
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
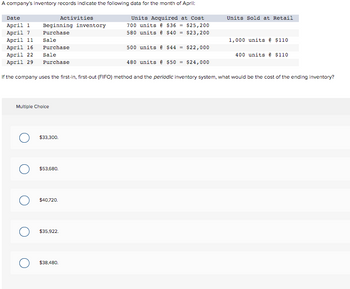
Transcribed Image Text:A company's inventory records indicate the following data for the month of April:
Date
April 1
April 7
April 11
Beginning inventory
Purchase
Sale
Purchase
Sale
Purchase
Multiple Choice
O $33,300.
O
April 16
April 22
April 29
If the company uses the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method and the periodic inventory system, what would be the cost of the ending inventory?
$53,680.
O $40,720.
Activities
$35,922.
$38,480.
Units Acquired at Cost
700 units @ $36 = $25,200
580 units @ $40 = $23,200
500 units @ $44 = $22,000
Units Sold at Retail
480 units @ $50 = $24,000
1,000 units @ $110
400 units @ $110
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A company reports the following beginning inventory and two purchases for the month of January. On January 26, the company sells 330 units. Ending inventory at January 31 totals 140 units. Units Unit Cost Beginning inventory on January 1 300 $ 2.80 Purchase on January 9 70 3.00 Purchase on January 25 100 3.14 Required: Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the FIFO method.arrow_forwardYou are given financial statements and a Dupont analysis for Tesco and Ahold. What do you conclude about the two companies’ performances based on these numbers?arrow_forwardWaterway Company uses a periodic inventory system. For April, when the company sold 450 units, the following information is available. April 1 inventory April 15 purchase April 23 purchase (a) Units Unit Cost 260 360 380 1,000 $29 Weighted average cost per unit 35 38 Total Cost $ $7,540 12,600 Calculate weighted average cost per unit. (Round answer to 2 decimal places, eg. 2.76) 14,440 $34,580arrow_forward
- Inventory Costing Methods: Periodic LIFO (Appendix 6B) Filimonov Inc. has the following information related to purchases and sales of one of its inventory items: Date Description Units Purchased at Cost Units Sold at Retail June 1 Beginning Inventory 150 units @ $6 = $900 Purchase 1 200 units @ $12 = $2,400 14 Sale 1 300 units @ $25 22 Purchase 2 250 units @ $14 = $3,500 29 Sale 2 225 units @ $25 Assume that Filimonov uses a periodic inventory system. Required: Calculate the cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using the LIFO inventory costing method. Cost of goods sold Cost of ending inventoryarrow_forwardThe following information is available for Zhang Company: Item Units Unit cost Total Beginning inventory h00 First purchase Second purchase $4 $400 180 5 900 220 7 1,540 500 $2,840 Assume that Zhang uses a periodic inventory system and that there are 150 units left at the end of the month. Required: Assuming that the Company is using the Average-cost method: 1- Compute the average cost per unit. 2- Compute the cost of ending inventory.arrow_forwardFIFO and LIFO costs under perpetual inventory system The following units of an item were available for sale during the year: Beginning inventory 23 units at $47 Sale 19 units at $68 First purchase 38 units at $49 Sale 36 units at $70 Second purchase 14 units at $50 12 units at $70 Sale The firm uses the perpetual inventory system, and there are 8 units of the item on hand at the end of the year. a. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to FIFO? $ b. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to LIFO? $arrow_forward
- Perpetual Inventory Using Weighted Average Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 310 units at $12 13 Sale 150 units 22 Purchase 340 units at $14 29 Sale 400 units a. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase. Round your answer to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 1per unit b. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the cost of goods sold on October 29. Round your "average unit cost" to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 2 c. Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine the inventory on October 31. Round your "average unit cost" to two decimal places.$fill in the blank 3arrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardThe following units of an inventory item were available for sale during the year. Beginning inventory First purchase Second purchase Third purchase 10 units at $55 25 units at $60 30 units at $65 15 units at $70 The firm uses the periodic inventory system. During the year, 60 units of the item were sold. The ending inventory cost using FIFO is a. $1,150 b. $1,250 c. $1,375 d. $1,350arrow_forward
- FIFO and LIFO Costs Under Perpetual Inventory System The following units of an item were available for sale during the year: Beginning inventory 35 units at $43 Sale 28 units at $65 First purchase 30 units at $45 Sale 25 units at $67 Second purchase 26 units at $46 Sale 19 units at $67 The firm uses the perpetual inventory system, and there are 19 units of the item on hand at the end of the year. a. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to FIFO? b. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to LIFO?arrow_forwardFIFO and LIFO Costs Under Perpetual Inventory System The following units of an item were available for sale during the year: Beginning inventory 24 units @ $45 Sale 18 units @ $70 First purchase 37 units @ $48 Sale 35 units @ $72 Second purchase 28 units @ $49 Sale 11 units @ $74 The firm uses the perpetual inventory system, and there are 25 units of the item on hand at the end of the year. a. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to FIFO? b. What is the total cost of the ending inventory according to LIFO? %24arrow_forwardDuring the year, TRC Corporation has the following inventory transactions. Date Transaction Number of Units Unit Cost Total Cost January 1 Beginning inventory 60 $52 $3,120 April 7 Purchase 140 54 7,560 July 16 Purchase 210 57 11,970 October 6 Purchase 120 58 6,960 530 $29,610 For the entire year, the company sells 450 units of inventory for $70 each. Required: 1-a & b. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold.1-c & d. Using FIFO, calculate sales revenue and gross profit.2-a & b. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold.2-c & d. Using LIFO, calculate sales revenue and gross profit.3-a & b. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold.3-c & d. Using weighted-average cost, calculate sales revenue and gross profit.4. Determine which method will result in higher profitability when inventory costs are rising.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education