
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Write out the half reaction as it would actuall Accur at the anode. And is there a min or a max standard reduction.
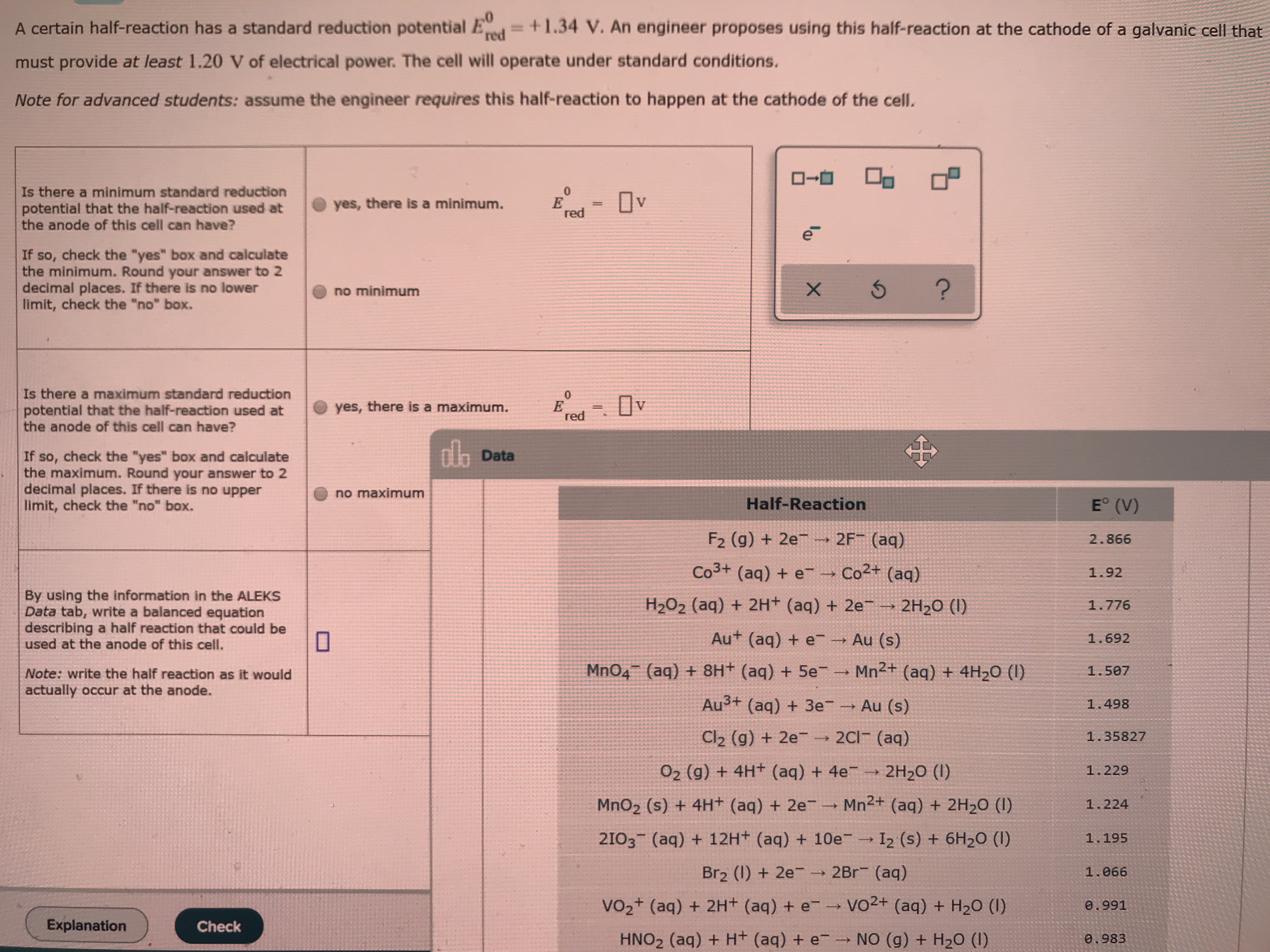
Transcribed Image Text:A certain half-reaction has a standard reduction potential Ed=+1.34 V. An engineer proposes using this half-reaction at the cathode of a galvanic cell that
must provide at least 1.20 V of electrical power. The cell will operate under standard conditions.
Note for advanced students: assume the engineer requires this half-reaction to happen at the cathode of the celI.
Is there a minimum standard reduction
potential that the half-reaction used at
the anode of this cell can have?
Ov
yes, there is a minimum.
red
If so, check the "yes" box and calculate
the minimum. Round your answer to 2
decimal places. If there is no lower
limit, check the "no" box.
no minimum
Is there a maximum standard reduction
potential that the half-reaction used at
the anode of this cell can have?
yes, there is a maximum.
red
dh Data
If so, check the "yes" box and calculate
the maximum. Round your answer to 2
decimal places. If there is no upper
limit, check the "no" box.
no maximum
E° (V)
Half-Reaction
F2 (g) + 2e → 2F¯ (aq)
2.866
Co3+ (aq) + e
-→ Co2+ (aq)
1.92
By using the information in the ALEKS
Data tab, write a balanced equation
describing a half reaction that could be
used at the anode of this cell.
H2O2 (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + 2e
2H2O (I)
1.776
Au+ (aq) + e Au (s)
1.692
Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (I)
MnO4 (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e-
1.507
Note: write the half reaction as it would
actually occur at the anode.
Au3+ (aq) + 3e Au (s)
1.498
2C1 (aq)
Cl2 (g) + 2e-
1.35827
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e →
2H20 (I)
1.229
Mn2+ (aq) + 2H2O (I)
MnO2 (s) + 4H+ (aq) + 2e¯ →
1.224
2103 (aq) + 12H+ (aq) + 10e
I2 (s) + 6H2O (I)
1.195
Br2 (1) + 2e- → 2Br (aq)
1.066
Vo2+ (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + e-→ vO2+ (aq) + H20 (1)
0.991
Explanation
Check
NO (g) + H20 (I)
HNO2 (aq) + H+ (aq) + e
0.983
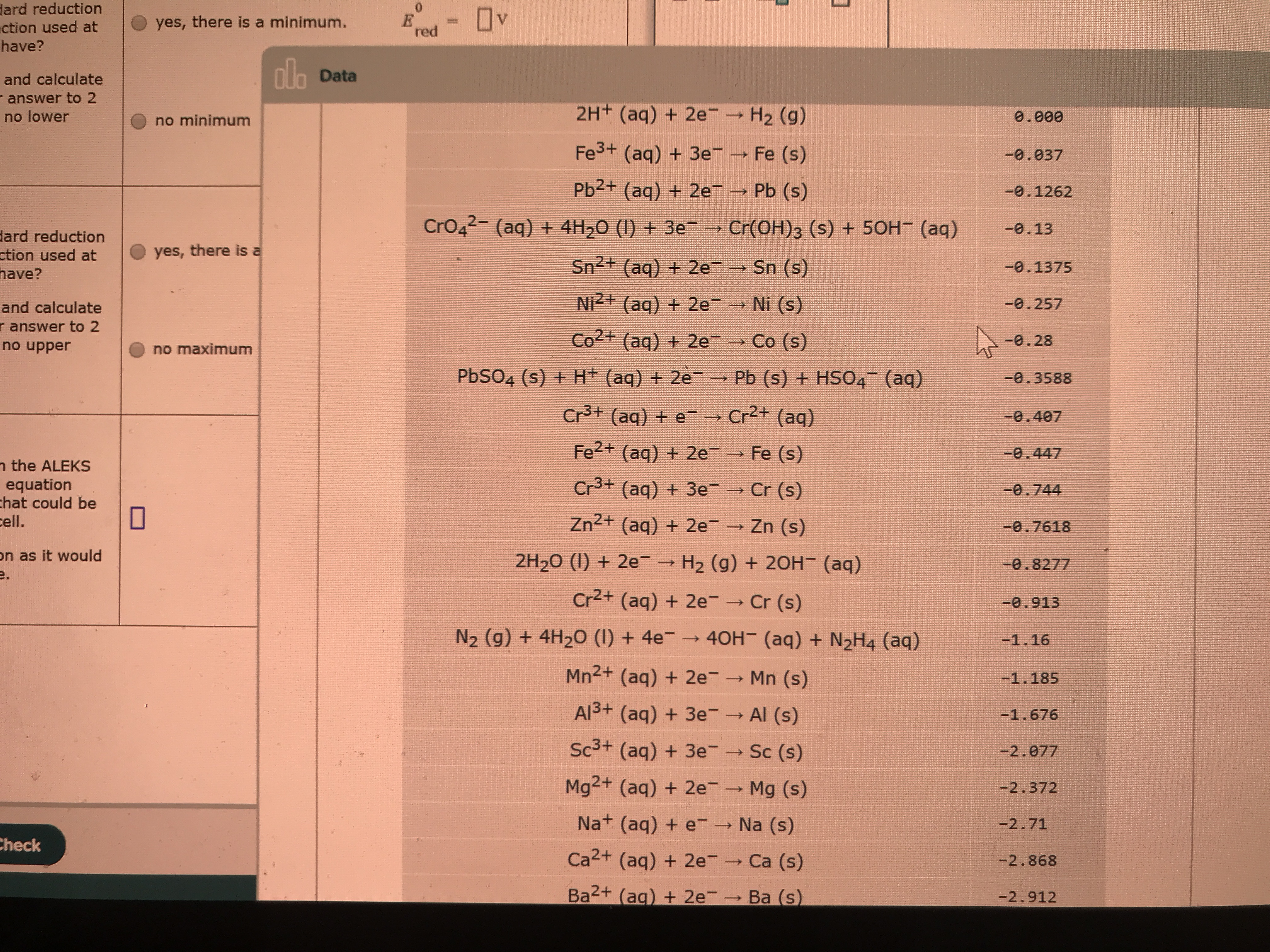
Transcribed Image Text:dard reduction
ction used at
Ov
yes, there is a minimum.
%3D
red
have?
ala
nh Data
and calculate
- answer to 2
no lower
2H+ (aq) + 2e- H2 (g)
0.000
no minimum
Fe3+ (aq) + 3e
Fe (s)
-0.037
Pb2+ (aq) + 2e
Pb (s)
-0.1262
CrO42- (aq) + 4H,0 (1) + 3e
→ Cr(OH)3 (s) + 50H (aq)
-0.13
dard reduction
ction used at
have?
yes, there is a
Sn2+ (aq) + 2e
Sn (s)
-0.1375
Ni2+ (aq) + 2e→ Ni (s)
-0.257
and calculate
r answer to 2
no upper
Co2+ (aq) + 2e
Co (s)
-0.28
no maximum
PBSO4 (s) + H+ (aq) + 2e
Pb (s) + HSO4 (aq)
-0.3588
Cr+ (aq) + e
Cr2+ (aq)
-0.407
Fe2+ (aq) + 2e
Fe (s)
-0.447
n the ALEKS
equation
chat could be
cell.
Cr3+ (aq) + 3e
Cr (s)
-0.744
Zn2+ (aq) + 2e
Zn (s)
-0.7618
on as it would
e.
2H20 (1) + 2e→ H2 (g) + 2OH- (aq)
-0.8277
Cr2+ (aq) + 2e
Cr (s)
=0.913
N2 (g) + 4H2O (I) + 4e → 40H- (aq) + N2H4 (aq)
-1.16
Mn2+ (aq) + 2e
Mn (s)
-1.185
Al3+ (aq) + 3e- Al (s)
-1.676
Sc3+ (aq) + 3e
Sc (s)
-2.077
Mg2+ (aq) + 2e
Mg (s)
-2.372
Na+ (aq) + e
Na (s)
-2.71
Check
Ca2+ (aq) + 2e
Ca (s)
-2.868
Ba2+ (ag) + 2e
Ba (s)
-2.912
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- help please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardA standard galvanic cell is constructed in which a Ni2t | Ni half cell acts as the cathode. Which of the following statements are correct? Hint: Refer to a table of standard reduction potentials. (Choose all that apply.) In the external circuit, electrons flow from the other compartment to the Ni2"|Ni compartment. The anode reaction could be Mn -> Mn2+ + 2e The cathode reaction is Ni -> Ni2+ + 2e Ni²+; is reduced at the cathode. The anode compartment could be F2|F".arrow_forwardellus_engine.html?ClassID=1907336612# dent Orie... One type of iron nail is coated with another metal in order to reduce corrosion. A solution of the metal, M(NO3)2 has a current of 20.00 A applied for 15.0 minutes. How many moles of M are formed during the electrolysis? [?] mol M Round only at the end. Use appropriate significant figures. Enterarrow_forward
- To work better as a sacrificial anode, an alloy can potentially be created to have a more (positive/negative/neutral) reduction potential than the original metal.arrow_forwardEnter electrons as e-. Use smallest possible integer coefficients. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. Use the table 'Standard Reduction Potentials' located in the 'Tables', to predict if a reaction will occur between Mg metal and F2(g), when the two are brought in contact via half-cells in a voltaic cell.If a reaction will occur, write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction, assuming that the product ions are in aqueous solution. If no reaction will occur, leave all boxes blank. + +arrow_forwardA certain half-reaction has a standard reduction potential Eed = +0.01 V. An engineer proposes using this half-reaction at the cathode of a galvanic cell that must provide at least 1.00 V of electrical power. The cell will operate under standard conditions. Note for advanced students: assume the engineer requires this half-reaction to happen at the cathode of the cell. olo ローロ Is there a minimum standard reduction potential that the half-reaction used at the anode of this cell can have? O yes, there is a minimum. = Uv red If so, check the "yes" box and calculate the minimum. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. If there is no lower limit, check the "no" box. O no minimumarrow_forward
- Determine the minimum voltage required to produce Br2 (1) in an AIBR3 (aq) cell with inert electrodes. Your answer should follow the format: a) Write the half reaction that occurs at the cathode b) Write the half reaction that occurs at the anode c) Write the overall net cell reaction d) Voltage Requiredarrow_forwardplease place it in the correct order and write down if its a aq,l,g or sarrow_forwardUse the Standard Reduction Table to answer the following questions. Write a balanced net redox equation and determine both the standard cell potential and the number of electrons transferred for the spontaneous redox process that occurs when the following couples are connected. Use the lowest possib matter under the given conditions in your answer. For the reaction arrow, please use an extensive arrow to the right (-->). d) Fe2+/Fe + Zn²+/Zn chemPad XX→← Zn (s) + Fe2+ (aq) → Zn²+ (aq) + Fe ( Zn (s) + Fe^2+ (aq) --> Zn^2+ (aq) + Fe (s) Correct. E° = .31 Reduction half-reactions Li¹+ (aq) + e¹- K¹+ (aq)+ e¹- Ba²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- Ca²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- Na¹ + (aq) + e¹- Mg²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- Al³+ (aq) + 3 e¹- U³+ (aq) + 3 e¹- Ti²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- Mn²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- 2 H₂O +2 e¹- Zn²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- Cr³+ (aq) + 3 e¹- HCHO(aq) + 2 H₂O +2e¹- Fe²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- 2 H₂O +2 e¹- X V Cd²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- PbSO4(s) + 2 e¹- In³+ (aq) + 3 e¹- Co²+ (aq) + 2 e¹- → Help Greek n (moles of e") = 2 E°(V) -3.04 -2.92 -2.92 -2.84…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY