
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
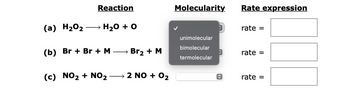
Transcribed Image Text:Reaction
(a) H₂O₂ → H₂O + O
(b) Br+ Br + M
(c) NO₂ + NO₂
→ Br₂ + M
2 NO + 0₂
Molecularity
unimolecular
bimolecular
termolecular
î
Rate expression
rate
rate =
rate =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following proposed reaction mechanism: (1) ClO (aq) + H,O(1) = (2)I (aq) + HCIO(aq) → HIO(aq) + cI (aq) [slow] (3) OH (aq) + HIO(aq) → H,O() + 10 (aq) [fast] HCIO(aq) + OH (aq) [fast] Ignoring the phases of matter, what is the global equation for the mechanism shown here? HCIO + CIO +I + OH → 10' + Cl' + OH " + HCIO O HIO + HCIO + CIO" +I + OH 1O + Cl + OH' + HCIO + HIO + - CIO +l – 10 + Cl O CIO' +I + OH → 10 + Cl' + OH |arrow_forwardThe reaction 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2 NOCl has the following rate law: Rate = k[NO]2 [Cl2]. The initial speed of the reaction was found to be 5.72×10‒6 M/s when the reaction was carried out at 25 °C with initial concentrations of 0.500 M NO and 0.250 M Cl2. What is the value of k?(a) 1.83×10‒4(b) 1.09×104(c) 9.15×10‒5(d) 5.72×10‒6arrow_forwardConsider the following balanced chemical equation: H;O2 (aq) + 3 1 (aq) + 2 H* (aq) (aq) + 2 H20 (I) If the concentration of iodide (I3') decreases from 0.718 M to 0.426 M in the first 15 seconds, what is the rate of reaction? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 0.0195 M/s 0.292 M/s -0.00195 M/s 0.00649 M/s 0.0973 M/sarrow_forward
- Using the information in the table, the value of the rate constant TOP A(g) + B(g) → C(g) + D(g) is [A], (M) 0.100 0.200 0.300 [B], (M) 2.50 Jay 2.50 1.25 Rate (M/s) 0.460 0.920 1.38 A) 4.6 s¹ B) 0.046 s¹ C) 1.84 M¹s¹ D) 115 M²S-1 E) 0.42 s¹arrow_forwardConsider a reaction A + B → C with corresponding rate law rate = k[A]n [B]m If n = 2, m = 1: (d) How will the initial reaction rate change if the initial concentration of A is doubled, without changing the initial concentration of B? (e) How will the initial reaction rate change if the initial concentrations of both A and B are doubled?arrow_forwardThe reaction O₂(g) + 2 NO(g) → 2 NO₂(g) was studied at a certain temperature with the following results: (a) What is the rate law for this reaction? O Ratek [0₂(9)] [NO(g)] O Ratek [0₂(9)]² [NO(g)] O Rate = k [0₂(9)] [NO(g)]² O Ratek [0₂(9)]² [NO(g)]² O Ratek [0₂(9)] [NO(g)]³ O Rate = k [O₂(g)]* [NO(g)] (b) What is the value of the rate constant? Experiment [0₂(9)] (M) 0.0235 0.0235 0.0470 0.0470 [NO(g)] (M) 0.0235 0.0470 0.0235 0.0470 Rate (M/S) 0.158 0.633 0.317 1.27 (c) What is the reaction rate when the concentration of O₂(g) is 0.0318 M and that of NO(g) is 0.0649 M if the temperature is the same as that used to obtain the data shown above?arrow_forward
- Consider the following Potential Energy Diagram for a four-step reaction mechanism. (a) What is the overall balanced equation for the reaction? (b) Does this reaction have a catalyst? Explain how you know. (c) Which step in the above mechanism is the rate-determining step? (d) Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? (e) The rate law equation was determined to be rate = k [NO2] [F2]. Is the proposed mechanism plausible?arrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) Suppose that at a particular moment during the reaction nitric oxide (NO) is reacting at the rate of 0.066 M/s. (a) At what rate is NO2 being formed? (b) At what rate is molecular oxygen reacting?arrow_forward(a) Consider the chlorination of methane, given below: 1 CH4(g) + 4 Cl2(g) 1 CCl4(g) + 4 HCl(g) If CH4(g) is decreasing at the rate of 0.600 mol/s, what are the rates of change of Cl2(g), CCl4(g), and HCl(g)?Cl2(g)/t = CCl4(g)/t = HCl(g)/t = (b) The decomposition reaction given below: 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + 1 O2(g) is carried out in a closed reaction vessel. If the partial pressure of N2O5(g) is decreasing at the rate of 806 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure in the vessel?Ptot /t =arrow_forward
- ki [2] Given the mechanism: NO(g) + O2(g) SNO;(g) [fast, reversible] k-1 (1) k2 NO:(g) + NO(g) → 2NO2(g) [slow] (2) (a) Write the equation for the overall reaction. (b) Which step is rate determining? (c) Which species is an intermediate? (d) Which species is a catalyst? (e) What is the rate law predicted by the above mechanism for the overall reaction?arrow_forwardThe reaction O₂(g) + 2 NO(g) → 2 NO₂(g) was studied at a certain temperature with the following results: (a) What is the rate law for this reaction? O Rate = k [0₂(g)] [NO(g)] O Rate = k [0₂(g)]² [NO(g)] O Rate = k [0₂(g)] [NO(g)]² O Rate = k [O₂(g)]² [NO(g)]²2 O Rate = k [O₂(g)] [NO(g)]³ O Rate = k [0₂(g)]4 [NO(g)] (b) What is the value of the rate constant? Experiment M/s 1 2 3 4 [0₂(g)] (M) 0.0231 0.0231 0.0462 0.0462 [NO(g)] (M) 0.0231 0.0462 0.0231 0.0462 Rate (M/s) 0.112 0.448 0.224 0.896 (c) What is the reaction rate when the concentration of O₂(g) is 0.0437 M and that of NO(g) is 0.0567 M if the temperature is the same as that used to obtain the data shown above?arrow_forwardIdentify each of the following elementary reactions as uni- molecular, bimolecular, or termolecular, and write the rate expression. (a) HCO + O2 → HO2 + CO (b) CH3 + O2 + N2 → CH;O2 + N2 (c) HO,NO2 –→ HO2 + NO2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY