labor
Factory overhead.
Property taxes
Depreciation
Utilities
Indirect labor
Ending balance December 31, 330 units, 40%
complete.
Direct materials
Conversion
Equivalent Units
Weighted Average
$ 28,750
62,100
39,100
Required:
1. Calculate equivalent units using the weighted-average and FIFO methods.
Weighted-average method
O FIFO method
6,600
33,500
FIFO
18,600
4,600
36,791
Completed 830 units and transferred
to finished goods inventory
$ 156,459
2. Use the given information to determine whether Holly Company is using the FIFO or weighted-average method. The beginning
balance of Work-in-Process (WIP) consists of $16,362 of direct materials and $12,388 of conversion costs.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Subject: acountingarrow_forwardWeighted Average Method, FIFO Method, Physical Flow, Equivalent Units Middelton Company manufactures a product that passes through two processes: Fabrication and Assembly. The following information was obtained for the Fabrication Department for October: All materials are added at the beginning of the process. Beginning work in process had 80,500 units, 30 percent complete with respect to conversion costs. Ending work in process had 14,000 units, 40 percent complete with respect to conversion costs. Started in process, 91,000 units. Required: 1. Prepare a physical flow schedule. Middelton Company Physical Flow Schedule Units to account for: Total units to account for Units accounted for: Units completed and transferred out: Total units accounted for 2. Compute equivalent units using the weighted average method. Weighted average method: Equivalent Units Direct Materials Conversion Costs 3.…arrow_forwardAcarrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress Production costs chargeable to the Sanding Department in July in Monty Company are $41,160 for materials, $14,700 for labor, and $12,740 for manufacturing overhead. Equivalent units of production are 29,400 for materials and 19,600 for conversion costs. Compute the unit costs for materials and conversion costs. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25.) Unit costs $ Materials $ Conversion Costsarrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] A manufactured product has the following information for June. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Units manufactured Standard Quantity and Cost 7 pounds @ $8 per pound 3 DLH @ $16 per DLH 3 DLH @ $12 per DLH Actual Results 62,900 pounds @ $8.20 per pound 26,500 hours @ $16.50 per hour 8,900 units $ 325,700 Compute the (1) direct labor rate variance and (2) direct labor efficiency variance. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance. Round "Rate per hour" answers to 2 decimal places.) AH Actual Hours SH Standard Hours Standard Rate AR Actual Rate SR Actual Cost G < Prev 8 of 8 Next Standard Costarrow_forwarda. Prepare a cost of production report for the Cutting Department. If an amount is zero or a blank, enter in "0". For the cost per equivalent unit computations, round your answers to two decimal places. The Cutting Department of Karachi Carpet Company provides the following data for January. Assume that all materials are added at the beginning of the process. Work in process, January 1, 8,200 units, 65% completed $103,894* *Direct materials (8,200 × $10.2) $83,640 Conversion (8,200 × 65% × $3.8) 20,254 $103,894 Materials added during January from Weaving Department, 126,400 units $1,301,920 Direct labor for January 219,708 Factory overhead for January 268,533 Goods finished during January (includes goods in process, January 1), 127,800 units — Work in process, January 31, 6,800 units, 40% completed — Cost of Production Report-Cutting Department For the Month Ended January 31 Unit Information Units charged to production: Number of…arrow_forward
- Weighted Average Method, FIFO Method, Physical Flow, Equivalent Units Middelton Company manufactures a product that passes through two processes: Fabrication and Assembly. The following information was obtained for the Fabrication Department for October: All materials are added at the beginning of the process. Beginning work in process had 125,000 units, 40 percent complete with respect to conversion costs. Ending work in process had 25,000 units, 20 percent complete with respect to conversion costs. Started in process, 175,000 units. Required: Question Content Area 1. Prepare a physical flow schedule. 2. Compute equivalent units using the weighted average method. 3. Compute equivalent units using the FIFO method. 4. Suppose that the cost of direct materials in beginning work in process is $560,000 and that the direct materials cost incurred for October is…arrow_forwardFollowing is a partial production cost report for Mitchell Manufacturing's Canning Department. Equivalent units of production (EUP) Completed and transferred out Ending Work in Process Cost per EUP Cost of beginning work in process Costs added this period Total costs % EUP from part (a) Cost per EUP Multiple Choice $158,400. $175,032. Direct Materials $ 41,800 140,100 $ 181,900 92,000 $ 1.98 per EUP The total direct materials costs transferred out of the Canning department equals: $181,900. $182,160. Units 80,000 12,000 $226,400. Direct Materials Percent Complete 100% 100% EUP 80,000 12,000 92,000 Conversion Percent Complete Conversation $ 61,500 188,500 $ 250,000 88,400 100% 70% $ 2.83 per EUP EUP 80,000 8,400 88,400arrow_forwardWork in Process—Assembly Department Bal., 3,000 units, 35% completed 7,395 To Finished Goods, 69,000 units ? Direct materials, 71,000 units @ $1.8 127,800 Direct labor 100,700 Factory overhead 39,200 Bal., ? units, 40% completed ? Cost per equivalent units of $1.80 for Direct Materials and $2.00 for Conversion Costs. a. Based on the above data, determine the different costs listed below. If required, round your interim calculations to two decimal places. 1. Cost of beginning work in process inventory completed this period $ 2. Cost of units transferred to finished goods during the period $ 3. Cost of ending work in process inventory $ 4. Cost per unit of the completed beginning work in process inventory (Rounded to the nearest cent.) $ b. Did the production costs change from the preceding period?Yes c. Assuming that the direct materials cost per unit did not change from the preceding period, did the conversion costs per equivalent unit…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education