
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
A block of 1:6 kg mass is on a plane inclined to 50 for which the kinetic friction coecient is c = 0:12. The block is connected to a spring of constant k = 5 N=m by a string. The latter passes without slipping through a pulley which is assimilated to a 1 kg disc having a radius of 0:15 m. If the system is initially at rest and the spring has a zero elongation, what is the module of the speed of the block when it has slipped by 0:Five feet down the incline?
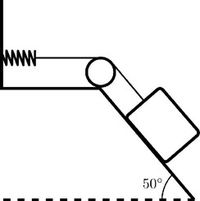
Transcribed Image Text:www
50°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- answer would be much appreciatedarrow_forwardWhat is the correct answer please explain mearrow_forwardTwo blocks are attached by strings of negligible mass to a physical pulley with two radii R1=027 m and R2=042 m. The strings are wrapped around their respective radii so that the masses can move either up or down. The pulley has a moment of inertia Ipcm=0249 kgm2, and is supported by a bearing with negligible friction. If block 1 has a mass of m1=4.1 kg, block 2 has a mass of m2=1.14 kg, and the tension in the rope connecting block 1 to the pulley is T1p=31.11 N, what is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the pulley?arrow_forward
- A 5.0 kg weight is hanging from an ideal spring with a k of 250N/m. The block is pulled down .075m from equilibrium. Will the new period for the motion of the block be greater than, less than, or equal to the period for the motion of the block if it were pulled down .15m? Why? The first block is brought to rest at equilibrium again. An identical block is launched up into the first block. The new block is moving with an initial speed of v=5.0m/s when it collides with and sticks to the original block. Calculate the maximum compression of the spring after the collision of the two blocks.arrow_forwardPlease solve only 4,5arrow_forwardQ9 / A Hartnell type governor with a central spring under compression has balls each of mass 2 kg. The ball and sleeve arms of the bell crank levers are respectively 100 mm and 60 mm long and are at right angles. In the lowest position of the governor sleeve, the radius of rotation of the balls is 80 mm and the ball arms are parallel to the govenor axis. Find the initial spring force in order that the sleeve may begin to lift at 300 rpm. If the stiffness of the spring is 30 kN / m, what is the equilibrium speed corresponding to a sleeve lift of 10 mm.arrow_forward
- Q4. A two-degree-of-freedom model consisting of two masses connected in series by two springs is shown in the figure below. The physical parameters have the values m, = 8 kg, m, = 2 kg, k, = 20 N/m, and k2 = 30 N/m. X1 X2 m1 m2 k1 k2 (A) Write down the equation of motion for mass m, (B) Write down the equation of motion for mass m, Calculate the first (larger) natural frequency of the system (D) Calculate the second (smaller) natural frequency of the systemarrow_forward6. A 12 lb. weight stretches a spring 2 feet. The mass-spring system is immersed in a medium offering resistance that is numerically equal to one quarter of the instantaneous velocity. The weight is released from a point 1 foot below equilibrium. Find its position at any future time.arrow_forward7. 2) The lawn roller has a mass m = 55 kg and a radius of gyration about its gravitational center G, kG = 196 mm. It has a handle that connects to its center axle, and the handle is pushed forward with a force F = 420 N at a 45° angle. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the roller and the ground are us = 0.11 and Hk = 0.08, respectively. For the sets of parameters listed below, determine the magnitude of the roller's angular acceleration (in rad/s²). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. F 45° 200 mm Aarrow_forward
- B6arrow_forwardFor the problem related to Fundamental.6 sketches of the system showing: • the respective velocity and acceleration and the frame of reference considered • the forces acting on the system of considered, in other words, a free body diagram (FBD) are mandatory. Their absences will automatically make the problem false. F The 77-kg man pushes on the 120-kg crate with a horizontal force F. The coefficient of static friction between the man's shoes and the surface is 0.82. What must be the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface if we observe an acceleration of the crate of 2.1 m/s²? Type your answer in the cell below.arrow_forwardDon't Use Chat GPT Will Upvote And Give Handwritten Solution Pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY