
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
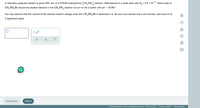
Transcribed Image Text:A chemistry graduate student is given 450. mL of a 0.50M methylamine (CH, NH,) solution. Methylamine is a weak base with K,=4.4 × 10 *. What mass of
CH,NH,Br should the student dissolve in the CH,NH, solution to turn it into a buffer with pH = 10.96?
You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the CH,NH,Br is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to
2 significant digits.
olo
x10
Ar
Explanation
Check
© 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
.........................................
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemistry graduate student is given 125. mL of a 1.10M pyrldine (C,H,N) solution. Pyridine is a weak base with K,=1.7x10. What mass of -9 9. C-H NHCI should the student dissolve in the C.H N solution to turn It Into a buffer with pH =5.77? You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the C_H.NHC1 is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to 2 significant digits. do Ar x10 Explanation Check 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Accessibility O 9:32 (hp esc & backspace ! @ #3 9. 6. 8. 3 4 1 y r W tab %3D entarrow_forward4. How many moles of NH4C1 must be added to 2.0 L of 0.10 M NH3 to form a buffer whose pH is 9.00? (Kb =1.8x10-5. Assume that the addition of NH4C1 does not change the volume of the solution.)arrow_forwardA chemistry graduate student is given 100. mL of a 1.50 M benzoic acid (HC H,CO,) solution. Benzoic acid is a weak acid with K,=6.3 × 10 -5 What mass a of KC H,CO, should the student dissolve in the HCH,CO, solution to turn it into a buffer with pH =4.38? %3D You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the KC H¸CO, is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- Consider the following titration curve of a weak base titrated with a strong acid. How would the pH be calculated at point 1 on the curve? 14 1 12 2. 10 3 4 10 20 30 40 30 60 HCl added (mL) O By subtracting the mol of weak base initially present from the mol of strong acid added to calculate the molarity of strong acid O As a weak acid equilibrium using the K, and the concentration of acid added O As a weak base equilibrium using the Ki and the concentration of base initially present As a buffer using using the K, and the ratio of weak base to conjugate acid Hdarrow_forwardWhat mass (in g) of sodium formate, HCOONA, must be added to 10.0 L of a 0.483 Maqueous solution of HCOOH to produce a buffer solution with a pH of 3.40? Ka (HCOOH) = 1.9 x 10-4 O 84.5 O 14.2 O 3.82 O 1.88 157arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak acid titrated with a strong base An analytical chemist Is titrating 235.4 mL of a 0.7900M solution of acetic acid (HCH,CO,) with a 1.100M solution of NaOH. The p K, of acetic acid is 4.70. D. Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 131.4 mL of the NaOH solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of NaOH solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH %3D Explanation Check 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved Tems of Use Privecy Accessibility A11:48 hp esc back ! @ # $ 8. 1 2 3 r t y W e tab // 11arrow_forward
- - 3 A chemistry graduate student is given 100. mL of a 0.30M diethylamine ((C,H,) NH) solution. Diethylamine is a weak base with K,= 1.3 × 10 °. what mass of (C,H5) NH,Br should the student dissolve in the (C,H,), NH solution to turn it into a buffer with pH = 10.94? 2 You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the (C,H,) NH,Br is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round 2 it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardA chemistry graduate student is given 300. ml of a 0.90M dimethylamine ((CH) NH solution. Dimethylamine is a weak base with K,=5.4 x 10. What mass of (CH,) NH,Br should the student dissolve in the (CH), NH solution to turn it into a buffer with pH - 10.21? You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the (CH,) NH,Br is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardA chemistry graduate student is given 100. mL of a 0.40M nitrous acid (HNO,) solution. Nitrous acid is a weak acid with K 4.5 x 10. What mass of -4 NaNO, should the student dissolve in the HNO, solution to turn it into a buffer with pH =3.16? %3D You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the NaNO, is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to 2 significant digits. x10 Submit Assignment Continue 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. AlI Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center | Accessibility MacBook Air F11 Figarrow_forward
- Determine the mass of solid NaCH₃COO that must be dissolved in an existing 500.0 mL solution of 0.200 M CH₃COOH to form a buffer with a pH equal to 5.00. The value of Ka for CH₃COOH is 1.8 × 10⁻⁵. Let x represent the original concentration of CH3COO- in the water. based on the given values, set up the ICE table in order to determine the unknownarrow_forwardDetermine the mass of solid NaCH₃COO that must be dissolved in an existing 500.0 mL solution of 0.200 M CH₃COOH to form a buffer with a pH equal to 5.00. The value of Ka for CH₃COOH is 1.8 × 10⁻⁵. Based on the information provided, set up a RICE/ICE Table to answer the question. Let x represent the original concentration of CH₃COOH in the water.arrow_forwardAn aqueous solution contains 0.313 M nitrous acid. How many mL of 0.351 M potassium hydroxide would have to be added to 150 mL of this solution in order to prepare a buffer with a pH of 3.880? mLarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY