
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
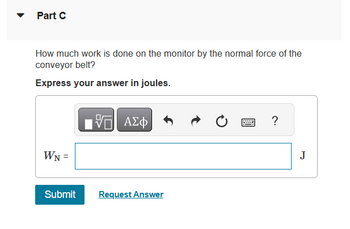
Transcribed Image Text:Part C
How much work is done on the monitor by the normal force of the
conveyor belt?
Express your answer in joules.
WN =
Submit
17 ΑΣΦ
Request Answer
Ć
www
?
J
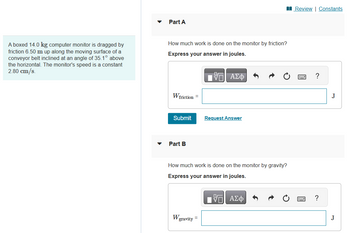
Transcribed Image Text:A boxed 14.0 kg computer monitor is dragged by
friction 6.50 m up along the moving surface of a
conveyor belt inclined at an angle of 35.1° above
the horizontal. The monitor's speed is a constant
2.80 cm/s.
Part A
How much work is done on the monitor by friction?
Express your answer in joules.
W friction =
Submit
Part B
W
OF
IVE ΑΣΦ
How much work is done on the monitor by gravity?
Express your answer in joules.
gravity =
Request Answer
- ΑΣΦ
Review | Constants
?
?
J
J
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part D, please. Thank you!arrow_forwardS 17 g My sister Sara is pulling a box along a horizontal surface with the force F inclined at an angle 0 with the horizontal. The box moves a distance d. F 1 say that the work done by the force of gravity is equal to zero. O True O False OL MAarrow_forwardTo stretch an ideal spring 8.00 cm from its unstretched length, 17.0 J of work must be done. Part C How much work must be done to compress this spring 4.00 cm from its unstretched length? Express your answer with the appropriate units. W = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part D What force is needed to compress the spring this distance? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? F = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- Hockey puck A has half the mass of hockey puck B. Starting from rest, both pucks are pulled the same distance across frictionless ice by strings with the same tension. Compare the work done on puck A and puck В. O The same amount of work was done on puck A and puck B. O The work done on puck A was twice as large as that done on puck B. O The work done on puck A was half as large as that done on puck B. O None of the above is true.arrow_forwardn eText Part B A microwave oven of mass 10.0 kg is pushed a distance 8.45 m up the sloping surface of a loading ramp inclined at an angle of 38.6 ° above the horizontal, by a constant force F with a magnitude 140 N and acting parallel to the ramp. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the oven and the ramp is Area What is the work done on the oven by the friction force? nent Sharing Take the free fall acceleration to be 9.80 m/s . 0.280. ettings e Tools Wi 185.09 J Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Part C Compute the increase in potential energy for the oven. Take the free fall acceleration to be 9.80 m/s . ΑΣΦ ? J P Pearson Copyright 2022 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. I Terms of Use | Privacy Policy I Permissions | Contact - Type here to search 080 080- TITarrow_forwardn 13 A 55 kg box is raised a distance of 2.0 m above a storeroom floor. ed What is the change of potential energy as a result of this move? lout ofarrow_forward
- Help me 3a and 3barrow_forwardAn object moving in the xy-plane is subjected to the force F = (2xyî+x²) N, where x and y are in m. Part A The particle moves from the origin to the point with coordinates (a, b) by moving first along the x-axis to (a,0), then parallel to the y-axis. How much work does the force do? Express your answer in terms of the variables a and b. W = Submit Part B W = Π| ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer The particle moves from the origin to the point with coordinates (a, b) by moving first along the y-axis to (0, b), then parallel to the x-axis. How much work does the force do? Express your answer in terms of the variables a and b. V—| ΑΣΦ ? Request Answer ?arrow_forwardReview Istants Sam, whose mass is 72 kg , straps on his skis and starts down a 64 m -high, 20° frictionless slope. A strong headwind exerts a horizontal force of 200 N on him as he skies. Part A Use work and energy to find Sam's speed at the bottom. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. µA ? Value Units V = Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- A block of weight w = 25.0 N sits on a frictionless inclined plane, which makes an angle θ = 30.0 ∘ with respect to the horizontal, as shown in the figure. A force of magnitude F = 12.5 N applied parallel to the incline, is just sufficient to pull the block up the plane at constant speed. Part A The block moves up an incline with constant speed. What is the total work Wtotal done on the block by all forces as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the incline? Include only the work done after the block has started moving at constant speed, not the work needed to start the block moving from rest. Part B What is Wg, the work done on the block by the force of gravity w⃗ as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the incline? Part C What is WF, the work done on the block by the applied force F⃗ as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the incline? Part D What is WN, the work done on the block by the normal force as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the inclined plane?arrow_forwardA 100 kg block is pulled at a constant speed of 4.0 m/s across a horizontal floor by an applied force of 141 N directed 37° above the horizontal. What is the rate at which the force does work on the block? Warrow_forwardA 61.5-kg hiker starts at an elevation of 1200 m and climbs to the top of a peak 2750 m high. Part A What is the hiker's change in potential energy? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ΔΡΕς = Submit Part B W min = Submit Part C What is the minimum work required of the hiker? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. O Yes O No Value Submit μA Request Answer ī μÅ Value Request Answer Units Can the actual work done be greater than this? Request Answer Units ? ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON