
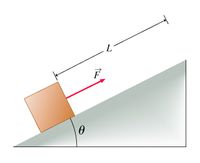
A block of weight w = 25.0 N sits on a frictionless inclined plane, which makes an angle θ = 30.0 ∘ with respect to the horizontal, as shown in the figure. A force of magnitude F = 12.5 N applied parallel to the incline, is just sufficient to pull the block up the plane at constant speed.
Part A
The block moves up an incline with constant speed. What is the total work Wtotal done on the block by all forces as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the incline? Include only the work done after the block has started moving at constant speed, not the work needed to start the block moving from rest.
Part B
What is Wg, the work done on the block by the force of gravity w⃗ as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the incline?
Part C
What is WF, the work done on the block by the applied force F⃗ as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the incline?
Part D
What is WN, the work done on the block by the normal force as the block moves a distance L = 2.70 m up the inclined plane?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- Review Istants Sam, whose mass is 72 kg , straps on his skis and starts down a 64 m -high, 20° frictionless slope. A strong headwind exerts a horizontal force of 200 N on him as he skies. Part A Use work and energy to find Sam's speed at the bottom. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. µA ? Value Units V = Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardThe force on a particle is directed along an x axis and given by F = Fo(x/xo - 1) where x is in meters and F is in Newtons. If Fo = 1.2 N and Xo = 2.7 m, find the work done by the force in moving the particle from x =0 to x = 2xo m. Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA 100 kg block is pulled at a constant speed of 4.0 m/s across a horizontal floor by an applied force of 141 N directed 37° above the horizontal. What is the rate at which the force does work on the block? Warrow_forward
- A 61.5-kg hiker starts at an elevation of 1200 m and climbs to the top of a peak 2750 m high. Part A What is the hiker's change in potential energy? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ΔΡΕς = Submit Part B W min = Submit Part C What is the minimum work required of the hiker? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. O Yes O No Value Submit μA Request Answer ī μÅ Value Request Answer Units Can the actual work done be greater than this? Request Answer Units ? ?arrow_forwardA A parent pulls a child in a wagon at a constant speed, exerting a force of F = 55N at an angle of 30° with respect to the horizontal sidewalk. (a) How much work do they do, if they pull the wagon for a distance of 30m? (b) What is the force of friction on the wagon?arrow_forwardA crate with mass m = 33.3 kg being pushed up an incline that makes an angle φ = 22.7 degrees with horizontal. The pushing force is horizontal, with magnitude P, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the incline is μ = 0.358. Consider the work done on the crate as it moves a distance d = 5.32 m at constant speed. a. What is work done by the pushing force, in joules? b. What is the work done by friction, in joules? c. What is the work done by gravity, in joules? d. What is the net work, in joules?arrow_forward
- itemt 2 A block of mass m is released from rest at the top of an incline that makes an angle a with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and incline is 4k. The top of the incline is a vertical distance h above the bottom of the incline. Part A Derive an expression for the work W; done on the block by friction as it travels from the top of the incline to the bottom. Express your answer in terms of the variables u, m, g, h, and a. Iνα ΑΣφ ? W; = Submit Request Answer Part B When a is decreased, does the magnitude of W; increase or decrease? O When a decreases, the magnitude of W, stay the same. When a decreases, the magnitude of W, increases. O When a decreases, the magnitude of W decreases. Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback MacBook Air DII DD 80 ODO F11 FV F10 F9 F7 FB F6 F5 esc F3 F4 F2 F1 & #3 2$ 3 4 6. 7 8. 1 2arrow_forwardThe force shown in the figure (Figure 1) moves an object from a=0 to z = 0.75 m. Figure Force, F (N) 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0.25 0.50 Position, x (m) 0.75arrow_forwardA farmer is using a rope and pulley to lift a bucket of water from the bottom of a well that is hy = 9.5 m deep. The farmer uses a force F1 = 59.5 N to pull the bucket of water directly upwards. The total mass of the bucket of water is mb + mw = 3.1 kg. a.Calculate how much work Wf in J the farmer does on the bucket of water (via the rope) to raise it to ground level. b.Calculate how much work Wg in J gravity does on the bucket filled with water as the farmer lifts it up the well. c. Calculate the net work Wnet in J done on the bucket of water by the two forces F1 and Fg.arrow_forward
- a In the figure, a constant force Ễ of magnitude 85.0 N is applied to a 7.0 kg shoe box at angle = 54.0°, causing the box to move up a frictionless ramp at constant speed. How much work is done on the box by Fa when the box has moved through vertical distance h = 0.35 m? а Use correct number of significant digits. The tolerance is + 1 in the 3rd significant digit. Number i 42.02 ! Units Jarrow_forwardA 2.11 kg cart moving along a horizontal track in the positive x direction has a changing force exerted on it. The force exerted on the cart is plotted in the graph shown. In the plot, Fmax has a value of 5.95 Newtons. Note that the friction between the cart and track is negligible. a.-Calculate the work done on the cart when it has reached a displacement of 21.3 cm along the track. b.- If the cart starts from rest, calculate how fast the cart is going when it has reached a displacement of 21.3 cm along the track.arrow_forwardYou push your physics book 2.40 m along a horizontal tabletop with a horizontal push of 3.00 N while the opposing force of friction is 0.700 N. a. How much work does your 3.00 N push do on the book? b. How much work does the normal force from the table do on the book? c.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





