
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
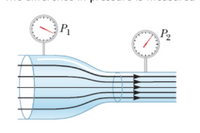
The Venturi tube shown in the figure below may be used as a fluid flowmeter. Suppose the device is used at a service station to measure the flow rate of gasoline (ρ = 7.00 ✕ 102 kg/m3) through a hose having an outlet radius of 1.31 cm. The difference in pressure is measured to be P1 − P2 = 1.70 kPa and the radius of the inlet tube to the meter is 2.62 cm.
The flow within a horizontal tube is depicted by five lines. The tube extends from left to right, with the left end wider than the right end. The five lines start at the left end, go horizontally to the right, curve slightly toward the center of the tube such that all five lines come closer together, and again go horizontally to the right to exit at the right end. Arrows on the lines point to the right to represent the direction of flow. The pressures at the left and right ends are represented by scale readings. The pressure at the left end is labeled P1, and P1 is greater than the pressure at the right end labeled P2.
(a) Find the speed of the gasoline as it leaves the hose.
m/s
(b) Find the fluid flow rate in cubic meters per second.
m3/s
m/s
(b) Find the fluid flow rate in cubic meters per second.
m3/s
Transcribed Image Text:P2
P1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The heat pumps blood at an average flow rate of 80.0cm^3/s into the aorta, which has a diameter of 1.5cm. Determine the average speed of the blood in the aorta. If the diameter of the aorta is reduced to a diameter of 1.2am, but the volumetric flow is the same, what will the new speed of the blood be?arrow_forwardA tall graduated cylinder contains 7 cm of oil (density of 825 kg/m3kg/m3) on top of 20 cm of water (density of 1000 kg/m3kg/m3). The cylinder is open to the air. What is the pressure in the water, 3 cm above the bottom of the cylinder? (in Pa) 1.0323×105 1.0335×105 1.0353×105 1.0294×105 1.0157×105arrow_forwardIn the process of loading a ship, a shipping container gets dropped into the water and sinks to the bottom of the harbor. Salvage experts plan to recover the container by attaching a spherical balloon to the container and inflating it with air pumped down from the surface. The dimensions of the container are 5.00 m long, 2.35 m wide, and 3.20 m high. As the crew pumps air into the balloon, its spherical shape increases and when the radius is 1.10 m, the shipping container just begins to rise toward the surface. Determine the mass of the container. You may ignore the weight of the balloon and the air in the balloon. The density of seawater is 1027 kg/m³. 434.54 X How does the weight of the container compare to the weight of the water displaced by the container and balloon when the container starts to rise? See if you can express the weight of the water displaced in terms of the density of the seawater and the dimensions of the container and balloon. kg Additional Materialsarrow_forward
- At a given instant, the blood pressure in the heart is 1.4 x 104 Pa. If an artery in the brain is 0.37 m above the heart, what is the pressure in the artery? Ignore any pressure changes due to blood flow.arrow_forwardA sphygornanorneter is a device used to measure blood pressure. It is consisted of an inflatable cuff and a manometer with one end connected to the cuff and the other to the open atmosphere. Blood pressure is measure by h, the difference in the heights between the two colurnns of mercury. If a normal heart pumps out blood with guage pressure 15931 Pa, what reading do we expect to read?arrow_forwardA 1.50 mL syringe has an inner diameter of 5.50 mm, a needle inner diameter of 0.230 mm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. What is the minimum force the nurse needs to apply to the syringe? The nurse empties the syringe in 2.10 s. What is the flow speed of the medicine through the needle?arrow_forward
- The blood pressure of an artery is measured at two heights: at the heart and 10 cm above the heart. The mass density of blood is about 1000 kg/m^3 and a typical artery has a diameter of 4 mm. (Use g = 10 m/s^2.) Compared to the pressure at heart height, the pressure 10 cm above is: Group of answer choices 100 P higher 1000 P lower 10 P higher 1000 P higher 100 P lowerarrow_forwardBlood plasma (at 37.0°C) is to be supplied to a patient at the rate of 2.80 × 10−6 m3/s. If the tube connecting the plasma to the patient’s vein has a radius of 2.00 mm and a length of 67.6 cm, what is the pressure difference between the plasma and the patient’s vein? Viscosity of blood plasma is 1.30 × 10−3 Pa·s. ____Paarrow_forwardThe average body density of a human is 1030 kg/m3, yet we typically float in seawater when we fill our lungs with air and sink when we exhale. Therefore, our effective density is similar to that of seawater, 1010 kg/m3. If the typical total volume (body density + lung capacity) of a human is 0.25 m3, what volume is due to body mass and what volume is due to lung capacity (you can assume the density of air is rair = 1.2 kg/m3)arrow_forward
- At a given instant, the blood pressure in the heart is 1.7 x 104 Pa. If an artery in the brain is 0.46 m above the heart, what is the pressure in the artery? Ignore any pressure changes due to blood flow.arrow_forwardA fluid with density 1200 kg/m flows through this pipe. As the first location, A, the fluid travels at 7.5 m/s and at the second location, B, the fluid travels at 11 m/s. What is the difference in pressure between the two points? O-1.9 x 10 Pa +3.8 x 103 Pa -2.5 x 104 Pa -3.9 x 10 Pa O +5.0 x 104 Paarrow_forwardNote: FBD is mandatory,So please include it.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON