
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
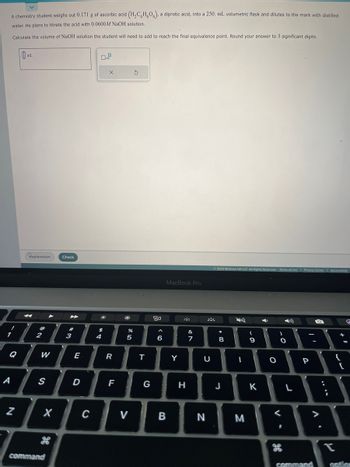
Transcribed Image Text:A chemistry student weighs out 0.171 g of ascorbic acid (H₂CH₂O), a diprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled
water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.0600M NaOH solution.
Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
!
A
N
Explanation Check
2
W
S
X
command
►
#
3
E
D
C
#
$ 4
x10
X
R
F
%
5
S
T
G
20
<6
MacBook Pro
B
Y
H
&
7
U
N
© 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center | Accessibility
*
8
J
I
M
(
9
K
4
O
)
V
O
28
L
-
P
command
O
V
{
T
G
=
[
action
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemistry student weighs out 0.0812 g of sulfurous acid (H₂SO3), a diprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1500M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mL x10 X S Elld ? ol Ararrow_forwardA lab prepared a solution of sulfuric acid with a volume of 5.0x10-4 m3. The solution is further concentrated to the half of the original volume, which is used to neutralize a potassium hydroxide solution. The potassium hydroxide solution has a volume of 30 mL, contains 30 g water, and has a density of 1.0141 g/cm3. What is the molarity of sulfuric acid in the concentrated solution? (The final answer keeps 4 digits after decimal. Please do NOT use scientific notation.)arrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.170 g of citric acid (H₂CH₂O₂), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1700 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 0mL x10 Xarrow_forward
- Suppose 4.47 g of barium acetate is dissolved in 350. mL of a 69.0 m M aqueous solution of ammonium sulfate. Calculate the final molarity of barium cation in the solution, You can assume the volume of the solution doesn't change when the barium acetate is dissolved in it. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. | Marrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.211 g of chloroacetic acid (HCH,CICO,) into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.0700 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NAOH solution the student will need to add to reach the equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. mL x10arrow_forwardCalculate the molarity of each of the following solutions. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. Part 1 of 3 6.59 g of methanol (CH3OH) in 1.50 × 10² mL of solution. Part 2 of 3 M Part 3 of 3 M x10 8.37 g of calcium chloride (CaCl₂) in 2.20 × 10² mL of solution. X M x10 X 7.02 g of naphthalene (C₁0Hg) in 85.2 mL of benzene solution. ☐ Ś x10 X S Śarrow_forward
- A chemistry student weighs out 0.0281 g of chloroacetic acid (HCH,CICO,) into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1400 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. ||mL x10arrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.0960 g of phosphoric acid (H,PO4), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1100 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. |mL ola х10 Ararrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.175 g of phosphoric acid (H,PO), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.0700M NAOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. ||mLarrow_forward
- If you titrate 25.00 ml of a 410. mg/L ascorbic acid solution and titrate it with 1.38x10 M KIO, what volume of titrant (ml) will you use? Please ensure that you include units (ml). Please report your answer to the correct number of significant figures. Answer: If you titrate 25.00 ml of a 480. mg/t ascorbic acid solution, boil it for 15 minutes and then titrate it with 125 mt of 1.34x10 M KIO, What is the concentration of Vitamin C in mg/g ascorbic acid ( original) (mg/9? Answer: And finally, If you boil 26.97 g of juice and then titrate it with 10.55 ml. of 1.16x10 M KIO, what is the concentration of vitamin C in mg per gram of juice (mg/g)? Piease remember to include units (mg/g) of Please remember to use the correct number of significant figures. tion Answer:arrow_forwardA chemist needs to neutralize a 2.6 M solution of HCI. If there are 420 mL of solution, what volume, in Liters, of a 2.0 M NaOH solution would have to be used? (Hint: You will need to write out the chemical equation and balance it first.) Be sure to report your answer to the correct number of significant figures. Do not report the units (L) in your answer.arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.264 g of an unknown diprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He then titrates this solution with 0.1900M NAOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds he has added 18.5 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY