
Concept explainers
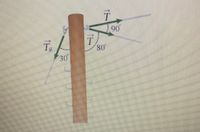
The pole in the figure below is at a 90° bend in a power line and is therefore subjected to more shear force than ones in straight parts of the line. The tension in each line is 3.60 x 104 N, at the angles shown.
The pole is 15.0 m tall, has a 24.0 cm diameter, and can be considered to have half the strength of hardwood. Assume Young's modulus to be 7.5 x 109 N/m2 and the shear modulus is 5.0 x 109 N/m2.
(a) Calculate the compression (in mm) of the pole. mm
(b) Find how much it bends (in mm) and in what direction magnitude mm direction --Select
(c) Find the tension (in N) in a guy wire used to keep the pole straight if it is attached to the top of the pole at an angle of 30.0° with the vertical. (Clearly, the guy wire must be in the opposite direction of the bend.) N
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- A beam of length 4m and flexural stiffness (EI) of 1.4 x10 Nm², is simply supported at its ends as shown in Fig. Q3. The beam is subjected to a concentrated load of 20 kN at a distance 1m and a clockwise couple of 15 kNm applied in the plane of bending at a distance of 3m, both measured from the left end. (i) (ii) (iii) RA A 1m 20KN B 3m 15kNm I O D RD Fig. Q3: Loaded structural beam Calculate the reaction forces at the two end supports. Macaulay's approach is to be used to find slopes and deflections along the beam. Write the general expression for the bending moment at a section X-X at distance x measured from the left end to enable the solution. Using 'double integration method', derive an expression for the vertical deflection along the beam; hence determine the vertical deflection at mid-span.arrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forwardAthin rectangular polymer plate PQRS of width b = 429 mm and height a = 140 mm is shown in the figure. The plate is deformed so that corner Q is displaced upward by c = 1.6 mm and corner R is displaced leftward by the same amount. Determine the shear strain at corner P after deformation. a Y = y i b Q S a X uradarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





