
Concept explainers
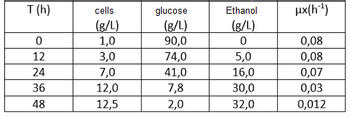
A fermentation process was carried out with a yeast in a chemically defined medium containing glucose (C6H12O6) as a carbon source aiming at the production of ethanol (C2H6O). For the evaluation of the process, samples were taken at different times of cultivation and the experimental results are shown in the Table below. Based on the experimental results, one can:
a) Calculate the overall substrate-to-cell conversion factor
b) Calculate the overall substrate to product conversion factor
c) Calculate the volumetric productivity of ethanol
d) Determine the theoretical maximum conversion of glucose to ethanol
e) Determine the efficiency of the process
f) Based on the MONOD equation, calculate the maximum specific growth rate and the value of the saturation constant
g) Determine the culture generation time
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- You perform Michaelis-Menten kenetics on i) trypsin and ii) a mutant form of the same enzyme (a single amino acid has been changed). The specificity constant for the mutant was 10 times larger than for trypsin. a) Define the specificity constant and explain using this definition how a larger value might occur. b) Explain how, if at all, a non-competitive inhibitor of trypsin would affect the specificity constant.arrow_forwardYeast Catalase Experiment Questions: 1) What is the purpose of having a 0ml hydrogen peroxide group in a yeast catalase experiment? 2) What reactants contain yeast catalase: H2O2 or yeast mixture? 3) What gas is being given when catalase and hydrogen peroxide react?arrow_forwardIn the differential absorption heterophile test, what findings are diagnostic of IM?arrow_forward
- Biology Questionarrow_forwardWhat medium is this? What is the result in tube at left? In second tube? What does it tell you about the biochemical abilities of these organisms? What is the reagent used to detect the red?arrow_forwardWhat can be interpreted when the Benedict's test is applied to enzymatic hydrolysis of sucrose (yeast- hydrolyzed sucrose)?arrow_forward
- Explain why phenol red is used in McConkey agar to detect the acid reaction of lactose fermentation.arrow_forwardBiochemical tests such as the fermentation test can be used when unknown bacterial cells are identified. true or false?arrow_forwardA microorganism is grown in a fermenter under steady-state conditions. The microorganism growth follows Monod kinetics and the following stoichiometric equation: C3H6O3 +a O2 +b NH3 → c biomass + d CO2 + e H₂O Given that the biomass yield is 0.415 grams of biomass per gram of substrate, determine the respiratory quotient.arrow_forward
- A purified protein sample was used in a reaction, resulting in an activity of 696.7 nmol min-1. The reaction volume was 145.0 µL and the final volume before loading the plate was 1,050 µL. The total reaction time was 4.25 min. The amount of protein used in the reaction was 4.270 µg. Calculate the specific activity of the sample (in nmol min-1 µg-1).arrow_forwardOutline the steps involved in the two paths of sulfate assimilation. Be sure to address the sulfur reduction pathway as a photoassimilation process.arrow_forwardroblem 1An aerobic biochemical process uses a CSTR w/o recycle. The feed characteristics are asfollows: Influent substrate concentration, So = 200 mg/L; half- velocity coefficient, Ks = 50mg/L; maximum, specific substrate utilization rate, k = 5 g/g- day; yield coefficient, Y = 0.5g Xa/g substrate consumed; microorganism decay coefficient, b = 0.10 day-1.1. The process goal is the production of active biomass. Determine the hydraulicretention time that the reactor should be operated in order to maximize the reactoractive biomass concentration (Xa). How does this retention time compare with theminimum solids retention time that the system can theoretically be operated?Calculate the solids retention time safety factor.2. Based on the solids retention time for maximum Xa calculated above, estimate theactive biomass concentration (Xa) and the substrate removal efficiency (E, %)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





