Question
A box slides on a horizontal, frictionless surface. A horizontal force P is applied to the box as it moves from x = −4 m to x = 0. The force P varies with position according to the graph on the right.
(a)What is the change in kinetic energy of the box?
(b)If the box has a mass of 150 kg and is at rest when it is at x = −4 meters, what is the speed of the box when it passes through the origin (x=0)?
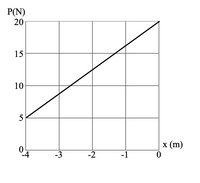
Transcribed Image Text:P(N)
20
15
10
5
x (m)
-4
-3
-2
-1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A sled and rider with a combined weight of 50 kg are at rest on the top of a hill 23 m high. (a) What is their total energy at the top of the hill?____ J(b) Assuming there is no friction, what would the total energy be on sliding halfway down the hill? ____Jarrow_forwardConsider a mass m=81.6 kg sliding on a frictionless surface as shown in the figure below. It begins with a speed of vi = 1.81 m/s at a height of yi = 21.4 m above the ground. It then travels down one hill and up the next until it momentarily comes to rest with a speed vi = 0. a) What is its kinetic energy of the mass at the start? b) What is its gravitational potential energy of the mass at the start?arrow_forwardA student, starting from rest, slides down a water slide. On the way down, a kinetic frictional force (a nonconservative force) acts on her. The student has a mass of 66 kg, and the height of the water slide is 11.1 m. If the kinetic frictional force does -6.4 × 103 J of work, how fast is the student going at the bottom of the slide? vf = Type your answer here Choose your answer herearrow_forward
- A 101-kg man is skiing across level ground at a speed of 9.5 m/s when he comes to the small slope 1.8 m higher than ground level shown in the following figure. a. If the skier coasts up the hill, what is his speed when he reaches the top plateau? Assume friction between the snow and skis is negligible. b. What is his speed when he reaches the upper level if an 80-N frictional force acts on the skis?arrow_forwardAt rest, a 59.0 kg cheetah can run at a top speed of 32.7 m/s, according to this video. In terms of net work (in J), how fast can a cheetah reach its maximum speed? A food Calorie is equal to 4186 J. For the cheetah to reach top speed, how many Calories of net work are needed? Cheetah's body produces a lot of energy, yet the amount calculated here is only a small fraction of what it needs.arrow_forwardA mass of 2 kg is separated from a wall via a spring (k=1500 N/m). You manage to compress the spring 1.3 meters before it slips through your hands and launches across the floor. If there is a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.25 between the block and the floor, how much force is friction applying to the block? How far will the block travel before coming to a stop? How much work did friction do on the block?arrow_forward
- A brick lies perilously close to the edge of the flat roof of a building. The roof edge is 50 ft above street level, and the brick has 260.0 J of potential energy with respect to street level. Someone edges the brick off the roof, and it begins to fall. What is the brick’s kinetic energy when it is 35 ft above street level? What is the brick’s kinetic energy the instant before it hits the street surface?arrow_forwardA different robot begins pushing a 10kg box that was already moving at 0.5m/s [Right] along a surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15. The robot pushes with only 3N [Right] of force. What is the acceleration of the box? Using the Work-Energy theorem, calculate how much work the robot does on the box accelerating it from 0.5m/s [Right] to 2m/s [Right]. What distance did the robot push the box? Use kinematics to check your work.arrow_forwardJustin, with a mass of 50 kg, is going down an 8.0-m-high water slide. He starts at rest, and his speed at the bottom is 12 m/s. How much thermal energy is created by friction during his descent? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Eth = μA Value Units ?arrow_forward
- The Elf on the Shelf has mass 0.500 kg and is sitting on a shelf some height y above the ground.The gravitational potential energy is 49.0 J? The Elf is bumped and falls off the shelf. How fast will the Elf be moving just before it strikes the ground?arrow_forwardIn the figure below, a block is sent sliding down frictionless ramp. Its speeds at points A and B are 1.83 m/s and 2.60 m/s, respectively. Next, it is again sent sliding down the ramp, but this time its speed at point A is 3.84 m/s. What then is its speed at point B? m/sarrow_forwardIn the figure, a block slides down an incline. As it moves from point A to point B, which are 4.1 m apart, force F acts on the block, with magnitude 4.8 N and directed down the incline. The magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block is 13 N. If the kinetic energy of the block increases by 44 J between A and B, how much work is done on the block by the gravitational force as the block moves from A to B? Number Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios