
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
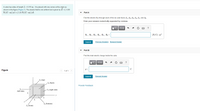
Transcribed Image Text:A cube has sides of length L = 0.370 m. It is placed with one corner at the origin as
shown in the figure (Figure 1). The electric field is not uniform but is given by E =( -5.69
N/(C . m) )æi+(3.20 N/(C - m) )zk.
Part A
Find the electric flux through each of the six cube faces S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and Sf-
Enter your answers numerically separated by commas.
να ΑΣφ
Đ1, D2 , P3 , Þ4 , 5 , Þ6 =
(N/C) - m?
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
Part B
Find the total electric charge inside the cube.
?
=b
C
Figure
1 of 1>
Submit
Request Answer
S2 (top)
S6 (back)
Provide Feedback
S3 (right side)
(left side)
L
S4 (bottom)
S, (front)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A closed surface with dimensions a=b=0.40 m and c=0.60 m is located as in the figure below. The left edge of the closed surface is located at position x= a. The electric field in the region is non-uniform and is given by E=(3.0+ 32x2 ) i N/C, where x is in meters. Calculate the net electric flux leaving the closed surface? E Select one: A. 3.07 В. 7.50 С. 4.30 D. 1.02 E. 10.70arrow_forwardPart A Suppose a disk with area A is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude E. The disk is oriented so that the vector normal to its surface, îñ, makes an angle 0 with the electric field, as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) What is the electric flux PE through the surface of the disk that is facing right (the normal vector to this surface is shown in the figure)? Assume that the presence of the disk does not interfere with the electric field. Express your answer in terms of E, A, and 0 • View Available Hint(s) Figure 1 of 1 ФЕarrow_forwardThe figures show cross sections of three-dimensional closed surfaces. They have a flat top and bottom surface above and below the plane of the page. However, the electric field is everywhere parallel to the page, so there is no flux through the top or bottom surface. The electric field is uniform over each face of the surface. Figure 10 N/C 10 N/C 10 N/C ▾ Part B For (Figure 2), does the surface enclose a net positive charge, a net negative charge, or no net charge? Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Submit an outward an inward zero no net charge a net negative charge a net positive charge There is flux through each side of the surface, which indicates that there is enclosed in this surface. Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining You filled in 2 of 2 blanks incorrectly. Reset Helparrow_forward
- answer please varrow_forwardA given thick spherical shell has a volume charge distribution of p = A/r, where A is a constant. An additional point charge Q is placed at the center (r = 0). The value of A is selected so that the electric field inside the thick shell is constant (does not depend on r). b What is the electric field (in N/C) inside the shell aarrow_forwardshow detailsarrow_forwardA solid ball of radius r has a uniform charge density p. Correct Part C Let E (r) represent the electric field due to the charged ball throughout all of space. Which of the following statements about the electric field are true? Check all that apply. ► View Available Hint(s) E(0) = 0. E(rb) = 0. lim,→∞ E(r) = 0. The maximum electric field occurs when r = 0. The maximum electric field occurs when r = b. The maximum electric field occurs as r →→∞. Submitarrow_forwardConducting Sphere 6 v.A If a total charge of +9.6 C accumulates on the inner surface of the hollow sphere (i.e. the cavity wall), what must be the charge Q of the enclosed point charge? Enter the numerical value in SI units. Type your answer... 7 metal What is the direction of the electric field at point P? A point charge Q is located in an enclosed cavity within a hollow conducting metal sphere. The region in the cavity between the point charge and the sphere is empty space. Point P is completely within the metal. O The electric field at point P is zero. O The direction depends on the value of the charge on the outer surface of the sphere.arrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.370 m. It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The electric field is not uniform but is given by E =(-5.69 N/(C. m) )æi+(3.20 N/(C - m) )zk. Part A Find the electric flux through each of the six cube faces S1, S2, S3, S4, S5. and S6. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Eν ΑΣφ ? d1, Þ2, Þ3 , 4 , Þ5 , Þ6 = (N/C) - m² Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Part B Find the total electric charge inside the cube. ΑΣφ ? q = Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer S2 (top) So (back) Provide Feedback S3 (right side) (left side) L L L. S, (bottom) S, (front)arrow_forwardplease answer all parts and explanation.arrow_forwardA 1.4 cm x 1.4 cm x 1.4 cm box with its edges aligned with the xyz-axes is in the electric field E = (370x + 150) i N/C, where x is in meters. Part A What is the net electric flux through the box? Nm2/Carrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.370 m. It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The electric field is not uniform but is given by E =( -5.69 N/(C. m) )æi+( 3.20 N/(C · m) )zk. Part A Find the electric flux through each of the six cube faces Sı, S2, S3, S4, S5, and Sg- Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. ν ΑΣφ D1, Þ2 , D3 , Þ4 , Þ5 , Þ6 = (N/C) - m² Submit Request Answer Part B Find the total electric charge inside the cube. q = Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer S2 (top) S6 (back) Provide Feedback S1 (left side) L - S3 (right side) y L L. S4 (bottom) S3 (front)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON