
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
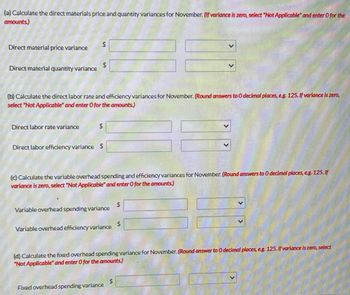
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Calculate the direct materials price and quantity variances for November. (If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable and enter O for the
amounts)
Direct material price variance
Direct material quantity variance
$
Direct labor rate variance
$
(b) Calculate the direct labor rate and efficiency variances for November. (Round answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125. If variance is zero,
select "Not Applicable and enter O for the amounts.)
$
Direct labor efficiency variance $
(c) Calculate the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances for November. (Round answers to 0 decimal places, eg. 125. If
variance is zero, select "Not Applicable and enter O for the amounts.)
Variable overhead spending variance
Variable overhead efficiency variance
Fixed overhead spending variance
$
(d) Calculate the fixed overhead spending variance for November. (Round answer to 0 decimal places, eg. 125. If variance is zero, select
"Not Applicable" and enter 0 for the amounts)
$
$
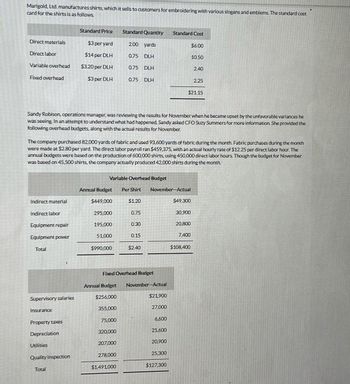
Transcribed Image Text:Marigold, Ltd. manufactures shirts, which it sells to customers for embroidering with various slogans and emblems. The standard cost
card for the shirts is as follows.
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable overhead
Fixed overhead
Indirect material
Indirect labor
Equipment repair
Equipment power
Total
Supervisory salaries
Insurance
Property taxes
Depreciation
Standard Price
$3 per yard
$14 per DLH
$3.20 per DLH
$3 per DLH
Utilities
Quality inspection
Total
Sandy Robison, operations manager, was reviewing the results for November when he became upset by the unfavorable variances he
was seeing. In an attempt to understand what had happened, Sandy asked CFO Suzy Summers for more information. She provided the
following overhead budgets, along with the actual results for November.
Annual Budget
$449,000
The company purchased 82,000 yards of fabric and used 93,600 yards of fabric during the month. Fabric purchases during the month
were made at $2.80 per yard. The direct labor payroll ran $459,375, with an actual hourly rate of $12.25 per direct labor hour. The
annual budgets were based on the production of 600,000 shirts, using 450,000 direct labor hours. Though the budget for November
was based on 45.500 shirts, the company actually produced 42,000 shirts during the month.
Variable Overhead Budget
295,000
195,000
51,000
Standard Quantity
200 yards
0.75 DLH
0.75 DLH
$990,000
0.75 DLH
75,000
320,000
207,000
278,000
$1,491,000
$1.20
0.75
0.30
0.15
Fixed Overhead Budget
Annual Budget November-Actual
$256,000
355,000
Per Shirt November-Actual
$2.40
$21,900
27,000
Standard Cost
6,600
25,600
20,900
25,300
$127,300
$6.00
$21.15
$49,300
10.50
30,900
20,800
7,400
2.40
$108,400
2.25
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Introduction
VIEW Step 2: Calculate the material price and quantity variance
VIEW Step 3: Calculate the direct labor rate and efficiency variance
VIEW Step 4: Calculate the variable overhead spending and efficiency variance
VIEW Step 5: Calculate the fixed overhead spending variance
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please do not Give image formatarrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] A manufactured product has the following information for June. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Units manufactured AQ = Actual Quantity SQ = Standard Quantity AP = Actual Price SP = Standard Price Actual Cost Compute the (1) direct materials price variance and (2) direct materials quantity variance. Note: Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance. Round "Cost per unit" answers to 2 decimal places. $ GA Standard Quantity and Cost 6 pounds @ $8 per pound 3 DLH @ $17 per DLH 3 DLH @ $12 per DLH 0 $ Actual Results 47,400 pounds @ $8.10 per pound 23,100 hours @ $17.50 per hour $ 286,100 0 0 7,800 units S $ 0 Standard Costarrow_forwardFor each of the following independent cases, fill in the missing amounts: Note: Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Round your per unit rates to 2 decimal places. Round your other final answers to the nearest whole numbers. Units produced Standard hours per unit Standard hours Standard rate per hour Actual hours worked Actual labor cost Direct labor rate variance Direct labor efficiency variance Casey Company 2,800 5.10 $ $ 31.70 13,500 5,200 F Kevin, Incorporated $ $ 1.70 2,890 3,005 2,900 F 1,518 U $ $ $ Jess Company 200 660 10.00 6,500 200 U Valerie, Incorporated $ 1,000 10.00 15,200 $ 140,000 $ 5,800 Uarrow_forward
- Aaha Inc. produces premium protective automotive covers. The direct materials and direct labour standards for one car cover are as follows: Standard Quantity or Hours Direct materials Direct labour 7.00 metres of cloth 0.30 hours Standard Price or Rate $8 per metre $ 16 per hour Standard Cost $56.00 $4.80 In September, the following activity was recorded: 17,500 metres of cloth were purchased at a cost of $7.50 per metre All of the purchased material was used to produce 2,500 car covers. 520 direct labour-hours were recorded at a total labour cost of $8,320. Required: 1. Compute all direct materials variances for September (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (ie., zero variance).) Answer is complete and correct. Direct materials price variance Direct materials quantity variance Total direct material cost variance $ 8,750 F $ $ 8,750 ( 0 None F 000arrow_forwardPlease provide answer in text (Without image)arrow_forwardFix the red pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education