
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
A hollow shaft has an inner diameter of 0.035 m and outer diameter of 0.086 m. Determine
the polar moment of inertia of the hollow shaft. A. 1.512 x 10-⁶ m⁴ B. 1.215 x 10-⁶ m⁴ C. 1.52 x 10-⁶ m⁴ D. 1.125 x 10-⁶m⁴
Please solve the Problem elaborately and Refer Machine Elements and Stresses Equations from the figures or use other shortcut Methods you have or you may Solve both or in more different methods the better ?. Your solution will be use as reference for my Future Board Exam preparation/review/study. Thank you so much dear your work will be appreciated much and rated excellently.
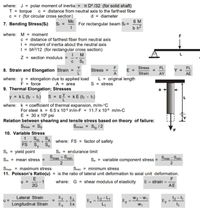
Transcribed Image Text:where: J = polar moment of inertia = T Dª /32 (for solid shaft)
c = distance from neutral axis to the farthest fiber
T = torque
c = r (for circular cross section)
7. Bending Stress(S:) Si =
d = diameter
For rectangular beam S = 6 M
b h?
Mc
where: M = moment
F
c = distance of farthest fiber from neutral axis
| = moment of inertia about the neutral axis
| = bh/12 (for rectangular cross section)
I M
c Sf
L
Z = section modulus
Y
8. Strain and Elongation Strain =
Stress
FL
Stress =
A
E
Strain
FL
Y =
AE
AY
where: y = elongation due to applied load
L = original length
F = force
A = area
S = stress
9. Thermal Elongation; Stresses
y = kL (t2 - t1) S = E! = kE (t2 - t1)
where: k = coeficient of thermal expansion, m/m-°C
For steel k = 6.5 x 10-6 in/in-F = 11.7 x 106 m/m-C
E = 30 x 10° psi
Relation between shearing and tensile stress based on theory of failure:
Samax = Sty /2
Smax = Sty
10. Variable Stress
1 Sm Sa
FS Sy S,
Sy = yield point
where: FS = factor of safety
Sn = endurance limit
Smax + Smin
S. = variable component stress =
Smax - Smin
Sm = mean stress =
2
2
Smax = maximum stress
11. Poisson's Ratio(u) = is the ratio of lateral unit deformation to axial unit deformation.
Smin = minimum stress
E
F
E = strain =-
AE
where: G = shear modulus of elasticity
2G
W2 – W1
Ey
t2 - ty
Lateral Strain
Ey Ez
Ex
L2 -L,
Ex
L1
Ez
Longitudin al Strain
Ex
t,

Transcribed Image Text:V1
Machine Elements
1. Cylinders Rolling in opposite direction:
Á. Tangential speed
B. Relation of diameter and speed
V, = V2 = T D, N, = r D2 N2
DI N1 = D2 N2
Speed of Driver
C. Speed Ratio =
Speed of the Driven
D. Center Distance = R, + R2 =
D, + D2
2. Cylinders Rolling in the same direction
Vi = V2 = n D, N; = n D2 N2
D, N1 = D2 N2
A. Tangential speed
B. Relation of diameter and speed
Speed of Driver
Speed of the Driven
D2 - D1
C. Speed Ratio =
D. Center Distance = R2 -R, =
Stresses
1. Stress (S) = a total resistance that a material offers to an applied load, Ib/in? , kg/cm² , KN/m?
2. Ultimate stress (Su ) - is the stress that would cause failure
3. Yield stress(Sy) - maximum stress without causing deformation
4. Allowable stress(Sal) = Ultimate stress/Factor of Safety
Sy
5. Design stress(Sa) - stress used in determining the size of a member. Sa =
or Sa =
FS
FS
where: FS = factor of safety
1. Tensile Stress (S.)
S =
For solid circular cross-section: A =
A
D2
#0,² -D²)
For hollow circular cross-section: A =
For rectangular cross-section: A = base x height = b x h
Fa
2. Compressive Stress(Sc)S. =
A
3. Shearing Stress(S.)
F
A. For single bolt of rivet needed to join to plates together. S, =
For single rivet: A = t/4 D²
For double riveted joint: A = 2(TT/4 D²)
where:
D
B. Shearing due to punching of hole.
S =
where A = 1 Dt (for punching a hole) A = 4 St (for square hole)
Where: S = length of side of square
C. Pressure needed to punch a hole, F: F = d x t x 80, tons
t = plate thickness
t = thickness, in
where: A = DL
Where: d = hole diameter, in
-Shear area
4. Bearing Stress(Sb)
Sp = Fb IA
a. Based on yield strength FS = Sy / Sall
5. Factor of safety(FS)
b. Based on ultimate strength FS = S,/ Sall
D
6. Torsional Shear Stress(Ss)
Projected Area
D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem #8: For the beam and loading shown below compute the state of stress at point B (components of the 3x3 matrix), report your answer in ksi to two decimal places. 1.5 in 1.5 in B l in F= 5 kip 3 in 1 in 15 in Fx = 4 kip 3 in Fy = 3 kiparrow_forwardA shaft is subjected to a torque of 28 kNm and a maximum bending moment of 25 kNm. The shaft is solid with a diameter of 125 mm. Using the Mohr circle method find the values for the principal stresses and themaximum shear stresses on the shaft i)Construct the Mohr circle on the graph paper provided. ii) Using the Mohr circle method find the values for the principal stresses and the maximum shear stresses on the shaft.iii) Show the orientations of the planes on which the principal stresses act on a rotatedelementarrow_forwardJust Solve a Use Abaqusarrow_forward
- The bar in the attached picture has a thickness of 16mm and a total width of 48mm. The pin has an diameter of 11mm.....arrow_forwardCompute the tensile stress for the rod shown in Fig. 1 at section A-A, the shearing stress across section B, the compressive stress between the pin and the rod, and the compressive stress between the pin and the yoke. Given n = 1 (3 / 4) in., a = (15 / 32) in., e = (27 / 32) in., b = (15 / 16) in., d = (19 / 32) in., f = 1".arrow_forwardPlz don't use chat gptarrow_forward
- For the stresses given with the cube below: 1. Compute the center, radius (R), principal normal stresses (0₁ and 03), max shear stress (Tmax) and draw the Mohr's Circle. 2. Compute the normal and shear stresses when the cube is rotated 20° clockwise from the horizontal plane and draw them on the cube. 3. The yield point stress (σyp) is 6 kPa. Determine if the material will fail under stresses shown using Tresca's Hexagon. вкра акра 6 экра 8 кра экра 4краarrow_forwardPlease help with the stress, mohir circle, etc. Thank youarrow_forwardHandwriting not allow pleasearrow_forward
- Please solve, include the diagrams, and do not copy from other bartleby answers. Handwritten solution is more preferred than typed. A flanged bolt coupling connects two shafts. The bolt circle diameter is 250 mm in which there are 12 bolts. The allowable shear stress is 56 MPa in the shafts and 22 MPa in the bolts. One shaft is hollow with outside diameter of 100 mm, while the other one is solid of diameter 50 mm. Determine the ratio of the outside and inside diameter of the hollow shaft and the bolt diameter so that both shafts and the flanged bolt coupling are having the same strength in torsion.arrow_forwardOne shaft is in torsion as shown below. If the magnitude of shear stress at point A is 345.6 MPa, calculate the magnitude of the shear stress at point B on the same cross-section as point A: MPa. Calculate your answer to 1 decimal place. 40 mm 30 mm Tarrow_forwardPlease help. This problem involves moment of inertia on a cross-section. Thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY