
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
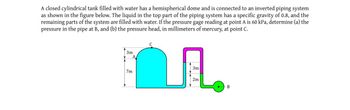
Transcribed Image Text:A closed cylindrical tank filled with water has a hemispherical dome and is connected to an inverted piping system
as shown in the figure below. The liquid in the top part of the piping system has a specific gravity of 0.8, and the
remaining parts of the system are filled with water. If the pressure gage reading at point A is 60 kPa, determine (a) the
pressure in the pipe at B, and (b) the pressure head, in millimeters of mercury, at point C.
3m
7m
C
L
3m
2m
-B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The pressure in a natural gas pipeline is measured by the manometer shown in the figure with one of the arms open to the atmosphere where the local atmospheric pressure is 14.2 psia. Determine the absolute pressure at the bottom of the natural gas pipeline. Take the height of the mercury column / to be 6 in. Take the density of water to be pw= 62.4 lbm/ft³, and the specific gravity of mercury to be 13.6 and its density is pHg = 848.6 lbm/ft3 (Natural) Gas 14 in -Mercury SG = 13.6 -Air 2 in 22 in -Water The absolute pressure at the bottom of the natural gas pipeline is psia.arrow_forwardDetermine the height of the mercury in the tube if the level of water in the tube is h = 0.3m and the depths of the oil and water in the tank are 0.6 and 0.5 m, respectively as shown in Figure Q5. Take po = 900 kg/m³, pw = 1000 kg/m³, and PHg= 13550 kg/m³. 0.6 m 0.5 m B h'=0.3 marrow_forwardThe tank is filled with water and gasoline at a temperature of 20∘C to the depths shown in (Figure 1). The absolute air pressure at the top of the tank is 140 kPa. The atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. Determine the gage pressue at the bottom of the tank. Also would the results be different if the tank had a flat bottom rather than a curved one?arrow_forward
- Determine the height h of the column of mercury in the tube if the level of water in the tube is 0.2 m and the dimensions of the oil and the water listed in the diagram. Let poil = 900 kg/m³, pwater = 1000 kg/m³, PMercury = 13,500 kg/m³. A 0.4 m Oil B 0.3 m h Water Mercury 0.2 marrow_forwardA cylinder of radius 0.17 m and height 0.71 m stands vertically and contains an oil with a density of 832.6 kg/m^3. The cylinder is sealed on one end by a moveable piston of mass 3.00 kg. An additional mass of 15.9 kg is placed on top of the moveable piston. Determine the resulting gauge pressure the oil in the bottom of the cylinder. Express your answer in PSI. (1 PSI = 6894.76 Pa)arrow_forwardThe open tank filled with a liquid in full as shown in the figure below has the height of h = 6.00 m. The inclined angle of the inclined wall is = 45.00 °. The width (perpendicular to the screen) of the inclined wall is w = 20.00 m. The specific weight of the liquid is = 9.81 kN/m3. (1) For the inclined wall, determine the average pressure on it._________ (kPa)arrow_forward
- The flow of water from a container is controlled by a 5-ft-wide L-shaped gate hinged at point A, as shown in the figure. If it is desired that the gate open when the height of the water is 10 ft, determine the weight W of the counterweight to achieve this. Take d= 5 ft and H = 16 ft. Give your answer in lb and without decimals.arrow_forwardThe tube shown in Fig. 32 is filled with oil. Determine the pressure heads at A and B in meters of water. (In the subject FLUID MECHANIC)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY