
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
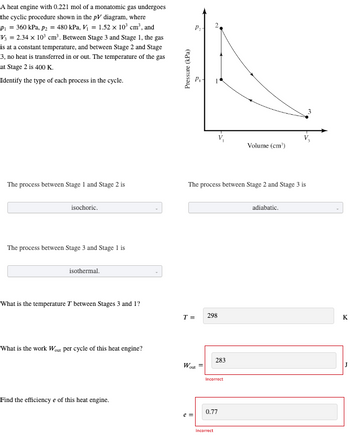
Transcribed Image Text:A heat engine with 0.221 mol of a monatomic gas undergoes
the cyclic procedure shown in the pV diagram, where
P₁ = 360 kPa, p2 = 480 kPa, V₁ = 1.52 x 10³ cm³, and
V₁ = 2.34 x 10³ cm³. Between Stage 3 and Stage 1, the gas
is at a constant temperature, and between Stage 2 and Stage
3, no heat is transferred in or out. The temperature of the gas
at Stage 2 is 400 K.
Identify the type of each process in the cycle.
The process between Stage 1 and Stage 2 is
isochoric.
The process between Stage 3 and Stage 1 is
isothermal.
What is the temperature 7 between Stages 3 and 1?
What is the work Wout per cycle of this heat engine?
Find the efficiency e of this heat engine.
Pressure (kPa)
P₁-
P₁-
T =
The process between Stage 2 and Stage 3 is
e =
Wout
298
283
Incorrect
0.77
Incorrect
Volume (cm³)
adiabatic.
K
J
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A gas has a constant pressure of 3000Pa. It is isobarically expanded from 0.75m^3 to 1.25m^3. During the process, 100J of thermal energy is added through heat. a) What is the work done on the gas? b) What is the change in internal energy of the gas?arrow_forwardThe heat engine shown in the figure uses 2.0 mol of a monatomic gas as the working substance. (Figure 1) igure p (kPa) 600- 400 200 0 0 0.025 0.050 V (m³) 1 of 1 Part E part. What is the engine's thermal efficiency? Express your answer using two significant figures. η = Submit VE ΑΣΦ Request Answer ? %arrow_forwardThe PV diagram shows the compression of 40.9 moles of an ideal monoatomic gas from state A to state B. Calculate Q, the heat added to the gas in the process A to B. Data: PA= 1.90E+5 N/m2 VA= 1.83E+0 m3 PB= 1.01E+5 N/m2 VB= 8.90E-1 m3›44arrow_forward
- A cylinder of volume 0.320 m3 contains 10.5 mol of neon gas at 17.4°C. Assume neon behaves as an ideal gas. (a) What is the pressure of the gas? Pa(b) Find the internal energy of the gas. J(c) Suppose the gas expands at constant pressure to a volume of 1.000 m3. How much work is done on the gas? J(d) What is the temperature of the gas at the new volume? K(e) Find the internal energy of the gas when its volume is 1.000 m3. J(f) Compute the change in the internal energy during the expansion. J(g) Compute ΔU − W. J(h) Must thermal energy be transferred to the gas during the constant pressure expansion or be taken away? This answer has not been graded yet. (i) Compute Q, the thermal energy transfer. J(j) What symbolic relationship between Q, ΔU, and W is suggested by the values obtained?arrow_forwardAnswer 1-10 , no need for solutionsarrow_forwardA heat engine with 0.221 mol of a monatomic gas undergoes the cyclic procedure shown in the ?? diagram, where ?1=360 kPa, ?2=480 kPa, ?1=1.52×103 cm3, and ?2=2.34×103 cm3. Between Stage 3 and Stage 1, the gas is at a constant temperature, and between Stage 2 and Stage 3, no heat is transferred in or out. The temperature of the gas at Stage 2 is 400 K. Identify the type of each process in the cycle. The process between Stage 1 and Stage 2 is The process between Stage 2 and Stage 3 is The process between Stage 3 and Stage 1 is What is the temperature ? between Stages 3 and 1? ?= What is the work ?out per cycle of this heat engine? ?out= Find the efficiency ? of this heat engine. ?=arrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardA particular thermodynamic cycle acting on a monatomic ideal gas (y = 1.67) includes an isobaric expansion, an isochoric cooling, and then a isothermic contraction. The PV diagram is shown in the image below. P V The isobaric expansion occurs at a pressure of 1.8 × 105 Pa and changes the volume of the gas from 6.7 x 10-2 m³ to 13.08 × 102m³. What is the efficiency of the process?arrow_forwardAn ideal monatomic gas undergoes changes in pressure and volume, as shown in the pV diagram below. The initial volume is 0.02 m3 and the final volume is 0.10 m3. The initial pressure is 1 atm and the final pressure is 2 atm. Recall that 1 atm = 101.3 kPa. (a) Calculate the magnitude, or absolute value, of the work done on the gas in this process. Answer = - 13429J (c) The initial temperature of the gas is 308 K. Calculate the temperature of the gas at the end of the process. Answer = 3080 k Just need answer with the following: (d) What is the change in thermal energy for the gas in this process? (e) Calculate the quantity of heat transfer added to (positive) or removed from (negative) the gas during this process.arrow_forward
- A heat engine with 0.221 mol of a monatomic gas undergoes the cyclic procedure shown in the pV diagram, where Pi = 360 kPa, p2 = 480 kPa, Vị = 1.52 × 10³ cm³, and V, = 2.34 x 103 cm³. Between Stage 3 and Stage 1, the gas is P2 - at a constant temperature, and between Stage 2 and Stage 3, no heat is transferred in or out. The temperature of the gas at Stage 2 is 400 K. Identify the type of each process in the cycle. The process between Stage 1 and Stage 2 is isochoric. Volume (em) The process between Stage 2 and Stage 3 is adiabatic. The process between Stage 3 and Stage 1 is isothermal. What is the temperature T between Stages 3 and 1? Т- K What is the work Wout per cycle of this heat engine? Wout = Find the efficiency y of this heat engine. Pressure (kPa)arrow_forwardA particular thermodynamic cycle acting on a monatomic ideal gas (y = 1.67) includes an isobaric expansion, an isochoric cooling, and then a isothermic contraction. The PV diagram is shown in the image below. P V The isobaric expansion occurs at a pressure of 2.265 × 105 Pa and changes the volume of the gas from 5.9 × 10 2 m³ to 10.98 × 10-2 m³. What is the efficiency of the process?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON