
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A film of oil, with an index of refraction of 1.52 and a thickness of 1.50 cm, floats on a pool of water, as shown in the figure. (see figure). A beam of light is incident on the oil at an angle of 60.0 degrees to the vertical.
A) Find the angle θ the light beam makes with the vertical as it travels through the water.
B) How does your answer to part A depend on the thickness of the oil film? Explain
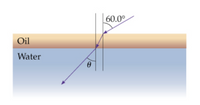
Transcribed Image Text:60.00
Oil
Water
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The critical angle for total internal reflection at a liquid-air interface is 45.0°. Part A If a ray of light traveling in the liquid has an angle of incidence at the interface of 34.0 °, what angle does the refracted ray in the air make with the normal? Express your answer in degrees. ΑΠΑΣΦ 0 = Submit Part B Request Answer 0 = ? If a ray of light traveling in air has an angle of incidence at the interface of 34.0 °, what angle does the refracted ray in the liquid make with the normal? Express your answer in degrees. —| ΑΣΦ 2 ? Oarrow_forwardThe indices of refraction for violet light (λ = 400 nm) and red light (λ = 700 nm) in diamond are 2.46 and 2.41, respectively. A ray of light traveling through air strikes the diamond surface at an angle of 51.0 to the normal. Part A Calculate the angular separation between these two colors of light in the refracted ray. Express your answer in degrees. Π ΑΣΦ Δθ = Submit Request Answer ?arrow_forwardA laser beam shines along the surface of a block of transparent material. (See the figure .) Half of the beam goes straight to a detector, while the other half travels through the block and then hits the detector. The time delay between the arrival of the two light beams at the detector is 6.10 ns. Part A What is the index of refraction of this material? n = -- ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer ? n = ? -2.50 m- Detectorarrow_forward
- A flat sheet of ice (n = 1.309) has a thickness of 2.7 cm. It is on top of a flat sheet of crystalline quartz (n = 1.544) that has a thickness of 1.5 cm. Light strikes the ice perpendicularly and travels through it and then through the quartz. In the time it takes the light to travel through the two sheets, how far (in cm) would it have traveled in a vacuum? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardIn order to identify an unknown material you are asked to solve for the critical angle of the material. In order to test this you set up a beam of light that strikes the unknown substance from air (n = 1.0) at an angle of 30° with respect to the normal. It continues on in the substance at an angle of 23° with respect to the normal. What is the critical angle for the unknown substance? 51° 55° 60° 63°arrow_forwardE. Light is incident from air (n = 1.0003) on the rectangular piece of glass shown below. 60° 30° 55° 35° 1. Determine the index of refraction of the glass Determine the speed of light in the glass shownarrow_forward
- A beam of light is incident from a liquid on the surface of transparent solid. The angle of incidence is 30°and the angle of refraction is 18°. Draw clear physics diagram of the problem – one for each part of the problem (3 total). label relevant angles. Find the critical angle for this solid when it is surrounded by the liquid. What is the angle between the reflected and refracted rays when the angle of incidence is 3°less than the critical angle?arrow_forwardWhite light is incident onto a 30° prism at the 40° angle shown in the figure. Violet light emerges perpendicular to the rear face of the prism. The index of refraction of violet light in this glass is 2.0% larger than the index of refraction of red light. (Figure 1) Figure White light 40⁰ 30° 1 of 1 Part A At what angle does red light emerge from the rear face? Express your answer with the appropriate units. 6 = ☐ O μA Value Submit Request Answer < Return to Assignment Units Provide Feedback ?arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, a light beam travels from air, through olive oil, and then into water. If the angle of refraction 82 for the light in the olive oil is 34.8°, determine the angle of incidence e, in air and the angle of refraction e3 in water. The index of refraction for olive oil is 1.47. 83 = air oil waterarrow_forward
- Use the exact values you enter to make later calculations.A ray of light strikes a flat, 2.00-cm-thick block of glass (n = 1.96) at an angle of ? = 32.4° with respect to the normal (see figure below). A light ray incident on a glass block of thickness 2.00 cm is shown. The ray travels down and to the right and is incident to the top of the block at an angle ? to the normal of the surface. The ray inside the block moves down and to the right but at a steeper slope than the incident ray. It is incident on the bottom surface of the block and exits moving down and to the right, in the same direction as the incident ray. A dashed line extends from the original path of the ray down in the block and is shown to be a distance d from the ray that exits the glass block. (a) Find the angle of refraction at the top surface and the angle of incidence at the bottom surface. °(b) Find the refracted angle at the bottom surface. °(c) Find the lateral distance d by which the light beam is shifted. cm(d)…arrow_forwardplease answerarrow_forwardA beam of light is incident on a square piece of glass with side s = 10.0 cm and index of refraction 1.50. The angles are shown in the figure to scale (you can count the blocks to measure them if you don't have a protractor). Where does the beam exit the glass? Assume the glass is in air (n = 1.00).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON