
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
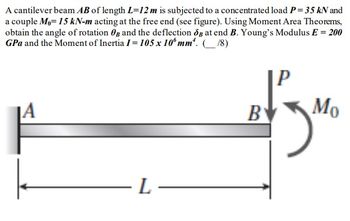
Transcribed Image Text:A cantilever beam AB of length L=12 m is subjected to a concentrated load P = 35 kN and
a couple Mo= 15 kN-m acting at the free end (see figure). Using Moment Area Theorems,
obtain the angle of rotation and the deflection og at end B. Young's Modulus E = 200
GPa and the Moment of Inertia 1 = 105 x 10 mm. (18)
JA
-L-
B
Mo
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A propped cantilever steel beam is constructedfrom a W12 x 35 section. The beam isloaded by its self-weight with intensity q. The lengthof the beam is 11.5 ft. Let E = 30,000 ksi.(a) Calculate the reactions at joints A and B.(b) Find the location of zero moment within span AB.(c) Calculate the maximum deflection of the beamand the rotation at joint B.arrow_forwardA cantilever beam AB, loaded by a uniform load and a concentrated load (see figure), is constructed of a channel section. 250 lb 22.5 lb/ft A 5.0 ft 3.0 ft- 0.617 in. 2.269 in. (a) Find the maximum tensile stress o, (in psi) and maximum compressive stress o, (in psi) if the cross section has the dimensions indicated and the moment of inertia about the z-axis (the neutral axis) is I = 3.10 in4. Note: The uniform load represents the weight of the beam. (Use the deformation sign convention.) O, = psi psi (b) Find the maximum value of the concentrated load (in Ib) if the maximum tensile stress cannot exceed 4 ksi and the maximum compressive stress is limited to 18.0 ksi. (Enter the magnitude.) Ib (c) How far from A (in ft) can load P = 250 lb be positioned if the maximum tensile stress cannot exceed 4 ksi and the maximum compressive stress is limited to 18.0 ksi? ftarrow_forwardA cantilever beam AB supports a distributed load of peak intensity g, acting over one-half of the length (see figure). (The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. Use the second-order differential equation of the deflection curve. Enter the magnitudes.) ly 90 A C В L/2- L/2 Derive the equations of the deflection curve for the beam. (Use the following as necessary: qo, L, E, I, x.) Osxs v(x) = sxsL vx) = Also, obtain formulas for the deflections 8, and 8. at points B and C, respectively. (Use the following as necessary: 9,, L, E, I.) 7 160 E·I 11 %0 L3 192 E·Iarrow_forward
- A cantilever beam carries a trapezoidal distributed load ( see figure) . Let wB=2.5 kN/ m, wA= 5.0kN/m, and L = 2.5 m. The beam has a modules E = 300 mm, Use the method of superposition and cases 1 and 8 in Table H-1 to calculate the deflection and rotation at B.arrow_forwardA simply supported beam is loaded with apoint load, as shown in the figure. The beam is a steelwide flange shape (W 12 X 35) in strong axis bending. Calculate the maximum deflection of the beam andthe rotation at joint A if L =10 ft, a = 7 ft, b = 3 ft,and P = 10 kips. Neglect the weight of the beam.arrow_forwardA beam ABC having flexural rigidityEI = 75 kN.m2 is loaded by a force P =800 N atend C and tied down at end A by a wire having axialrigidity EA = 900 kN (see figure).What is the deflection at point C when the loadP is applied?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY