
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
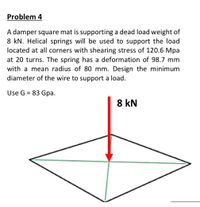
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 4
A damper square mat is supporting a dead load weight of
8 kN. Helical springs will be used to support the load
located at all corners with shearing stress of 120.6 Mpa
at 20 turns. The spring has a deformation of 98.7 mm
with a mean radius of 80 mm. Design the minimum
diameter of the wire to support a load.
Use G = 83 Gpa.
%3D
8 kN
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1 Obtain a preliminary design of the shaft by performing the following tasks. Note that forces Tj=2880 N and T2=432 N. The maximum bending moment is at x=230 mm (point B), and it equals M= 698.3 N•m completely reversed, where the torque is constant at 612 N.m at the same point. The shaft material is AISI 1020 CD steel. Take the stress concentration conditions at B to be Shoulder fillet-sharp, with notch radius r=0.6 mm (Table 7-1). 230 mm T, 280 mm 30-mm dia. 300 mm 250-mm dia. 400-mm dia. 270 N 1800 N a) Sketch a general shaft layout in 2D (x – y axes), including all components and torques, then calculate all reactions. b) Based on the current shaft dimensions and using only forces at B and C, find the lowest critical speed of the shaft. c) Determine the fatigue factor of safety of the rotating shaft with the current dimensions using the DE-Gerber criteria. Use Eqs. 6-8 and 6-18 to find the endurance limit, account only for ka and k, in Eq. 6-18 and assume all remaining…arrow_forwardHelp. Answer select 6 that answers the questions.arrow_forwardPlease don't use chatgpt, use the strain energy concept. Looking for a responsible tutor.arrow_forward
- A system requires a metal component with the design specification that it not experience more than 0.1% linearized strain. During operation, the component experiences uniaxial extensional stresses ranging from 0 to 1000 kPa. Assuming isothermal LEHI behavior, what is the minimum Young's modulus that the metal must possess to be used to make the part?arrow_forwardExpress the following quantities in SI units: 23.4 grams = 2.34 x 10^-2 124 millimeters = 1 hour and 24 min = 0.12 centimeters =arrow_forwardPlease help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Member BC has a square cross section. The diameter of the pins at A and B are 3 cm and 2 cm respectively. If the allowable normal stress for member BC is allow = 25 MPa and the allowable shear stress for the pins iS Tallow = 12 MPa, calculate the maximum force intensity w (in N/m). 4 cm В 50° 3 m A Warrow_forwardIf the solid shaft is made from red brass C83400 having allowable shear stress of tallow = 4 ksi, determine the maximum allowable torque T that can be applied at B.arrow_forwardDetermine the moment M that will produce a maximum stress of 70 MPa on the cross-section.arrow_forward
- Important question, Please answer it correctly. Don't use chatgpt or any other tools . (Confused in a strain energy concept)arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions. 1. Calculate the elongation of the cable due to load, if a steel cable of 4cm diameter is used to lift a load of 350kg. Given that and the length of cable is 10m and E=3x10'kg/cm. 2. A tensile test was conducted on mild steel bar. The load at elastic limit was 200KN and the diameter of the steel bar was 3cm. What will be the value of stress? 3. A steel bar 600mm long and having 30mm diameter, is turned down to 25mm diameter for one fourth of its length. It is heated at 30 C above room temperature, clamped at both ends and then allowed to cool to room temperature. If the distance between the clamps is unchanged, the maximum stress in the bar ( a = 12.5 x 10" per C and E = 200 GN/m) is 4. Determine the yield stress of a steel rod 15 mm diameter, if the yield load on the steel rod is 70KN. 5. Where do the maximum BM occurs for the below diagram. 10 KN 2M OMarrow_forwardwritten solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON